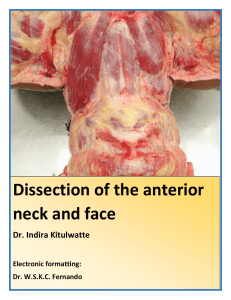
Muscles - Solutions - VCC Library
... tubules can generate action potentials(can be excited or depolarized) ...
... tubules can generate action potentials(can be excited or depolarized) ...
Fall Anatomy Final Review 11
... ____1. The pituitary gland is known as the "master gland" because it produces hormones to regulate other glands? ____2. The zygomatic bones are the cheekbones of the face. ____3. Iodine is important for the pituitary gland to function properly. ____4. Smooth muscle cells possess central nuclei but l ...
... ____1. The pituitary gland is known as the "master gland" because it produces hormones to regulate other glands? ____2. The zygomatic bones are the cheekbones of the face. ____3. Iodine is important for the pituitary gland to function properly. ____4. Smooth muscle cells possess central nuclei but l ...
Muscular System: Labeling the Muscles of the Body
... Anatomy Drill Practice (Muscle Tissue / The Muscular System) http://www.wiley.com/college/apcentral/anatomydrill/ Anatomy Arcade (Poke-A-Muscle) http://www.anatomyarcade.com/games/gamesMuscular.html Get Body Smart (Muscle Physiology Quiz) http://www.getbodysmart.com/ Purpose Games http://www.purpose ...
... Anatomy Drill Practice (Muscle Tissue / The Muscular System) http://www.wiley.com/college/apcentral/anatomydrill/ Anatomy Arcade (Poke-A-Muscle) http://www.anatomyarcade.com/games/gamesMuscular.html Get Body Smart (Muscle Physiology Quiz) http://www.getbodysmart.com/ Purpose Games http://www.purpose ...
Q = quadratus lumborum The quadratus lumborum (QL) muscle is a
... The QL can be a common source of lower back pain as it connects to the pelvis as well as the vertebra. The cause of pain can be when the erector spinae back muscles are weak or inhibited, which can occur through poor posture for long periods of time such as in a seated position. The QL will take ove ...
... The QL can be a common source of lower back pain as it connects to the pelvis as well as the vertebra. The cause of pain can be when the erector spinae back muscles are weak or inhibited, which can occur through poor posture for long periods of time such as in a seated position. The QL will take ove ...
Manual Muscle Testing
... The amount of pressure used to test may vary between persons performing the test. The amount of strength loss must be greater than approximately 20to 30% to be dependably measurable Comparison of both sides is a better indicator of loss ...
... The amount of pressure used to test may vary between persons performing the test. The amount of strength loss must be greater than approximately 20to 30% to be dependably measurable Comparison of both sides is a better indicator of loss ...
Manual Muscle Testing - Harrison High School
... The amount of pressure used to test may vary between persons performing the test. The amount of strength loss must be greater than approximately 20to 30% to be dependably measurable Comparison of both sides is a better indicator of loss ...
... The amount of pressure used to test may vary between persons performing the test. The amount of strength loss must be greater than approximately 20to 30% to be dependably measurable Comparison of both sides is a better indicator of loss ...
Smooth muscles
... cells junctions whose purpose is to facilitate the passage of an electrical impulse from cell to cell and to keep the cells bound together during constant contractile activity. ...
... cells junctions whose purpose is to facilitate the passage of an electrical impulse from cell to cell and to keep the cells bound together during constant contractile activity. ...
to see the ppt on rotator cuffs - Aman Singh`s LSA Web Portfolio
... Group 3: Rotator Cuff (Partial) BY: AMAN SINGH & WILL BOULTINGHOUSE ...
... Group 3: Rotator Cuff (Partial) BY: AMAN SINGH & WILL BOULTINGHOUSE ...
Tissues__Jan_29__student_version
... • Most rigid connective tissue • Contains matrix of inorganic salts • Supports, protects, attachment for muscles ...
... • Most rigid connective tissue • Contains matrix of inorganic salts • Supports, protects, attachment for muscles ...
Webquest- Skeletal and Muscular System
... 14 Where are involuntary muscles found and how do they move? ...
... 14 Where are involuntary muscles found and how do they move? ...
Muscle of mastication
... • It is the most superficial and powerful muscle of mastication it is quadrilateral in shape • Origen: it is origin is from the inferior and medial surface of Zygomatic bone and temporal process of zygomatic bone from here it extends downwards and posterior • Insertion : lateral surface of the Ramus ...
... • It is the most superficial and powerful muscle of mastication it is quadrilateral in shape • Origen: it is origin is from the inferior and medial surface of Zygomatic bone and temporal process of zygomatic bone from here it extends downwards and posterior • Insertion : lateral surface of the Ramus ...
Exercise Warming Up and Cooling Down
... A good cool-down should include five minutes of continued mild activity. Gradually, decrease the intensity to a slow walk. Also, spend a few minutes on slow stretching exercises to re-stretch the muscles. The cool-down will gradually slow down the heart’s pumping action and it will prevent blood fro ...
... A good cool-down should include five minutes of continued mild activity. Gradually, decrease the intensity to a slow walk. Also, spend a few minutes on slow stretching exercises to re-stretch the muscles. The cool-down will gradually slow down the heart’s pumping action and it will prevent blood fro ...
types of muscle tissue
... each fiber is uniform throughout its length and they do not branch out. Skeletal/ voluntary muscle is divided into two; a) Slow twitch These muscles are also called red muscles. They are dense in capillaries and rich in mitochondria and myoglobin, giving the muscle its red colour. It can carry more ...
... each fiber is uniform throughout its length and they do not branch out. Skeletal/ voluntary muscle is divided into two; a) Slow twitch These muscles are also called red muscles. They are dense in capillaries and rich in mitochondria and myoglobin, giving the muscle its red colour. It can carry more ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
... Myotubes the growth of muscle depends of the rate of fusion of Myotubes • Myobfilament & organelles develop in the cytoplasm of Myotubes • The muscle cells are long & narrow that’s why they are called Muscle fibers • These muscle fibers are wrapped in connective tissue sheath known as ...
... Myotubes the growth of muscle depends of the rate of fusion of Myotubes • Myobfilament & organelles develop in the cytoplasm of Myotubes • The muscle cells are long & narrow that’s why they are called Muscle fibers • These muscle fibers are wrapped in connective tissue sheath known as ...
Chap 10 - Muscles
... long axis of the muscle (e.g., sartorius) Fusiform – spindle-shaped muscles (e.g., biceps brachii) Pennate – short fascicles that attach obliquely to a central tendon running the length of the muscle (e.g., rectus femoris) Convergent – fascicles converge from a broad origin to a single tendon insert ...
... long axis of the muscle (e.g., sartorius) Fusiform – spindle-shaped muscles (e.g., biceps brachii) Pennate – short fascicles that attach obliquely to a central tendon running the length of the muscle (e.g., rectus femoris) Convergent – fascicles converge from a broad origin to a single tendon insert ...
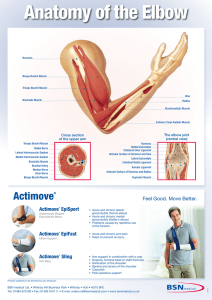
Actimove® - BSN medical India
... Humerus Medial Epicondyle Collateral Ulnar Ligament Articular Surface of Humerus and Ulna ...
... Humerus Medial Epicondyle Collateral Ulnar Ligament Articular Surface of Humerus and Ulna ...
Explain somite formation. Describe the development of
... Describe the development of limb musculature. Enlist the derivatives of Primaxial & Abaxial domains. Define the relation of muscle with its nerve supply. Understand the development of skull. Understand the development of limbs. Explain the mechanism of limb innervation. Discuss the anomalies of the ...
... Describe the development of limb musculature. Enlist the derivatives of Primaxial & Abaxial domains. Define the relation of muscle with its nerve supply. Understand the development of skull. Understand the development of limbs. Explain the mechanism of limb innervation. Discuss the anomalies of the ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.