Noun – names a person, place, thing, or idea.
... - may come before or after the word it modifies - may be used as a subject complement Demonstrative adjectives – point out definite persons, places, and things. - this, that, these, those Interrogative adjectives – are used in questions. - what, which, whose Indefinite adjectives – refer to any or a ...
... - may come before or after the word it modifies - may be used as a subject complement Demonstrative adjectives – point out definite persons, places, and things. - this, that, these, those Interrogative adjectives – are used in questions. - what, which, whose Indefinite adjectives – refer to any or a ...
Present - Grade 4 Merlins
... Verbs in the present have two forms The correct form to use depends on what the subject of the sentence. 1. Add s to the verb when the noun in the subject is singular. The dog barks at the snowman. Jill laughs. 2. Do NOT add s to the verb when the noun in the subject is plural. The boys shovel. T ...
... Verbs in the present have two forms The correct form to use depends on what the subject of the sentence. 1. Add s to the verb when the noun in the subject is singular. The dog barks at the snowman. Jill laughs. 2. Do NOT add s to the verb when the noun in the subject is plural. The boys shovel. T ...
Week 21
... • A verb should agree in number with its subject. • The number of a subject is not changed by a phrase following the subject • Example: These shades of blue are my favorite ...
... • A verb should agree in number with its subject. • The number of a subject is not changed by a phrase following the subject • Example: These shades of blue are my favorite ...
Phrases - Huber Heights City Schools
... Verbal phrase- [NOT a verb phrase] = looks like a verb but does not act like a verb Participial phrase (present and past) = always serves as an adjective modifying nouns or pronouns Ex. = I saw two kittens playing happily. Thinking about the snow, Joe pulled on his cap. The very frightened cat ran u ...
... Verbal phrase- [NOT a verb phrase] = looks like a verb but does not act like a verb Participial phrase (present and past) = always serves as an adjective modifying nouns or pronouns Ex. = I saw two kittens playing happily. Thinking about the snow, Joe pulled on his cap. The very frightened cat ran u ...
verb notes - TeacherWeb
... underlined words are nouns. Some students get carried away with making common nouns proper. They seem to think that every word they capitalize suddenly becomes exciting or important. Too many capitals ...
... underlined words are nouns. Some students get carried away with making common nouns proper. They seem to think that every word they capitalize suddenly becomes exciting or important. Too many capitals ...
Mid-term project
... Students will be able to define a noun, a verb and an adjective. Students will be able to identify nouns, adjectives and verbs. Students will be able to identify the different parts of speech within a sentence. ...
... Students will be able to define a noun, a verb and an adjective. Students will be able to identify nouns, adjectives and verbs. Students will be able to identify the different parts of speech within a sentence. ...
Name - Scarsdale Schools
... Objective- These nouns do one of two things: receive the action of the verb. Ex: The boy threw the ball to Sue. appear at end of prep. phrase. Ex: The boy threw the ball (to Sue.) Possessive: These nouns show possession, or ownership. Ex: Tom’s team won. Method to determine case: 1. Verb: Find t ...
... Objective- These nouns do one of two things: receive the action of the verb. Ex: The boy threw the ball to Sue. appear at end of prep. phrase. Ex: The boy threw the ball (to Sue.) Possessive: These nouns show possession, or ownership. Ex: Tom’s team won. Method to determine case: 1. Verb: Find t ...
Grammar for Writing
... When using verbs in past time, do not use a helper verb with the past form; however, use a helper verb with the past participle. This rule applies to all verbs, but focus on irregular verbs as their past tense and past participle forms are different from each other. For example: Mary took the le ...
... When using verbs in past time, do not use a helper verb with the past form; however, use a helper verb with the past participle. This rule applies to all verbs, but focus on irregular verbs as their past tense and past participle forms are different from each other. For example: Mary took the le ...
File - teacherver.com
... over, above, below, on, in to the office, to my church, to our disadvantage To = infinitive (followed by a verb) To talk, to deny, to eat, to find ...
... over, above, below, on, in to the office, to my church, to our disadvantage To = infinitive (followed by a verb) To talk, to deny, to eat, to find ...
document
... to a system of endings for nouns that reveal a noun’s function in a sentence is a bit bland, but the way to do it. In modern English, we are left only with one case for nouns and three cases for pronouns. The one surviving case is genitive, which shows possession (ex, Donna’s garden). ...
... to a system of endings for nouns that reveal a noun’s function in a sentence is a bit bland, but the way to do it. In modern English, we are left only with one case for nouns and three cases for pronouns. The one surviving case is genitive, which shows possession (ex, Donna’s garden). ...
Latin I: Unit IV Test Review Guide
... nouns from the vocabulary. a. Ex. puella: [ m / f / n ] [ 1st / 2nd ] b. When you study your vocabulary, be sure to memorize the genitive form of each noun, as this form tells you what declension it is, and memorize the gender of the noun along with its meaning. Cases and Syntax I. You are given sev ...
... nouns from the vocabulary. a. Ex. puella: [ m / f / n ] [ 1st / 2nd ] b. When you study your vocabulary, be sure to memorize the genitive form of each noun, as this form tells you what declension it is, and memorize the gender of the noun along with its meaning. Cases and Syntax I. You are given sev ...
Subject-Verb Agreement - Student Academic Success Services
... In the present tense, verbs agree with their subjects in number (singular or plural) and in person (first, second, or third). If the subject is third-person singular (he/she/it), the presenttense ending of the verb will generally be -s (or -es, e.g., she gives). Otherwise, the verb takes no ending ( ...
... In the present tense, verbs agree with their subjects in number (singular or plural) and in person (first, second, or third). If the subject is third-person singular (he/she/it), the presenttense ending of the verb will generally be -s (or -es, e.g., she gives). Otherwise, the verb takes no ending ( ...
spanish grammar - Lingue in Piazza
... medicine and they study law.) / Hablas español ? Do you speak Spanish? (informal)/ Habla Ud. español? Do you speak Spanish? (formal) Note: The verb forms are the same for él, ella and Ud. as are the verb forms for ellos, ellas and Uds, although In Spanish the subject pronouns are not always required ...
... medicine and they study law.) / Hablas español ? Do you speak Spanish? (informal)/ Habla Ud. español? Do you speak Spanish? (formal) Note: The verb forms are the same for él, ella and Ud. as are the verb forms for ellos, ellas and Uds, although In Spanish the subject pronouns are not always required ...
PartsofSpeech
... Other useful things to know about verbs: Tense: past, present, future Agreement: Remember to use that –s form! Auxiliaries are helping verbs: do, be, have, and modals ...
... Other useful things to know about verbs: Tense: past, present, future Agreement: Remember to use that –s form! Auxiliaries are helping verbs: do, be, have, and modals ...
Trimester One Grammar
... its = possessive (What is its name?) it’s = it is (It’s going to rain.) their = possessive (Where is their game?) they’re = they are (They’re going to the game.) there = place (I want to go there!) Forming and Using Plural Nouns Most nouns are changed from singular to plural by adding –s ...
... its = possessive (What is its name?) it’s = it is (It’s going to rain.) their = possessive (Where is their game?) they’re = they are (They’re going to the game.) there = place (I want to go there!) Forming and Using Plural Nouns Most nouns are changed from singular to plural by adding –s ...
Present participles, gerunds and `–ing`
... instead of using identifying relative clauses that use ‘who’, ‘which’, ‘when’ or ‘that’ and a complete verb. I knew some of the people playing (relative clause): I knew some of the people that were playing Is that her dancing with your brother? (relative clause): Is that her who is dancing with your ...
... instead of using identifying relative clauses that use ‘who’, ‘which’, ‘when’ or ‘that’ and a complete verb. I knew some of the people playing (relative clause): I knew some of the people that were playing Is that her dancing with your brother? (relative clause): Is that her who is dancing with your ...
Stage 4 Check 7 – Answers
... 3-4. (W4:2, Sp 4:19,20) Homophones are words that sound the same but have different meanings and different spellings. ...
... 3-4. (W4:2, Sp 4:19,20) Homophones are words that sound the same but have different meanings and different spellings. ...
Parts of Speech Noun Pronoun Verb Adjective Adverb Preposition
... tells what, to whom, for what, or for whom an action is done. Verbs that often take indirect objects include bring, give, hand, lend, make, send, show, teach, tell, and write. The rescue team gives hot food. (Gives food to or for whom?) The rescue team gives the survivors hot food. ...
... tells what, to whom, for what, or for whom an action is done. Verbs that often take indirect objects include bring, give, hand, lend, make, send, show, teach, tell, and write. The rescue team gives hot food. (Gives food to or for whom?) The rescue team gives the survivors hot food. ...
Eight parts of speech
... together and shows the relation between them. "My hand is on the table" shows relation between hand and table. Prepositions are so called because they are generally placed before the words whose connection or relation with other words they point out. Examples of common English Prepositions: above, a ...
... together and shows the relation between them. "My hand is on the table" shows relation between hand and table. Prepositions are so called because they are generally placed before the words whose connection or relation with other words they point out. Examples of common English Prepositions: above, a ...
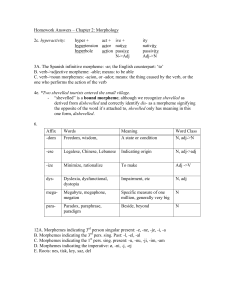
Homework Answers – Chapter 2
... 7a. to form an infinitive in Dutch: root + -en b. to form the Dutch past participle form: ge- + root + -d (this is a circumfix, not a prefix and a suffix; without both morphemes, no meaning is added) 8a. nouns: -toto ‘child’, -tu ‘person’, -kapu ‘basket’, -su ‘knife’; verbs: -fika ‘to arrive’, -lala ...
... 7a. to form an infinitive in Dutch: root + -en b. to form the Dutch past participle form: ge- + root + -d (this is a circumfix, not a prefix and a suffix; without both morphemes, no meaning is added) 8a. nouns: -toto ‘child’, -tu ‘person’, -kapu ‘basket’, -su ‘knife’; verbs: -fika ‘to arrive’, -lala ...
Feb. 2017 Language notes
... • Possessive Pronouns: shows ownership It replaces a possessive noun. There are two kinds of possessive pronouns. One kind is used before a noun. The other kind stands alone. Possessive Pronouns with Nouns my your his, her, its our their ...
... • Possessive Pronouns: shows ownership It replaces a possessive noun. There are two kinds of possessive pronouns. One kind is used before a noun. The other kind stands alone. Possessive Pronouns with Nouns my your his, her, its our their ...
Inventory of grammatical areas Verbs Regular and irregular forms
... Type 2: I would tell you the answer if I knew it / If I were you, I wouldn’t do that again. ...
... Type 2: I would tell you the answer if I knew it / If I were you, I wouldn’t do that again. ...
World Languages: Spanish I YEAR AT A GLANCE
... Days, Months, Seasons Colors Geography of the Spanish-speaking world ...
... Days, Months, Seasons Colors Geography of the Spanish-speaking world ...
Modern Greek grammar

The grammar of Standard Modern Greek, as spoken in present-day Greece and Cyprus, is basically that of Demotic Greek, but it has also assimilated certain elements of Katharevousa, the archaic, learned variety of Greek imitating Classical Greek forms, which used to be the official language of Greece through much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Modern Greek grammar has preserved many features of Ancient Greek, but has also undergone changes in a similar direction as many other modern Indo-European languages, from more synthetic to more analytic structures.