Fact Sheet - Center for Middle Eastern Studies
... true faith that was once embodied in Judaism and Christianity, but had been later obscured or corrupted by the passage of time. The central repository of divine revelation is the Qur'an (also spelled Koran), which Muslims believe came to Muhammad from God via the Arch-Angel Gabriel. Within this Holy ...
... true faith that was once embodied in Judaism and Christianity, but had been later obscured or corrupted by the passage of time. The central repository of divine revelation is the Qur'an (also spelled Koran), which Muslims believe came to Muhammad from God via the Arch-Angel Gabriel. Within this Holy ...
Sunni Shi’ite Split - University of Mount Union
... – Abu Bakr and his next two successors, Umar and Uthman, were considered illegitimate by Ali’s followers – 656 AD – Uthman was murdered by some of Ali’s followers – Ali was named as the successor – 661 AD – Ali was assassinated by forces of Uthman ...
... – Abu Bakr and his next two successors, Umar and Uthman, were considered illegitimate by Ali’s followers – 656 AD – Uthman was murdered by some of Ali’s followers – Ali was named as the successor – 661 AD – Ali was assassinated by forces of Uthman ...
Islam-Submission to Allah
... Iran, Iraq, and Israel. The Shiite ("partisans"), are the followers of Ali, a more orthodox and militant caliph, mainly in Iran, Iraq, and Israel. In 656, Ali and Fatima's son Hussein led a fight against the Sunnis. Hussein was tortured and beheaded, and today the Shiites of Iran honor the memory of ...
... Iran, Iraq, and Israel. The Shiite ("partisans"), are the followers of Ali, a more orthodox and militant caliph, mainly in Iran, Iraq, and Israel. In 656, Ali and Fatima's son Hussein led a fight against the Sunnis. Hussein was tortured and beheaded, and today the Shiites of Iran honor the memory of ...
Sunni and Shia Islam: Historical Context to Modern Conflict
... Iraqi Shias hitting themselves with swords on Ashura (Source: Arabian Business) ...
... Iraqi Shias hitting themselves with swords on Ashura (Source: Arabian Business) ...
Lesson D Sunni and Shia Flipped learning
... Islam: “submission, self-surrender”; monotheistic world religion closely related to Judaism and Christianity; adherents of Islam, called Muslims, comprise about 20-25% of the world (1.2–1.5 billion in 2000 CE). Sunni or Sunnite: Majority branch of Islam (ca. 85% of all Muslims worldwide). The branch ...
... Islam: “submission, self-surrender”; monotheistic world religion closely related to Judaism and Christianity; adherents of Islam, called Muslims, comprise about 20-25% of the world (1.2–1.5 billion in 2000 CE). Sunni or Sunnite: Majority branch of Islam (ca. 85% of all Muslims worldwide). The branch ...
File
... • The man who occupied the position at the time of Hussein’s death was Muawiya bin Abi Sufiyan. • He was said to have murdered his predecessor, Ali, who served as Islam’s fourth caliph Sunnis • 80-90 Percent of Muslims are Sunnis • Majority in most Muslim countries in Africa, Asian, and the Arab wor ...
... • The man who occupied the position at the time of Hussein’s death was Muawiya bin Abi Sufiyan. • He was said to have murdered his predecessor, Ali, who served as Islam’s fourth caliph Sunnis • 80-90 Percent of Muslims are Sunnis • Majority in most Muslim countries in Africa, Asian, and the Arab wor ...
The Impact of the Spread of Islam Task: Carefully read your
... However, in the West it was joined by the second and most powerful of the historical forces of the time, the rise of Islam and its expansion across the fertile lands of the Near East and South Asia. Movements of people by definition involve the exchange of ideas, economic systems, social usage, poli ...
... However, in the West it was joined by the second and most powerful of the historical forces of the time, the rise of Islam and its expansion across the fertile lands of the Near East and South Asia. Movements of people by definition involve the exchange of ideas, economic systems, social usage, poli ...
325 Glossary of Islamic Terms
... and political applications in the Middle-East; Asad’s foreign policy toward Israel and Lebanon; the culture approach to understanding the Middle-East. Dr. Bukay has written a number of articles on Middle-East issues and for Nativ. Anthony J. Dennis is a lawyer, human rights activist, and independent ...
... and political applications in the Middle-East; Asad’s foreign policy toward Israel and Lebanon; the culture approach to understanding the Middle-East. Dr. Bukay has written a number of articles on Middle-East issues and for Nativ. Anthony J. Dennis is a lawyer, human rights activist, and independent ...
Ch.8 Rise of Islam - Miami Beach Senior High School
... •After Muhammad’s death in 632, the Arabs conquests gave birth to a dynamic and religious society known as the Islamic Caliphate (empire ruled by a Caliph- political and religious leader) also known as Dar al Islam (house of submission). Stretched from Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) to the I ...
... •After Muhammad’s death in 632, the Arabs conquests gave birth to a dynamic and religious society known as the Islamic Caliphate (empire ruled by a Caliph- political and religious leader) also known as Dar al Islam (house of submission). Stretched from Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) to the I ...
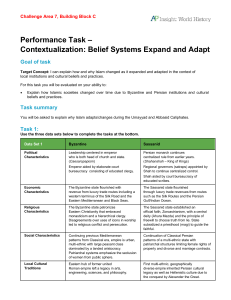
Belief Systems Expand and Adapt
... Two central tenets of Islam, part of the Five Pillars of Islam, are the principle of charity or support of the unfortunate in the community (Zakat), as well as pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj). ...
... Two central tenets of Islam, part of the Five Pillars of Islam, are the principle of charity or support of the unfortunate in the community (Zakat), as well as pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj). ...
Glossary of Arabic Terms `alim — a Muslim religious scholar
... Ikhwan al Muslimin — Muslim Brotherhood imam — leader of prayer; extended to mean leader of the community, particularly among shi‘is; title used by shi‘i religious rulers imama — leadership of the Muslim community Ismailis — a Shi‘i faction that under the leadership of the Aga Kahn, located mainly i ...
... Ikhwan al Muslimin — Muslim Brotherhood imam — leader of prayer; extended to mean leader of the community, particularly among shi‘is; title used by shi‘i religious rulers imama — leadership of the Muslim community Ismailis — a Shi‘i faction that under the leadership of the Aga Kahn, located mainly i ...
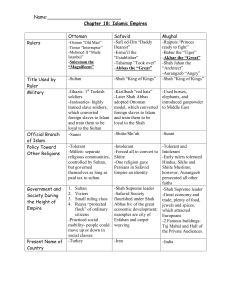
Ottoman - mikephillips
... -Kizilbash “red hats” -Later Shah Abbas adopted Ottoman model, which converted foreign slaves to Islam and train them to be loyal to the Shah ...
... -Kizilbash “red hats” -Later Shah Abbas adopted Ottoman model, which converted foreign slaves to Islam and train them to be loyal to the Shah ...
Political Islam
... Rise of the Abbasid Dynasty (750-1258 AD) a. The Abbasids were _____________ rebels against the Umayyads b. Managed to kill all but one Umayyad prince => c. Abbasids moved capital to _________________, in Iraq => ...
... Rise of the Abbasid Dynasty (750-1258 AD) a. The Abbasids were _____________ rebels against the Umayyads b. Managed to kill all but one Umayyad prince => c. Abbasids moved capital to _________________, in Iraq => ...
Chapter 10.2 ppt
... Focus Q: Nov. 17 What are the 5 pillars of Islam? Which would be the easiest for you to comply with? The hardest? Why? ...
... Focus Q: Nov. 17 What are the 5 pillars of Islam? Which would be the easiest for you to comply with? The hardest? Why? ...
Geographic influences on the origin and spread of Islam
... • Believed successors to successor Muhammad should by the community •Believed in an intermediary called an Imam •Those with religious authority(middle-man) should rule government too • Do not believe in intermediary between Allah and people ...
... • Believed successors to successor Muhammad should by the community •Believed in an intermediary called an Imam •Those with religious authority(middle-man) should rule government too • Do not believe in intermediary between Allah and people ...
Chapter 7
... Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia ...
... Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia ...
Historic Contributions of the Islamic Civilizations
... Great libraries, academies, and schools. Translated classical Greek scholarship into Arabic—preserving it for posterity Achievements in Medicine, astronomy, and Mathematics Muslim states in West break away from Abbasid control beginning in 756. Seljuk Turks convert to Islam and conquer Abb ...
... Great libraries, academies, and schools. Translated classical Greek scholarship into Arabic—preserving it for posterity Achievements in Medicine, astronomy, and Mathematics Muslim states in West break away from Abbasid control beginning in 756. Seljuk Turks convert to Islam and conquer Abb ...
The Expansive Realm of Islam
... = Islamic Spain, conquered by Berbers in 700s Continued to be governed by Umayyids (caliphs) Participated in Islamic economy Crops -> urban growth and businesses Elaborate capital at Cordoba (lighted roads, free ...
... = Islamic Spain, conquered by Berbers in 700s Continued to be governed by Umayyids (caliphs) Participated in Islamic economy Crops -> urban growth and businesses Elaborate capital at Cordoba (lighted roads, free ...
Muslim Dynasties PowerPoint
... Empire Building: Three of the great empires of history— the Ottomans in Turkey, the Safavids in Persia, and the Mughals in India—emerged in the Muslim world between the 14th and the 18th centuries. Cultural Diffusion: As powerful societies moved to expand their empires, Turkish, Persian, Mongol, and ...
... Empire Building: Three of the great empires of history— the Ottomans in Turkey, the Safavids in Persia, and the Mughals in India—emerged in the Muslim world between the 14th and the 18th centuries. Cultural Diffusion: As powerful societies moved to expand their empires, Turkish, Persian, Mongol, and ...
Islamic Culture and Art - Central Kitsap High School
... He is the administrator of the caliphate and a relgious leader The word derives from the Arabic خليفةKhalīfah (help·info), which means "successor" or "representative“ Requirements differ depending on sect ...
... He is the administrator of the caliphate and a relgious leader The word derives from the Arabic خليفةKhalīfah (help·info), which means "successor" or "representative“ Requirements differ depending on sect ...
pages - Western Civilisation
... The legitimacy of this claim is based on Mohammed's alleged designation of Ali as his successor. Alit right to rule was passed on, after his death in AD 66I, to his son Hasan (who chose not to claim it), and after Hasan's death, to Husayn, Ali's younger son. The evolution into a religious doctrine o ...
... The legitimacy of this claim is based on Mohammed's alleged designation of Ali as his successor. Alit right to rule was passed on, after his death in AD 66I, to his son Hasan (who chose not to claim it), and after Hasan's death, to Husayn, Ali's younger son. The evolution into a religious doctrine o ...
Islam in Iran
The Islamic conquest of Persia (637–651) led to the end of the Sassanid Empire and the eventual decline of the Zoroastrian religion in Persia. However, the achievements of the previous Persian civilizations were not lost, but were to a great extent absorbed by the new Islamic polity. Islam has been the official religion of Iran since then, except short duration after Mongol raid and establishment of Ilkhanate. Iran became an Islamic republic after the Islamic Revolution of 1979.Before the Islamic conquest, the Persians had been mainly Zoroastrian, however, there were also large and thriving Christian and Jewish communities, especially in the territories of at that time northwestern, western, and southern Iran, mainly Caucasian Albania, Asorestan, Persian Armenia, and Caucasian Iberia. Eastern Sassanian Iran, what is now solely composed of Afghanistan and Central Asia, was predominantly Buddhist. There was a slow but steady movement of the population toward Islam. When Islam was introduced to Iranians, the nobility and city-dwellers were the first to convert, Islam spread more slowly among the peasantry and the dihqans, or landed gentry. By the late 11th century, the majority of Persians had become Muslim, at least nominally.Islam is the religion of 99.4% of Iranians. 90-95% of Iranians are Shi'a and 5-10% are Sunni. Most Sunnis in Iran are Larestani people (from Larestan), Turkomen, Baluchs, and Kurds living in the south, southeast, northeast and northwest. Almost all of Iranian Shi'as are Twelvers.Though Iran is known today as a stronghold of the Shi'a Muslim faith, it did not become so until much later, around the 15th century. The Safavid dynasty made Shi'a Islam the official state religion in the early sixteenth century and aggressively proselytized on its behalf. It is also believed that by the mid-seventeenth century most people in Iran and the territory of the contemporary neighboring Republic of Azerbaijan had become Shi'as, an affiliation that has continued. Over the following centuries, with the state-fostered rise of a Persian-based Shi'ite clergy, a synthesis was formed between Persian culture and Shi'ite Islam that marked each indelibly with the tincture of the other.