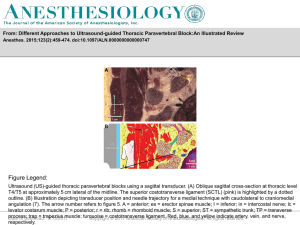
Muscle and NerveKD13
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
... • Has features of both skeletal and smooth muscle - Like skeletal muscle, it has strong contractions and striated appearance - Like smooth muscle, it is under involuntary control and has rhythmic contraction ...
BI212 Animal Form and Function Week 1 Vocabulary Terms
... How are muscles, joints, bones and tendons associated to result in a moving set of bones? Understand the difference between muscle antagonists and synergists. Understand the hierarchical structure of a vertebrate muscle from the gross muscle all the way to myofilaments. What is a sarcomere and what ...
... How are muscles, joints, bones and tendons associated to result in a moving set of bones? Understand the difference between muscle antagonists and synergists. Understand the hierarchical structure of a vertebrate muscle from the gross muscle all the way to myofilaments. What is a sarcomere and what ...
Lab Linked Tissues Worksheet
... ____1. tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock ____2. transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances ____3. withstand unidirectional tensile stress ____4. supports, reinforces, stands up to wear & tear ____5. reserve fuel source, insulates against heat ...
... ____1. tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock ____2. transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances ____3. withstand unidirectional tensile stress ____4. supports, reinforces, stands up to wear & tear ____5. reserve fuel source, insulates against heat ...
NAME: GLORY P.A. BRIGGS MATRICULATION NUMER: 14/MHS06
... Skeletal muscles are long cylindrical cells with many nuclei per cell. It has a stripy appearance because of the repeating structure of the muscle. There are many myofibrils each one of each is made up of repeating units called muscle sarcomeres, each sarcomere being 2.5mm long. Skeletal muscles are ...
... Skeletal muscles are long cylindrical cells with many nuclei per cell. It has a stripy appearance because of the repeating structure of the muscle. There are many myofibrils each one of each is made up of repeating units called muscle sarcomeres, each sarcomere being 2.5mm long. Skeletal muscles are ...
Study guide for final exam
... What protects the spinal cord? You should be able to label the structures found in the cross section of the spinal cord. What is flaccid paralysis and how can it be caused? What is the structure of a nerve? Types of nerves (sensory, motor, mixed) What do spinal nerves give rise to? (slide 16) Know t ...
... What protects the spinal cord? You should be able to label the structures found in the cross section of the spinal cord. What is flaccid paralysis and how can it be caused? What is the structure of a nerve? Types of nerves (sensory, motor, mixed) What do spinal nerves give rise to? (slide 16) Know t ...
Connective tissue
... Most skeletal muscle is attached to bone on its ends by tendons. As the muscles contract, they exert force on the bones, which help to support and move our body along with its appendages. In most cases, one end of the muscle is fixed in its position, while the other end moves during contraction. The ...
... Most skeletal muscle is attached to bone on its ends by tendons. As the muscles contract, they exert force on the bones, which help to support and move our body along with its appendages. In most cases, one end of the muscle is fixed in its position, while the other end moves during contraction. The ...
muscles
... Cardiac Muscle • Same mechanism as skeletal • Less calcium stored but longer T-tubules & more released with a single impulse • Impulses travel rapidly from cell to cell so it is self-stimulating ...
... Cardiac Muscle • Same mechanism as skeletal • Less calcium stored but longer T-tubules & more released with a single impulse • Impulses travel rapidly from cell to cell so it is self-stimulating ...
The following are Biology 201 terms that will be used in Biology 202
... 201 and since we stress homeostasis in both courses there will be a fair amount of information from biology 201 that is used in 202. The following terms you are expected to know and be able to use in biology 202. Anatomical position Directional terms Body planes and sections Body cavities Homeostasi ...
... 201 and since we stress homeostasis in both courses there will be a fair amount of information from biology 201 that is used in 202. The following terms you are expected to know and be able to use in biology 202. Anatomical position Directional terms Body planes and sections Body cavities Homeostasi ...
the muscular system
... The Muscular system in the body is composed of muscle cells and tissues that brings about movement of an organ or body part. There are three kinds of muscle: skeletal muscle, which is attached to bones and allows the voluntary movement of limbs; smooth muscle, which is found in internal organs and a ...
... The Muscular system in the body is composed of muscle cells and tissues that brings about movement of an organ or body part. There are three kinds of muscle: skeletal muscle, which is attached to bones and allows the voluntary movement of limbs; smooth muscle, which is found in internal organs and a ...
Intramuscular Injections
... • Given into the muscle layer beneath the dermis and subcu tissue • Intermediate absorption rate • 3 mL syringe • 19 – 25g needle • 1 to 3 inch needle length ...
... • Given into the muscle layer beneath the dermis and subcu tissue • Intermediate absorption rate • 3 mL syringe • 19 – 25g needle • 1 to 3 inch needle length ...
Test Review
... Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Know your diagram. 1. The connective tissue wrappings _____________________________ each cell and __________________________the whole muscle AND provide entry & exit points for ______________ & _________________. 2. Skeletal muscle is dependent on its nerve supply because it ...
... Skeletal Muscle Anatomy: Know your diagram. 1. The connective tissue wrappings _____________________________ each cell and __________________________the whole muscle AND provide entry & exit points for ______________ & _________________. 2. Skeletal muscle is dependent on its nerve supply because it ...
NAME____________________________________ MUSCULAR
... http://www.cyh.com/HealthTopics/HealthTopicDetailsKids.aspx?p=335&np=152&id=2457 ...
... http://www.cyh.com/HealthTopics/HealthTopicDetailsKids.aspx?p=335&np=152&id=2457 ...
Powerpoint
... - controls the involuntary beating of the heart - appears striated under a microscope. ...
... - controls the involuntary beating of the heart - appears striated under a microscope. ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.