* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 factors of soil formation
Survey
Document related concepts
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Entomopathogenic nematode wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Soil respiration wikipedia , lookup
Soil erosion wikipedia , lookup
Terra preta wikipedia , lookup
Crop rotation wikipedia , lookup
Soil salinity control wikipedia , lookup
Soil compaction (agriculture) wikipedia , lookup
No-till farming wikipedia , lookup
Canadian system of soil classification wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Soil horizon wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Soil microbiology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
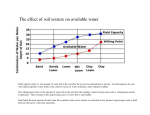
12.1 Soil Formation Chapter 12 – Soil and Agriculture Arable – farmable land DIRT = bad word SOIL – complex plant-supporting system made of disintegrating rock, remains and wastes of organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and microorganisms. Renewable/sustainable hundreds to thousands of years to renew 1 inch of topsoil finite = limited 5 factors of soil formation desert rain mountains 1. Landforms – mountains and valleys affect sun, rain and wind exposure Steep slopes promote erosion. 2. Time – soil formation takes decades, centuries, or millennia 3. Climate – soil created faster in warm, wet weather 4. Organisms – earthworms and other burrowing animals aerate soil and add organic matter, and speed decomposition 5. Parent material (bedrock) – the rock soil is made from has different chemical and physical properties 12.1 soil horizons – layers of soil soil profile – cross-section of soil from surface to bedrock few soils contain all of the six layers O Horizon = Litter Layer A Horizon = Topsoil E Horizon = Leaching B Horizon = Subsoil C Horizon = Weathered Parent Material R Horizon = Parent Material - Bedrock topsoil – most important to humans and what we degrade soil characteristics – color, texture, structure, pH (measurement of acidy) Color – darker the soil, the richer in nutrients Texture – clay (smallest), silt, sand (largest) Loam – mixture of each of the particles BEST = silty or loamy Structure – arrangement of soil particles BEST = clumpy pH = affects ability for plants to grow deposition – taking soil from one area & putting into another o usually caused by erosion o helps with primary succession Humus – dark, spongy, crumbly mass of material that is high in nutrients = ideal soil