Dar al-Islam - Okemos Public Schools
... separate party with orthodox called “Shia” Islamic • Served as caliph theologians 656-661 CE, then assassinated along with most of his followers ...
... separate party with orthodox called “Shia” Islamic • Served as caliph theologians 656-661 CE, then assassinated along with most of his followers ...
Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia
... Conclusion: Legacy of the Abbasid Age Despite instability of the Abbasid, Islam’s central position in global history was solidified. The expanding Muslim world linked ancient civilizations through conquest and commercial networks. Islam was the civilizer of nomadic peoples in Asia & Africa. Its cult ...
... Conclusion: Legacy of the Abbasid Age Despite instability of the Abbasid, Islam’s central position in global history was solidified. The expanding Muslim world linked ancient civilizations through conquest and commercial networks. Islam was the civilizer of nomadic peoples in Asia & Africa. Its cult ...
Lesson Five - Shaykh Dr. Abdalqadir as-Sufi
... revival, the U.S. has been guided towards a pro-Shi‘a doctrine, and this on rabbinical advice. With a Shi‘a leadership crippling Pakistan, the awful Zardari/Bhutto regime, the Shi‘a in the north, Afghanistan, are protected and used by NATO. The USA having given Muslim Iraq to the Shi‘a, this new doc ...
... revival, the U.S. has been guided towards a pro-Shi‘a doctrine, and this on rabbinical advice. With a Shi‘a leadership crippling Pakistan, the awful Zardari/Bhutto regime, the Shi‘a in the north, Afghanistan, are protected and used by NATO. The USA having given Muslim Iraq to the Shi‘a, this new doc ...
Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and
... Al-Ghazali: brilliant Islamic theologian; attempted to fuse Greek and Qur’anic traditions. Sufis: Islamic mystics; spread Islam to many Afro-Asian regions. Mongols: central Asian nomadic peoples; captured Baghdad in 1258 and killed the last Abbasid caliph. Chinggis Khan: (1162–1227); Mongol ruler; d ...
... Al-Ghazali: brilliant Islamic theologian; attempted to fuse Greek and Qur’anic traditions. Sufis: Islamic mystics; spread Islam to many Afro-Asian regions. Mongols: central Asian nomadic peoples; captured Baghdad in 1258 and killed the last Abbasid caliph. Chinggis Khan: (1162–1227); Mongol ruler; d ...
Religion
... – By 632 A.D. he persuaded most of the Arabian Peninsula to follow his religion – By 1500 A.D. Islam dominates Arabia, Africa and Asia ...
... – By 632 A.D. he persuaded most of the Arabian Peninsula to follow his religion – By 1500 A.D. Islam dominates Arabia, Africa and Asia ...
Islamic (Muslim) Empire
... Sunni – believed the caliph should be chosen by Muslim leaders; do not view his as a religious authority. ...
... Sunni – believed the caliph should be chosen by Muslim leaders; do not view his as a religious authority. ...
Lecture: 9. Islam
... - a Turkic Sufi leader who traced his Shi’ite origins back to Ali - as his followers, the Red Hats, spread his doctrine among the Turkic tribes a more activist Shi’ite faith was adopted 2. Shah Ismâ’il (1487-1524) - a descendant of Sail al-Din, founder of Safavid Dynasty - a Safavid leader who led h ...
... - a Turkic Sufi leader who traced his Shi’ite origins back to Ali - as his followers, the Red Hats, spread his doctrine among the Turkic tribes a more activist Shi’ite faith was adopted 2. Shah Ismâ’il (1487-1524) - a descendant of Sail al-Din, founder of Safavid Dynasty - a Safavid leader who led h ...
Islam: A History of Submission
... It was during one of these excursions that Mohammad claimed to have been visited by the angel Gabriel to be chosen to receive God’s final warning to mankind and to “share” this message. Mohammad, being illiterate, recited his revelations to his wife and family who in turned believed his experience a ...
... It was during one of these excursions that Mohammad claimed to have been visited by the angel Gabriel to be chosen to receive God’s final warning to mankind and to “share” this message. Mohammad, being illiterate, recited his revelations to his wife and family who in turned believed his experience a ...
Islamic Words and Definitions
... Ilkhanids: (pronounced ill-KHAH-nihd) Mongol rulers in Iran who converted to Islam and became great patrons of the arts. The Mongols, people from modern-day Mongolia and Central Asia with a distinct cultural identity, invaded the Middle East in the 1200s. Islam: religion based on the revelations bel ...
... Ilkhanids: (pronounced ill-KHAH-nihd) Mongol rulers in Iran who converted to Islam and became great patrons of the arts. The Mongols, people from modern-day Mongolia and Central Asia with a distinct cultural identity, invaded the Middle East in the 1200s. Islam: religion based on the revelations bel ...
Branches of Islam - Ms. Johnson`s Comparative Religion
... Muhammad as leader of the emerging Muslim community after his death. To understand them, we need to know a bit about the Prophet's life and political and spiritual legacy. ...
... Muhammad as leader of the emerging Muslim community after his death. To understand them, we need to know a bit about the Prophet's life and political and spiritual legacy. ...
Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization
... interaction usually occurred First invasion in 711 a result of pirate attacks on Arab traders Conquered peoples left alone, treated as dhimmi This initial contact brought Indian culture and learning to Islam, particularly numerals ...
... interaction usually occurred First invasion in 711 a result of pirate attacks on Arab traders Conquered peoples left alone, treated as dhimmi This initial contact brought Indian culture and learning to Islam, particularly numerals ...
Chapter 6 Lesson 2
... the legacy of the fourth caliph, Ali, who was Muhammad's son-inlaw. After Ali was assassinated, the Umayyad Dynasty became the leaders of Islam. But followers of Ali, refusing to recognize the Umayyads as caliphs, formed their own branch of Islam that came to be called Shia. Another branch, called S ...
... the legacy of the fourth caliph, Ali, who was Muhammad's son-inlaw. After Ali was assassinated, the Umayyad Dynasty became the leaders of Islam. But followers of Ali, refusing to recognize the Umayyads as caliphs, formed their own branch of Islam that came to be called Shia. Another branch, called S ...
CHAPTER 13 - THE ISLAMIC HEARTLANDS AND INDIA (ca
... northern India during the thirteenth century and four later Muslim dynasties controlled the Delhi sultanate through the fifteenth century. It then was limited by the rise of independent Islamic states such as that of the Bachmanids; they were famous for the intellectual life of their court and for t ...
... northern India during the thirteenth century and four later Muslim dynasties controlled the Delhi sultanate through the fifteenth century. It then was limited by the rise of independent Islamic states such as that of the Bachmanids; they were famous for the intellectual life of their court and for t ...
Religious/ethnic groups of the middle east
... The Kurds are an ethnic group who live in several different countries in the Middle East. Most Kurds are found in mountainous areas where Syria, Turkey, Iran and Iraq come together. The Kurds see themselves as a distinct ethnic group from others in the area. They speak their own language, known as K ...
... The Kurds are an ethnic group who live in several different countries in the Middle East. Most Kurds are found in mountainous areas where Syria, Turkey, Iran and Iraq come together. The Kurds see themselves as a distinct ethnic group from others in the area. They speak their own language, known as K ...
AP World History Chapter 6
... • The Islamic foothold in the Indus Valley allowed for contact. • Math, medicine, music, astronomy • Hindu mathematicians and astronomers traveled to Baghdad in the 8th century. • Algebra and Geometry were translated into Arabic. • Indian numbers used by Arab Abbasids then passed on to Europeans cal ...
... • The Islamic foothold in the Indus Valley allowed for contact. • Math, medicine, music, astronomy • Hindu mathematicians and astronomers traveled to Baghdad in the 8th century. • Algebra and Geometry were translated into Arabic. • Indian numbers used by Arab Abbasids then passed on to Europeans cal ...
Resisting European global dominance
... • The Black Death put a severe strain on the on Afro-Eurasia but nonetheless societies coped and built up new dynasties • The world of Islam was re-ordered, with the Ottomans in the west and the Mughals in the east expanding their territory and taking in new influences, which the Safavids looked bac ...
... • The Black Death put a severe strain on the on Afro-Eurasia but nonetheless societies coped and built up new dynasties • The world of Islam was re-ordered, with the Ottomans in the west and the Mughals in the east expanding their territory and taking in new influences, which the Safavids looked bac ...
Who will Replace Muhammad?
... Muhammad is the prophet of Islam and the founder of one of the world’s largest and most influential religions. His guidance and inspiration have led his people to create the most powerful empire in Southwest Asia and build a religious movement that will influence history for thousands of years. It i ...
... Muhammad is the prophet of Islam and the founder of one of the world’s largest and most influential religions. His guidance and inspiration have led his people to create the most powerful empire in Southwest Asia and build a religious movement that will influence history for thousands of years. It i ...
Islam - Central Kitsap High School
... Well-disciplined armies - For the most part, the Muslim commanders were able, war tactics were effective, and the armies were efficiently organized. Weakness of the Byzantine and Persian Empires - As the Islamic armies spread north, they were aided by the weakness of the empires they sought to c ...
... Well-disciplined armies - For the most part, the Muslim commanders were able, war tactics were effective, and the armies were efficiently organized. Weakness of the Byzantine and Persian Empires - As the Islamic armies spread north, they were aided by the weakness of the empires they sought to c ...
Other traditions - University of Exeter
... • The areas where people who follow the Islamic religion live are far apart and have different cultures and cultures • In what sense can religious identity be said to be more important than class, gender, nation, culture or history, especially when discussing a political system? ...
... • The areas where people who follow the Islamic religion live are far apart and have different cultures and cultures • In what sense can religious identity be said to be more important than class, gender, nation, culture or history, especially when discussing a political system? ...
Introduction to Islam - Georgia State University
... penitential and redemptive aspect (NOTE: this does not make Shi`ism any more “extreme” or liable to a death cult than other traditions, but it does help explain some Shi`ite ways of acting. b. Belief in necessity of the Imam—necessary for existence of world, and infallible guide ...
... penitential and redemptive aspect (NOTE: this does not make Shi`ism any more “extreme” or liable to a death cult than other traditions, but it does help explain some Shi`ite ways of acting. b. Belief in necessity of the Imam—necessary for existence of world, and infallible guide ...
Sunni and Shia (Shiite) Islam
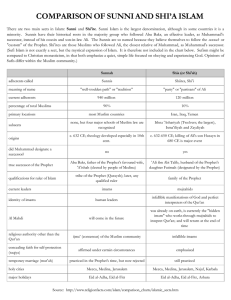
... Sunni and Shia (Shiite) Islam There are two main sects in Islam: Sunni and Shi'ite. Sunni Islam is the largest denomination, although in some countries it is a minority. Sunnis have their historical roots in the majority group who followed Abu Bakr, an effective leader, as Muhammad's successor, inst ...
... Sunni and Shia (Shiite) Islam There are two main sects in Islam: Sunni and Shi'ite. Sunni Islam is the largest denomination, although in some countries it is a minority. Sunnis have their historical roots in the majority group who followed Abu Bakr, an effective leader, as Muhammad's successor, inst ...
Stearns 6
... Need to limit converts to secure taxes and shares in booty Role of the Dhimmi (“People of the Book”) ...
... Need to limit converts to secure taxes and shares in booty Role of the Dhimmi (“People of the Book”) ...
COMPARISON OF SUNNI AND SHI`A ISLAM
... There are two main sects in Islam: Sunni and Shi'ite. Sunni Islam is the largest denomination, although in some countries it is a minority. Sunnis have their historical roots in the majority group who followed Abu Bakr, an effective leader, as Muhammad's successor, instead of his cousin and son-in-l ...
... There are two main sects in Islam: Sunni and Shi'ite. Sunni Islam is the largest denomination, although in some countries it is a minority. Sunnis have their historical roots in the majority group who followed Abu Bakr, an effective leader, as Muhammad's successor, instead of his cousin and son-in-l ...
Quick Facts about Islam - The Center for Middle Eastern Studies
... Islam is the second largest religion in the world. The word “Islam” is an Arabic word meaning submission to God. A Muslim is someone who follows Islam. Islam is one of the three primary monotheistic faiths of the Abrahamic traditions (Christianity and Judaism being the other two) and all three share ...
... Islam is the second largest religion in the world. The word “Islam” is an Arabic word meaning submission to God. A Muslim is someone who follows Islam. Islam is one of the three primary monotheistic faiths of the Abrahamic traditions (Christianity and Judaism being the other two) and all three share ...
File
... 16) This Pope called out to the Christian world to attack the major cities in the Middle East. Pope Urban II 17) This city is the most contested city in the Middle East, due to its religious importance. Jerusalem 18) This famous king led the 3rd Crusade. King Richard the Lionhearted 19) This small p ...
... 16) This Pope called out to the Christian world to attack the major cities in the Middle East. Pope Urban II 17) This city is the most contested city in the Middle East, due to its religious importance. Jerusalem 18) This famous king led the 3rd Crusade. King Richard the Lionhearted 19) This small p ...
Islam in Iran
The Islamic conquest of Persia (637–651) led to the end of the Sassanid Empire and the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion in Persia. However, the achievements of the previous Persian civilizations were not lost, but were to a great extent absorbed by the new Islamic polity. Islam has been the official religion of Iran since then, except short duration after Mongol raid and establishment of Ilkhanate. Iran became an Islamic republic after the Islamic Revolution of 1979.Before the Islamic conquest, the Persians had been mainly Zoroastrian, however, there were also large and thriving Christian and Jewish communities, especially in the territories of at that time northwestern, western, and southern Iran, mainly Caucasian Albania, Asorestan, Persian Armenia, and Caucasian Iberia. Eastern Sassanian Iran, what is now solely composed of Afghanistan and Central Asia, was predominantly Buddhist. There was a slow but steady movement of the population toward Islam. When Islam was introduced to Iranians, the nobility and city-dwellers were the first to convert, Islam spread more slowly among the peasantry and the dihqans, or landed gentry. By the late 11th century, the majority of Persians had become Muslim, at least nominally.Islam is the religion of 99.4% of Iranians. 90-95% of Iranians are Shi'a and 5-10% are Sunni. Most Sunnis in Iran are Larestani people (from Larestan), Turkomen, Baluchs, and Kurds living in the south, southeast, northeast and northwest. Almost all of Iranian Shi'as are Twelvers.Though Iran is known today as a stronghold of the Shi'a Muslim faith, it did not become so until much later, around the 15th century. The Safavid dynasty made Shi'a Islam the official state religion in the early sixteenth century and aggressively proselytized on its behalf. It is also believed that by the mid-seventeenth century most people in Iran and the territory of the contemporary neighboring Republic of Azerbaijan had become Shi'as, an affiliation that has continued. Over the following centuries, with the state-fostered rise of a Persian-based Shi'ite clergy, a synthesis was formed between Persian culture and Shi'ite Islam that marked each indelibly with the tincture of the other.