Chapter 7. Periodic Properties of the Elements
... • Second electron placed in p orbital, electron–electron repulsion increases, when electron removed, the s2p3 configuration more stable than starting s2p4 configuration, therefore a decrease in ionization energy • Ionization energy decreases down a group • means the outermost electron more readily r ...
... • Second electron placed in p orbital, electron–electron repulsion increases, when electron removed, the s2p3 configuration more stable than starting s2p4 configuration, therefore a decrease in ionization energy • Ionization energy decreases down a group • means the outermost electron more readily r ...
Ch. 11.4 Notes (Periodicity) teacher 2012
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. Noble __________ gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. Noble __________ gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
Review for Chemistry Unit Test #2 (Chapters 4, 11, and 12) Chapter
... How do the chemical and physical properties of elements change on the periodic table? Where are the transition metals found on the periodic table? List a few of their characteristics. What is the “magic number” in the repeating pattern on the periodic table? What are metalloids generally used for ma ...
... How do the chemical and physical properties of elements change on the periodic table? Where are the transition metals found on the periodic table? List a few of their characteristics. What is the “magic number” in the repeating pattern on the periodic table? What are metalloids generally used for ma ...
Intro to Periodic Table and Lewis Structures
... • The modern PT is still organized in this way! ...
... • The modern PT is still organized in this way! ...
CHEMISTRY OF MAIN GROUP ELEMENTS Classification -1 s
... Oxidation state = M2+ ,Be2+,Mg2+ ,Ca2+ ,Ba2+ ,Sr2+ Except Be- all other members are strong reducing agents that is obvious from their standard reduction potentials. The reducing character increases down the group. Due to their higher ionisation potential they are less reducing than group 1 elements. ...
... Oxidation state = M2+ ,Be2+,Mg2+ ,Ca2+ ,Ba2+ ,Sr2+ Except Be- all other members are strong reducing agents that is obvious from their standard reduction potentials. The reducing character increases down the group. Due to their higher ionisation potential they are less reducing than group 1 elements. ...
PPT format
... Periodic Table: The group number of the group of a column for the main group elements in the periodic table is the number of valence electrons possessed by the neutral atom = atomic number = number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Group number (GN for main group elements) = number of valence el ...
... Periodic Table: The group number of the group of a column for the main group elements in the periodic table is the number of valence electrons possessed by the neutral atom = atomic number = number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Group number (GN for main group elements) = number of valence el ...
Midterm Review
... 38. In any physical or chemical change, mass is neither created nor destroyed (conserved) 39. In a chemical reaction, the new substances formed are called ...
... 38. In any physical or chemical change, mass is neither created nor destroyed (conserved) 39. In a chemical reaction, the new substances formed are called ...
Midterm Review
... 38. In any physical or chemical change, mass is neither created nor destroyed (conserved) 39. In a chemical reaction, the new substances formed are called ...
... 38. In any physical or chemical change, mass is neither created nor destroyed (conserved) 39. In a chemical reaction, the new substances formed are called ...
Year 11 Chemistry: Chapter 3 ~ The Periodic Table
... Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements chemical combine in fixed proportions. Each compound has its own characteristic set of properties, which are quite different from those of the elements it contains. Example: Sodium Chloride ( ____ ) ~ common salt, always contains 39.3% Sodium a ...
... Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements chemical combine in fixed proportions. Each compound has its own characteristic set of properties, which are quite different from those of the elements it contains. Example: Sodium Chloride ( ____ ) ~ common salt, always contains 39.3% Sodium a ...
PeriodicTableNotes
... the square. (typically has a decimal point with numbers after it) o The _____________ ____________ is the number given to element that represents its place on the periodic table. This number is generally the smaller of the two numbers and is normally at the top of the square. It is also the number o ...
... the square. (typically has a decimal point with numbers after it) o The _____________ ____________ is the number given to element that represents its place on the periodic table. This number is generally the smaller of the two numbers and is normally at the top of the square. It is also the number o ...
wahideh chemistry eportfolio hw
... rubidium, cesium, and francium. The members of the alkali metals family are among the most active elements. Compounds of sodium have been known, of course, throughout human history. But sodium metal was not prepared until 1807. The reason is that sodium attaches itself very strongly to other element ...
... rubidium, cesium, and francium. The members of the alkali metals family are among the most active elements. Compounds of sodium have been known, of course, throughout human history. But sodium metal was not prepared until 1807. The reason is that sodium attaches itself very strongly to other element ...
groups - Northside Middle School
... – Full set of valence electrons: most elements have 8 valence electrons, except Helium with 2 valence electrons, but it is still associated with this group because its properties match these elements. – Extremely stable and occur as monoatomic gases in nature – Although they do not readily combine w ...
... – Full set of valence electrons: most elements have 8 valence electrons, except Helium with 2 valence electrons, but it is still associated with this group because its properties match these elements. – Extremely stable and occur as monoatomic gases in nature – Although they do not readily combine w ...
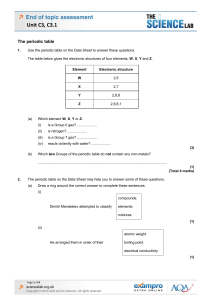
Unit C3, C3.1
... Use the periodic table on the Data Sheet to answer these questions. The table below gives the electronic structures of four elements, W, X, Y and Z. ...
... Use the periodic table on the Data Sheet to answer these questions. The table below gives the electronic structures of four elements, W, X, Y and Z. ...
Packet 4 - 16-17 Periodic Table
... heat and electricity; non-metals are usually gases, molecular solids or network solids (exception is bromine which is a liquid at room temperature). • Metalloids: Have some properties of both metals and nonmetals. • Noble Gases: Are all gases. Have 8 valence electrons (helium is the exception with 2 ...
... heat and electricity; non-metals are usually gases, molecular solids or network solids (exception is bromine which is a liquid at room temperature). • Metalloids: Have some properties of both metals and nonmetals. • Noble Gases: Are all gases. Have 8 valence electrons (helium is the exception with 2 ...
File
... halogens in its properties Ans 9)Hydrogen has single electron in its valence shell and forms a positively charged this is similar to alkali metals such as sodium .There fore hydrogen resembles alkali metals.However its chemical properties are not similar to alkali metals.Hydrogen is gaseous and form ...
... halogens in its properties Ans 9)Hydrogen has single electron in its valence shell and forms a positively charged this is similar to alkali metals such as sodium .There fore hydrogen resembles alkali metals.However its chemical properties are not similar to alkali metals.Hydrogen is gaseous and form ...
The Periodic Table - Crestwood Local Schools
... The changing of one element into another Alchemists tried to change such things as lead into gold. Modern chemists have produced elements with larger nuclei using equipment called particle accelerators ...
... The changing of one element into another Alchemists tried to change such things as lead into gold. Modern chemists have produced elements with larger nuclei using equipment called particle accelerators ...
bg`d xng gmz moxa gmog dbcxd gmz tovd gmog
... Period is the row that a given element is in. Group is the column that a given element is in. Elements within a group have similar chemical properties. The period of an elements can be determined from the electron configuration: For example, arsenic, As, has a configuration [Ar]3d104s24p3. The 4 in ...
... Period is the row that a given element is in. Group is the column that a given element is in. Elements within a group have similar chemical properties. The period of an elements can be determined from the electron configuration: For example, arsenic, As, has a configuration [Ar]3d104s24p3. The 4 in ...
PreAP Chemistry
... _______________ are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. _______________ _______________ are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. _______________ _______________ metals are in g ...
... _______________ are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. _______________ _______________ are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. _______________ _______________ metals are in g ...
The Periodic Table
... - Liquids: Bromine and mercury - Gases: H2, N2, O2, F2 , Cl2, and all the noble gases. - Solids: All other elements ...
... - Liquids: Bromine and mercury - Gases: H2, N2, O2, F2 , Cl2, and all the noble gases. - Solids: All other elements ...
The Periodic Table
... Transition metals = Groups 3-12 Inner transition elements (metals) = Element #’s 57-71 (Lantanides) and ...
... Transition metals = Groups 3-12 Inner transition elements (metals) = Element #’s 57-71 (Lantanides) and ...
What is matter? - Waterford Public Schools
... • The atom consists of positive, negative, and neutral entities (protons, electrons, and neutrons) • Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, which is small • Protons determine element’s identity • There can be a variable number of neutrons for the same number of protons – isotop ...
... • The atom consists of positive, negative, and neutral entities (protons, electrons, and neutrons) • Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, which is small • Protons determine element’s identity • There can be a variable number of neutrons for the same number of protons – isotop ...
Chapter 22 Chemistry of The NonMetals
... All elements have high ionization energies. He is the most important noble gas as liquid helium is used as a coolant. The heavier noble gases react more readily than the lighter ones. The most common compounds of noble gases are xenon fluorides. Xenon fluorides have Xe in the +2 to +8 oxidation stat ...
... All elements have high ionization energies. He is the most important noble gas as liquid helium is used as a coolant. The heavier noble gases react more readily than the lighter ones. The most common compounds of noble gases are xenon fluorides. Xenon fluorides have Xe in the +2 to +8 oxidation stat ...
Families of elements
... Will gain one electron to become stable -1 ions Reaction of chlorine (a halogen) with sodium (an alkali metal) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xT4OFS03jE ...
... Will gain one electron to become stable -1 ions Reaction of chlorine (a halogen) with sodium (an alkali metal) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1xT4OFS03jE ...