* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Muscular System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
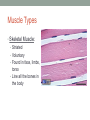
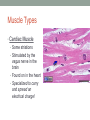
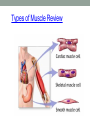
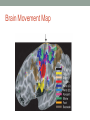
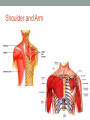
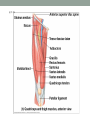
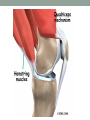
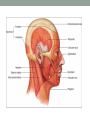
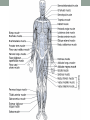
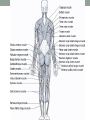
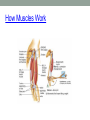
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Unit 5 Unit Goals • Describe the functions and structures of the muscular system including muscle fibers, fascia, tendons, and the three types of muscle • Recognize, define, spell and pronounce the terms related to muscle movements and explain how the muscles are named. • Recognize, define, pronounce and spell the terms related to the pathology and diagnostic and treatment procedures of the muscular system* • Time Permitting Enrichment Terms (see attachment) • antagonist- muscle that acts in opposition to the action of • • • • • • • another muscle, its agonist atrophy- wasting away, decrease in size contraction- shortening or development of tension in muscle tissue contracture- permanent shortening of tendons and ligaments of a joint resulting from atrophy of muscle dystrophy- muscle disorder resulting from defective or faulty nutrition, abnormal development, infection myalgia- muscle pain paralysis- loss or impairment of motor function posture- attitude or position of the body Terms Cont. • prime mover- muscle that acts directly to bring about a • • • • • • desired movement, agonist range of motion- active or passive movement of muscle groups to full extent possible, used to prevent contracture sarcomere- repeating units of muscle fibers with the ability to contract skeletal- pertaining to the framework of the body stimulus- any agent, act, or influence that produces a change in the development or function of tissues tonus- slight, continuous contraction of muscle visceral- pertaining to any large interior organ in any one of the cavities of the body What is a muscle? • Contractile Tissue (group of cells working together) • Produces force and motion Muscle Types • Smooth Muscle: • Automatically stimulated • No striations • Found in digestive system, hair follicles, and reproductive system Muscle Types • Skeletal Muscle: • Striated • Voluntary • Found in face, limbs, torso • Line all the bones in the body Muscle Types • Cardiac Muscle • Some striations • Stimulated by the vagus nerve in the brain • Found on in the heart • Specialized to carry and spread an electrical charge! Types of Muscle Review How does the muscle flex? • Muscle movement begins in the brain • Control of movement occurs in the primary motor cortex (M1) • Sends out nerve impulses to specific areas of skeletal muscle “Excitation” • The site of interaction b/t a neuron and any other cell is known as a synapse. • The synapse b/t a neuron and a muscle is known as the neuromuscular junction. • Excitation causes a reaction involving Na+, K+, and Ca2+ Brain Movement Map Muscle Action Terms • Flexion: decrease in joint angle from anatomical position (ex: bicep flex) • Extension: Return of body to anatomical pos. after flexion • Abduction: movement of limbs away from body (ex: jumping jacks/ snow angels) • Adduction: return of limbs back to anatomical pos. after abduction More Terms • Inversion: turning soles of feet to face each other (ex: common ankle sprain) • Eversion: soles of feet turn laterally • Protraction: horizontal movement in anterior direction (ex: jutting jaw forward) • Retraction: return to regular from horizontal More Terms • Elevation: To move in superior direction (ex: shoulder shrug) • Depression: move inferiorly (ex: drop shoulders) Last Terms • Supination: lateral rotation of the hand (ex: palms down to palms up, as if holding a bowl of soup) • Pronation: medial rotation of the hands (ex:palms up to palms down, dribbling position) • Plantarflexion: increasing the angle b/t the shin and top of foot (ex: stand on toes) • Dorsiflexion: decreasing the angle b/t the shin and top of foot • REVIEW TOGETHER Sample Movements- Hand Muscular System • There are over 600 muscles • Functions include: • Movement • Posture Maintenance • Generation of Heat • Breathing/ Digestion (compression of abdomen) • Trapezius: Extends/abducts head, rotates scapula • Deltoid: Abducts arm, flexes, extends, rotates (delts) • Pectoralis Major: Flexes, adducts arm (pecs) • Latissimus Dorsi: Extends, adducts arm (lats) • Biceps Brachii: Flexes arm, supinates hand (bis) • Triceps Brachii: Extends, adducts arm (tris) Individual Muscle GroupsShoulder and Arm Shoulder and Arm Individual Muscle GroupsHip and Thigh • Sartorius: Flexes and Laterally rotates thigh • Quadriceps: (grp of 4) Extend leg, flex thigh (Rectus Femoris, Vastus Lateralus/Medialis) • Hamstring Group: Extend thigh/ flex leg (Biceps Femoris) Individual Muscle GroupsLeg and Foot • Gastrocnemius: flex leg/ plantarflexes foot (also known as the calf muscle) • Soleus: Plantar flexes foot • Tibialis anterior: inverts foot/dorsiflexes foot Individual Muscle GroupsHead and Neck • Masseter: Closes mandible, largest mammalian mandible found on the rat • Zygomaticus: elevates the corners of the mouth, attached at zygomatic bone, responsible for your smile! • (Sternocleidomastoid, Orbicularius oculi/oris) Individual Muscle Groups Trunk • External Oblique: Compresses abdominal wall, • • • • laterally rotates trunk (love handles) Transverse Abdominis: same fxn Rectus Abdominis: Flexes vertebral column, compresses abdominal wall External intercostals: Elevates ribs (increase volume) Internal intercostals: Depresses ribs (decreases volume) How Muscles Work