English
... “B” horizon. This horizon is referred to as the subsoil. It is often called the “zone of accumulation” since chemicals leached from the A and E horizons accumulate here. This accumulation is called illuviation. The B horizon will have less organic matter and more clay than the A horizon. Together, t ...
... “B” horizon. This horizon is referred to as the subsoil. It is often called the “zone of accumulation” since chemicals leached from the A and E horizons accumulate here. This accumulation is called illuviation. The B horizon will have less organic matter and more clay than the A horizon. Together, t ...
Soils Background
... Crops and Soils Club Phone: 715-425-3395 Department of Plant & Earth Science University of WI – River Falls ...
... Crops and Soils Club Phone: 715-425-3395 Department of Plant & Earth Science University of WI – River Falls ...
powerpoint
... If evapotranspiration exceeds precipitation, water and minerals may be drawn upwards by the process of capillary movement. ...
... If evapotranspiration exceeds precipitation, water and minerals may be drawn upwards by the process of capillary movement. ...
VERT-EXPERT “TRADITION”: Organic Mineral “Slow Release
... Improving the physical soil characteristics as well as the C.E.C (Cation Exchange Capacity): ...
... Improving the physical soil characteristics as well as the C.E.C (Cation Exchange Capacity): ...
soil type and areas of peat(uk) - British Council Schools Online
... smaller amount of clay . •Types of loam soils: sandy loam, silty loam, clay loam, sandy clay loam, silty clay loam, and loam. •Loam soils generally contain more nutrients, moisture, and humus than sandy soils, have better drainage and infiltration of water and air than silt soils, and are easier to ...
... smaller amount of clay . •Types of loam soils: sandy loam, silty loam, clay loam, sandy clay loam, silty clay loam, and loam. •Loam soils generally contain more nutrients, moisture, and humus than sandy soils, have better drainage and infiltration of water and air than silt soils, and are easier to ...
Lecture 1 - Introduction to Soils in the Environment
... the wife gets pregnant. Without a permit, their childand will aquifers be put in cold storage at Remediation of contaminated soils, waters Quality/Ecological Indicators birth. Later, Soil if they can obtain a permit, the government will unfreeze the baby Soil/Landscape and return it. The couple'sAna ...
... the wife gets pregnant. Without a permit, their childand will aquifers be put in cold storage at Remediation of contaminated soils, waters Quality/Ecological Indicators birth. Later, Soil if they can obtain a permit, the government will unfreeze the baby Soil/Landscape and return it. The couple'sAna ...
File - leavingcertgeography
... As a result, the boundary between the A and B horizons can be ill defined in unploughed examples. Horizon B is mostly composed of mineral matter which has been weathered from the parent material, but it often contains inclusions of more organic material carried in by organisms, especially earthworms ...
... As a result, the boundary between the A and B horizons can be ill defined in unploughed examples. Horizon B is mostly composed of mineral matter which has been weathered from the parent material, but it often contains inclusions of more organic material carried in by organisms, especially earthworms ...
NEW HORIZONS the next revolution in agriculture
... pastures at the end of a season yy saline sub-soils or soils with very high or very low pH levels which are hostile to root growth yy high sodium and boron concentration in soils, toxic to plant growth ...
... pastures at the end of a season yy saline sub-soils or soils with very high or very low pH levels which are hostile to root growth yy high sodium and boron concentration in soils, toxic to plant growth ...
soil study guide 2015
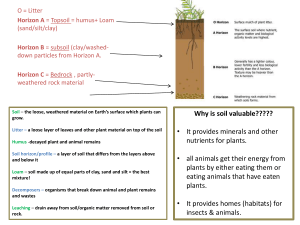
... Soil – the loose, weathered material on Earth’s surface which plants can grow. Litter – a loose layer of leaves and other plant material on top of the soil Humus -decayed plant and animal remains Soil horizon/profile – a layer of soil that differs from the layers above and below it ...
... Soil – the loose, weathered material on Earth’s surface which plants can grow. Litter – a loose layer of leaves and other plant material on top of the soil Humus -decayed plant and animal remains Soil horizon/profile – a layer of soil that differs from the layers above and below it ...
forensic soil analysis ii
... and chromatographic techniques used for their analysis. • To highlight the study of soil fauna-microbe (DNA) as well as to publicize the MISAFE project, corresponding to a FP7 European project. • Comunication of the current situation of this kind of analytical investigations related to legal studi ...
... and chromatographic techniques used for their analysis. • To highlight the study of soil fauna-microbe (DNA) as well as to publicize the MISAFE project, corresponding to a FP7 European project. • Comunication of the current situation of this kind of analytical investigations related to legal studi ...
File
... on acid rocks such as sandstone while more alkaline brown earths form on lime rich parent material. 4 Humus content- brown earth soil have a high humus content because of the action of humification. Humification is a soilforming process that occurs when dead organic matter is converted into humus by ...
... on acid rocks such as sandstone while more alkaline brown earths form on lime rich parent material. 4 Humus content- brown earth soil have a high humus content because of the action of humification. Humification is a soilforming process that occurs when dead organic matter is converted into humus by ...
Soils - Nmsu
... Increases the pop. of beneficial microorganisms to out compete the disease organisms. ...
... Increases the pop. of beneficial microorganisms to out compete the disease organisms. ...
Example format for answering text review questions and key word
... PV=NRT or the ideal gas law can be used to explain thermal expansion. As the temperature goes up, so must the pressure of the gas on its container or, if the gas is uncontained, higher temperatures result in higher volumes or greater gas diffusion. This same idea can be applied to rocks. At higher t ...
... PV=NRT or the ideal gas law can be used to explain thermal expansion. As the temperature goes up, so must the pressure of the gas on its container or, if the gas is uncontained, higher temperatures result in higher volumes or greater gas diffusion. This same idea can be applied to rocks. At higher t ...
Soils Atlas of Europe
... This section of the Atlas has introduced you to the 23 major soil types of Europe1. The colour used in the box surrounding the soil group name is the same colour that is used for that soil type in all the maps in the next sections of the Atlas. In this way, when you see a red area (i.e. an Andosol) ...
... This section of the Atlas has introduced you to the 23 major soil types of Europe1. The colour used in the box surrounding the soil group name is the same colour that is used for that soil type in all the maps in the next sections of the Atlas. In this way, when you see a red area (i.e. an Andosol) ...
TYPES OF SOIL Mansi Jain B.Ed VDIT SOIL
... and coarse. 90% sand & 5% clay. Rich in Nitrates & Phosphates. Poor in Nitrogen & Humus. Friable, sandy & low moist content. 1.4 Lakh sqkm. ...
... and coarse. 90% sand & 5% clay. Rich in Nitrates & Phosphates. Poor in Nitrogen & Humus. Friable, sandy & low moist content. 1.4 Lakh sqkm. ...
BBRO Advisory Bulletin No 15 - W/C 15th August 2016 Moisture
... Moisture stress - A number of crops and especially those on the thinner, lighter loams and sandy soils are now showing signs of moisture stress with wilting occurring at the hottest part of the day and further yellowing developing in the areas of the fields where rooting has been restricted. Many so ...
... Moisture stress - A number of crops and especially those on the thinner, lighter loams and sandy soils are now showing signs of moisture stress with wilting occurring at the hottest part of the day and further yellowing developing in the areas of the fields where rooting has been restricted. Many so ...
Higher Geography Biosphere For this unit you should be able to
... Brown earth forms on gently sloping and low lands. Land is well drained and allows biological activity Indistinct horizon boundaries – Soil is well mixed due to earthworm and soil bacteria activity. A horizon – well aerated, humus enriched mineral soil (pH 5.8). Dark brown in colour because humus re ...
... Brown earth forms on gently sloping and low lands. Land is well drained and allows biological activity Indistinct horizon boundaries – Soil is well mixed due to earthworm and soil bacteria activity. A horizon – well aerated, humus enriched mineral soil (pH 5.8). Dark brown in colour because humus re ...
Soils, Landforms, and Vegetation of Bidwell Park
... Bidwell Park provides a great outdoor classroom to explore the relationships between landform, soils, and the vegetation occurring on those soils. The geological processes that shape the land and create soil can be revealed by walking through this dramatic landscape. Differences in vegetation often ...
... Bidwell Park provides a great outdoor classroom to explore the relationships between landform, soils, and the vegetation occurring on those soils. The geological processes that shape the land and create soil can be revealed by walking through this dramatic landscape. Differences in vegetation often ...
Soil Color - Soils @ UGA
... • A cartographic unit is a naturally occurring body that can be delineated on a map of some form (“soil phase”) – Cartographic units, in most cases, contain individuals from several taxonomic units – One or more soils may be dominant in the landscape unit delineated on the map, but there are always ...
... • A cartographic unit is a naturally occurring body that can be delineated on a map of some form (“soil phase”) – Cartographic units, in most cases, contain individuals from several taxonomic units – One or more soils may be dominant in the landscape unit delineated on the map, but there are always ...
Soil Science Big Ideas
... From these rocks different types of soils over time have formed. Rocks are made of a mineral or cemented minerals. Soil is made up of many different components – either disintegrated rocks and living or dead organic matter. Organic matter is made of the organic compounds – carbon / oxygen / phosphor ...
... From these rocks different types of soils over time have formed. Rocks are made of a mineral or cemented minerals. Soil is made up of many different components – either disintegrated rocks and living or dead organic matter. Organic matter is made of the organic compounds – carbon / oxygen / phosphor ...
Soils NR 200
... a) O- organic layer i) How is this formed?? ii) Sub classes i and a b) A- topsoil – the most productive soil i) With the addition of the acids from the higher organic material leaching of the easily soluble compounds calcium, calcite and gypsum will move down into the lower horizons of the profile a ...
... a) O- organic layer i) How is this formed?? ii) Sub classes i and a b) A- topsoil – the most productive soil i) With the addition of the acids from the higher organic material leaching of the easily soluble compounds calcium, calcite and gypsum will move down into the lower horizons of the profile a ...