Muscular System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al
... tube. The myoblasts adhere to each other as in developing skeletal muscle, but the intervening cell membranes do not disintegrate; these areas of adhesion give rise to intercalated discs. Myofibrils develop as in skeletal muscle, but myoblasts do not fuse. Late in the embryonic period, special bundl ...
... tube. The myoblasts adhere to each other as in developing skeletal muscle, but the intervening cell membranes do not disintegrate; these areas of adhesion give rise to intercalated discs. Myofibrils develop as in skeletal muscle, but myoblasts do not fuse. Late in the embryonic period, special bundl ...
The Muscular System
... range of motion- active or passive movement of muscle groups to full extent possible, used to prevent contracture sarcomere- repeating units of muscle fibers with the ability to contract skeletal- pertaining to the framework of the body stimulus- any agent, act, or influence that produces a change i ...
... range of motion- active or passive movement of muscle groups to full extent possible, used to prevent contracture sarcomere- repeating units of muscle fibers with the ability to contract skeletal- pertaining to the framework of the body stimulus- any agent, act, or influence that produces a change i ...
of the smooth muscles
... It is characterized by the instability of its membrane potential and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potentia ...
... It is characterized by the instability of its membrane potential and by the fact that it shows continuous, irregular contractions that are independent of its nerve supply. This maintained state of partial contraction is called tonus or tone. There is no true "resting" value for the membrane potentia ...
of the smooth muscles
... The membrane potential usually becomes larger, the spikes decrease in frequency, and the muscle relaxes. Norepinephrine exerts both α and β actions on the muscle. The β action, reduced muscle tension in response to excitation, is mediated via cyclic AMP and is due to increased intracellular binding ...
... The membrane potential usually becomes larger, the spikes decrease in frequency, and the muscle relaxes. Norepinephrine exerts both α and β actions on the muscle. The β action, reduced muscle tension in response to excitation, is mediated via cyclic AMP and is due to increased intracellular binding ...
anatomical relationships be able to demonstrate and describe
... be able to give examples of each tissue type are organs made of one or more tissues? skeletons what are the functions of bone, other than support and protection of organs? be able to distinguish types of bones on the basis of location (axial vs appendicular), development (endochondral vs intramembra ...
... be able to give examples of each tissue type are organs made of one or more tissues? skeletons what are the functions of bone, other than support and protection of organs? be able to distinguish types of bones on the basis of location (axial vs appendicular), development (endochondral vs intramembra ...
Stage 3 – Learning Plan DIFFERENTIATION (I
... Learning Activities: Objective: Unit 3: Health & Fitness SWBAT locate the 10 major muscle groups on a chart and know which muscles are used in which strength training exercises. Students will participate in the muscle mania game in which they try to group the muscles groups with the exercises th ...
... Learning Activities: Objective: Unit 3: Health & Fitness SWBAT locate the 10 major muscle groups on a chart and know which muscles are used in which strength training exercises. Students will participate in the muscle mania game in which they try to group the muscles groups with the exercises th ...
histology of muscles
... Characteristics Of Smooth Muscle Smooth muscle cell are described as spindle shaped. Wide in the middle and narrow to almost a point at both ends. Single centrally located nucleus. Smooth muscle cells do not have visible striations although they do Contains the same contractile proteins as skeletal ...
... Characteristics Of Smooth Muscle Smooth muscle cell are described as spindle shaped. Wide in the middle and narrow to almost a point at both ends. Single centrally located nucleus. Smooth muscle cells do not have visible striations although they do Contains the same contractile proteins as skeletal ...
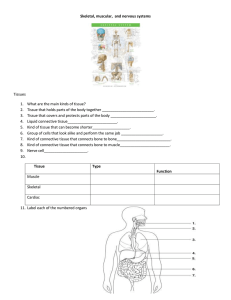
Skeletal, muscular, and nervous systems
... 30. The human skeleton is made up of about (106 / 206) bones. 31. There are three small bones located in the (nose / ears). 32. The largest bone in the body is located in the (thighs / arms). 33. The outer covering of a bone is called the (compact bone / periosteum). 34. The hardest part of a bone i ...
... 30. The human skeleton is made up of about (106 / 206) bones. 31. There are three small bones located in the (nose / ears). 32. The largest bone in the body is located in the (thighs / arms). 33. The outer covering of a bone is called the (compact bone / periosteum). 34. The hardest part of a bone i ...
Gross Anatomy: Muscles of the Trunk
... 2. State the action of the major muscles of the human body 3. State the origin and insertion of the major muscles of the human body ...
... 2. State the action of the major muscles of the human body 3. State the origin and insertion of the major muscles of the human body ...
article
... Before explaining how stretching works, it is important to understand how muscles work. Without making this an anatomy lesson, muscles are comprised of fibers and fibers and more fibers and then some connective tissue. Imagine if that was how biology class was taught. We would all have been A-studen ...
... Before explaining how stretching works, it is important to understand how muscles work. Without making this an anatomy lesson, muscles are comprised of fibers and fibers and more fibers and then some connective tissue. Imagine if that was how biology class was taught. We would all have been A-studen ...
Revision Questions/ Answers
... 3. What is the position we refer to the body in standing plane? 4. Name a bone distal to the metacarpals 5. Name the most medial bone in the body 6. What bones make up the shoulder girdle? 7. Arrange the vertebral column from superior to inferior bones 8. Define posterior 9. Define superior 10. What ...
... 3. What is the position we refer to the body in standing plane? 4. Name a bone distal to the metacarpals 5. Name the most medial bone in the body 6. What bones make up the shoulder girdle? 7. Arrange the vertebral column from superior to inferior bones 8. Define posterior 9. Define superior 10. What ...
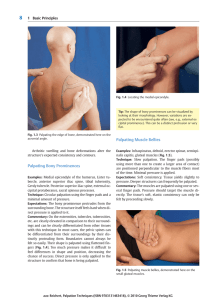
calf injuries - Sports Physio Norwest
... Following this, treatment to restore range of movement (such as stretches and gentle massage), and later to strengthen the healed muscle is required. When returning from a calf injury, a lack of pain in the muscle is a poor indicator of when it is safe to return to sport. A recent study found that w ...
... Following this, treatment to restore range of movement (such as stretches and gentle massage), and later to strengthen the healed muscle is required. When returning from a calf injury, a lack of pain in the muscle is a poor indicator of when it is safe to return to sport. A recent study found that w ...
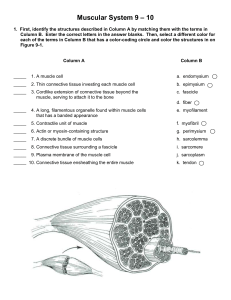
Muscle
... and color in the coding circle and corresponding muscles on Figure 10-1. ____________________________ Used to form the horizontal frown cease on the forehead or to raise your eyebrows ____________________________ Prime mover of head flexion; a two-headed muscle ____________________________ Prime mov ...
... and color in the coding circle and corresponding muscles on Figure 10-1. ____________________________ Used to form the horizontal frown cease on the forehead or to raise your eyebrows ____________________________ Prime mover of head flexion; a two-headed muscle ____________________________ Prime mov ...
Upper body
... This muscle is also known as the “boxer’s muscle” because the serratus anterior helps with horizontal arm movement like punching and pushing during horizontal adduction. ...
... This muscle is also known as the “boxer’s muscle” because the serratus anterior helps with horizontal arm movement like punching and pushing during horizontal adduction. ...
Skeletal System Webquest
... For the remaining questions, Do Research on the Internet. 1. What are the 5 functions of the skeletal system and give a description of each. ...
... For the remaining questions, Do Research on the Internet. 1. What are the 5 functions of the skeletal system and give a description of each. ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.