Soils of Zimbabwe
... Sodic soils occur in the low rainfall areas, which include the Save and Zambezi Valleys. In moderate rainfall areas, interaction of parent material and relief results in significant soils for example Gokwe, Chivu and Chegutu. The soils have undesirable physical and chemical properties for example, t ...
... Sodic soils occur in the low rainfall areas, which include the Save and Zambezi Valleys. In moderate rainfall areas, interaction of parent material and relief results in significant soils for example Gokwe, Chivu and Chegutu. The soils have undesirable physical and chemical properties for example, t ...
Soil Taxonomy and Soil Geography
... Strongly indu rated5 bedrock W Water layers within or und erlying so il (1) The symbols in parentheses illustrate the appropriate lower case modifiers used to describe specific features of master horizons. (2) The term illuvial refers to material transported into a horizon from layers above it. (3) ...
... Strongly indu rated5 bedrock W Water layers within or und erlying so il (1) The symbols in parentheses illustrate the appropriate lower case modifiers used to describe specific features of master horizons. (2) The term illuvial refers to material transported into a horizon from layers above it. (3) ...
Area 3 Envirothon – April 25, 2012 – Soils Test
... B. If a building is built, there are major problems which must be overcome, usually at additional cost. * C. This soil is well suited to buildings. D. Rock is at depths less than 20 inches. 13. Some soils are poorly suited for septic tank absorption fields due to ____________________. A. flooding B. ...
... B. If a building is built, there are major problems which must be overcome, usually at additional cost. * C. This soil is well suited to buildings. D. Rock is at depths less than 20 inches. 13. Some soils are poorly suited for septic tank absorption fields due to ____________________. A. flooding B. ...
Presentation
... is below the C-horizon. Remember that the Coastal Plain does not have bedrock under the soil profile, but it has layers of sand, clay and gravel. That is because of the sea level changes over time and the rivers that flowed over it. ...
... is below the C-horizon. Remember that the Coastal Plain does not have bedrock under the soil profile, but it has layers of sand, clay and gravel. That is because of the sea level changes over time and the rivers that flowed over it. ...
File
... Soils that form in limestone bedrock are rich in calcium, Soils that formed from materials at the bottom of lakes are high in clay. ...
... Soils that form in limestone bedrock are rich in calcium, Soils that formed from materials at the bottom of lakes are high in clay. ...
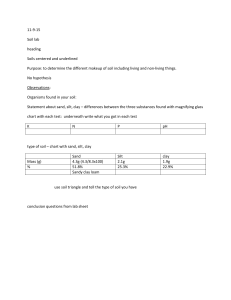
11-9-15 Soils Lab
... Soils centered and underlined Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each t ...
... Soils centered and underlined Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each t ...
New soil test - Washtenaw County
... Cost: Mailers for landscapes, vegetable & flower gardens are available at your local MSU Extension office for $25.00. Sampling: for garden soils, sample 6 inches to 8 inches deep. For lawns, lift the sod and sample 3 inches deep. Take 15 or 20 sub samples in the area you are testing and mix them tho ...
... Cost: Mailers for landscapes, vegetable & flower gardens are available at your local MSU Extension office for $25.00. Sampling: for garden soils, sample 6 inches to 8 inches deep. For lawns, lift the sod and sample 3 inches deep. Take 15 or 20 sub samples in the area you are testing and mix them tho ...
5 factors of soil formation
... 3. Climate – soil created faster in warm, wet weather 4. Organisms – earthworms and other burrowing animals aerate soil and add organic matter, and speed decomposition 5. Parent material (bedrock) – the rock soil is made from has different chemical and physical properties ...
... 3. Climate – soil created faster in warm, wet weather 4. Organisms – earthworms and other burrowing animals aerate soil and add organic matter, and speed decomposition 5. Parent material (bedrock) – the rock soil is made from has different chemical and physical properties ...
LOCATION LEETONIA VA+MD PA WV
... RANGE IN CHARACTERISTICS: Solum thickness ranges from 17 to 42 inches. Depth to bedrock is 40 inches or more. Coarse fragments of quartzite or sandstone range from 35 to 65 percent by volume in the control section. These soils are gravelly or very gravelly sand, loamy sand or loamy fine sand through ...
... RANGE IN CHARACTERISTICS: Solum thickness ranges from 17 to 42 inches. Depth to bedrock is 40 inches or more. Coarse fragments of quartzite or sandstone range from 35 to 65 percent by volume in the control section. These soils are gravelly or very gravelly sand, loamy sand or loamy fine sand through ...
Soils of the Mornington Peninsula
... The red volcanic soils of the Red Hill area (described as red ferrosols) are deep, have good structure, drain well and are highly fertile. They are widely used for vineyards, orchards and berry production. Rosebud (Ro) The Rosebud surface unit consists of low fertility dark grey sands to 300mm with ...
... The red volcanic soils of the Red Hill area (described as red ferrosols) are deep, have good structure, drain well and are highly fertile. They are widely used for vineyards, orchards and berry production. Rosebud (Ro) The Rosebud surface unit consists of low fertility dark grey sands to 300mm with ...
How to make biochar
... micro-particle matrix in soils. which converts to humic substances results in directly more Soil Organic Matter. ...
... micro-particle matrix in soils. which converts to humic substances results in directly more Soil Organic Matter. ...
Soil science facts
... generally begins at the surface of rocks and progresses in depth over the course of time, whereby layers are formed with ...
... generally begins at the surface of rocks and progresses in depth over the course of time, whereby layers are formed with ...
soil matrix - School of Earth and Environment
... the physical and chemical parameters of soils which set primary conditions for life on Earth ...
... the physical and chemical parameters of soils which set primary conditions for life on Earth ...
Data/hora: 06/05/2017 14:31:12 Biblioteca(s): Embrapa Cerrados
... Biotite- slightly altered biotite - pseudomorph of kaolinite. Gibbsite occurs in high amounts in areas which have a short dry season or in slightly drier ones. Iron oxide aggregates occur in the coarser fractions of every profile and are composed of gibbsite and quartz coated by amorphus iron oxides ...
... Biotite- slightly altered biotite - pseudomorph of kaolinite. Gibbsite occurs in high amounts in areas which have a short dry season or in slightly drier ones. Iron oxide aggregates occur in the coarser fractions of every profile and are composed of gibbsite and quartz coated by amorphus iron oxides ...
POSITION PAPER
... Soil is one of the most important natural resources of the planet, but until now its ecological significance has been greatly underestimated. The availability of elements essential for life depends on soil, as well as climate change adaptation and water availability. Soil is home of a wide variety o ...
... Soil is one of the most important natural resources of the planet, but until now its ecological significance has been greatly underestimated. The availability of elements essential for life depends on soil, as well as climate change adaptation and water availability. Soil is home of a wide variety o ...
Microbial adaptation to temperature increases the vulnerability of
... Arctic, Boreal, temperate, Mediterranean and tropical ecosystems. This study represents one of the most extensive investigations undertaken into the potential for thermal acclimation, and/or enhancement, under contrasting environmental conditions. We also attempted to disentangle the mechanisms unde ...
... Arctic, Boreal, temperate, Mediterranean and tropical ecosystems. This study represents one of the most extensive investigations undertaken into the potential for thermal acclimation, and/or enhancement, under contrasting environmental conditions. We also attempted to disentangle the mechanisms unde ...
Soils of Britain
... on chalk downland and other limestone hills. Limestone dissolves in rainwater and so weathering leaves little material for soil formation. The profile consists of a few decimetres of mixed organic matter, chalk fragments and limited amounts of impurities and windblown imports. The productivity of mo ...
... on chalk downland and other limestone hills. Limestone dissolves in rainwater and so weathering leaves little material for soil formation. The profile consists of a few decimetres of mixed organic matter, chalk fragments and limited amounts of impurities and windblown imports. The productivity of mo ...
Soil Stories
... Bedrock: This is solid rock that formed before the soil above it. It will wait until erosion or an earthquake exposes it to the surface. Then it will be weathered to become parent material. ...
... Bedrock: This is solid rock that formed before the soil above it. It will wait until erosion or an earthquake exposes it to the surface. Then it will be weathered to become parent material. ...
Soil and Water Science Department University of Florida Field
... integrates three separate projects, which all utilize phosphate rock (PR), into an integrated synergetic one. The primary objectives are to: 1) assess long-term effectiveness of P amendments in immobilizing lead in contaminated soils; 2) explore the feasibility of using PR to remediate lead contamin ...
... integrates three separate projects, which all utilize phosphate rock (PR), into an integrated synergetic one. The primary objectives are to: 1) assess long-term effectiveness of P amendments in immobilizing lead in contaminated soils; 2) explore the feasibility of using PR to remediate lead contamin ...
Soil The loose mixture of small mineral fragments, organic material
... also known as topsoil. This is the layer where most plants grow. Leaves and other organic material fall to the ground becoming litter. This litter eventually breaks down and becomes humus. Humus is the decayed organic material that makes the soil so fertile. The layer directly below Horizon A and is ...
... also known as topsoil. This is the layer where most plants grow. Leaves and other organic material fall to the ground becoming litter. This litter eventually breaks down and becomes humus. Humus is the decayed organic material that makes the soil so fertile. The layer directly below Horizon A and is ...
ABSTRACT FORM
... «northern», «western», «southeastern» and «southern» parts of the STS, specified in this way according to their geographic location at the test site territory. In spite being closely located to testing spots, radiological situation at the most of conditionally «background» territories mainly depends ...
... «northern», «western», «southeastern» and «southern» parts of the STS, specified in this way according to their geographic location at the test site territory. In spite being closely located to testing spots, radiological situation at the most of conditionally «background» territories mainly depends ...
The house appears to be bisected along its length with two good
... These differing soils were not a problem when the house was constructed with all portions of the building sitting on grade. Until the 20th Century there were little more than crawlspaces underneath and these did not reach to the depth of the clay. But in the last 60 years, the the wings and hyphens ...
... These differing soils were not a problem when the house was constructed with all portions of the building sitting on grade. Until the 20th Century there were little more than crawlspaces underneath and these did not reach to the depth of the clay. But in the last 60 years, the the wings and hyphens ...
Pyrus calleryana `Aristocrat`
... Medium sized tree with firmly attached horizontal branching and pyramidal to oval form Greyish-brown bark Green leaves in summer with an undulate margin, and spectacular red and orange autumn leaf colour White flowers in spring Small pea-sized red-brown fruits ...
... Medium sized tree with firmly attached horizontal branching and pyramidal to oval form Greyish-brown bark Green leaves in summer with an undulate margin, and spectacular red and orange autumn leaf colour White flowers in spring Small pea-sized red-brown fruits ...