Chapter 19
... Since prokaryotes do not recognize introns, the DNA which is complementary to the mRNA must be used. ...
... Since prokaryotes do not recognize introns, the DNA which is complementary to the mRNA must be used. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Organizer
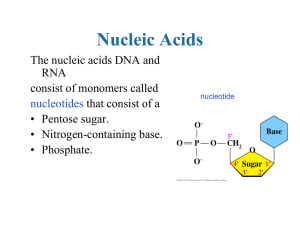
... 2. RNA, like DNA, is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides. What are the four differences between DNA and RNA? a. ...
... 2. RNA, like DNA, is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides. What are the four differences between DNA and RNA? a. ...
Study Guide MBMB 451A Fall 2002
... and IIH. What are TAFs and are they important for basal transcription. 7. What is an enhancer? What is a response element? 8. Describe two models for how an enhancer could effect the level of transcription. 9. What are the transcription factors called that are used by Pol I and Pol III? 10. Discuss ...
... and IIH. What are TAFs and are they important for basal transcription. 7. What is an enhancer? What is a response element? 8. Describe two models for how an enhancer could effect the level of transcription. 9. What are the transcription factors called that are used by Pol I and Pol III? 10. Discuss ...
國立嘉義大學九十一學年度
... 1.The region of DNA that is upstream from a prokaryotic gene(s) and to which a repressor or activator binds. 2.The entire complement of genetic material of an organism, virus, or organelle. 3.A DNA sequence that is used to detect the presence of a complementary sequence by hybridization with a nucle ...
... 1.The region of DNA that is upstream from a prokaryotic gene(s) and to which a repressor or activator binds. 2.The entire complement of genetic material of an organism, virus, or organelle. 3.A DNA sequence that is used to detect the presence of a complementary sequence by hybridization with a nucle ...
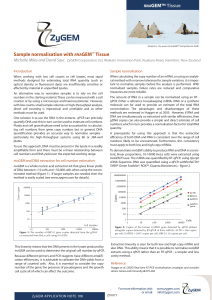
Sample normalisation with RNAGEM™ Tissue
... methods are reviewed in Hugget et al. 2005. However, if RNA and DNA are simultaneously co-extracted with similar efficiencies, then gDNA copies can also provide a simple and direct estimate of cell numbers which in turn provides a normalisation factor for total RNA quantity. A prerequisite for using ...
... methods are reviewed in Hugget et al. 2005. However, if RNA and DNA are simultaneously co-extracted with similar efficiencies, then gDNA copies can also provide a simple and direct estimate of cell numbers which in turn provides a normalisation factor for total RNA quantity. A prerequisite for using ...
DNA REVIEW SHEET (answer in COMPLETE sentences on another
... structure of DNA? Draw a diagram of how this technique works. ExplainJames Watson and Francis Crick contribution to biology? List the 3 parts of a DNA nucleotide. What are the 4 nucleotide bases of DNA? List Chargaff’s Rules (1947). What did Chargaff’s research help Watson and Crick deduce about DNA ...
... structure of DNA? Draw a diagram of how this technique works. ExplainJames Watson and Francis Crick contribution to biology? List the 3 parts of a DNA nucleotide. What are the 4 nucleotide bases of DNA? List Chargaff’s Rules (1947). What did Chargaff’s research help Watson and Crick deduce about DNA ...
Genetic Engineering Powerpoint
... Can be cut up using Restriction Enzymes They cut DNA at specific nucleotide ...
... Can be cut up using Restriction Enzymes They cut DNA at specific nucleotide ...
Chapter 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7 Study Guide Key terms: Ribonucleic acid
... 28. Which types of point mutations cause a frame shift mutation? 29. Create a DNA sequence of 12 nucleotides. Transcribe the DNA sequence into mRNA. Finally, use the amino acid table to write the amino acid sequence. ...
... 28. Which types of point mutations cause a frame shift mutation? 29. Create a DNA sequence of 12 nucleotides. Transcribe the DNA sequence into mRNA. Finally, use the amino acid table to write the amino acid sequence. ...
Isolation of DNA from 96 Well Plates
... Incubate at -20oC for at least 30 minutes until precipitated DNA is visible as long threads under tissue culture microscope. 7. Quickly invert plate over sink to dump out liquid then blot on paper towel. 8. Rinse 3 times with 100μl 70% ethanol. With each rinse, quickly invert plate over sink then bl ...
... Incubate at -20oC for at least 30 minutes until precipitated DNA is visible as long threads under tissue culture microscope. 7. Quickly invert plate over sink to dump out liquid then blot on paper towel. 8. Rinse 3 times with 100μl 70% ethanol. With each rinse, quickly invert plate over sink then bl ...
A Comparison of Concentration Methods for Low Copy Number
... samples these methods are highly controversial as a result of stochastic effects which complicate the data analysis interpretation process. However, LCN typing techniques may be avoided or reduced by improved processes prior to amplification of purified DNA such as improved sample storage, DNA colle ...
... samples these methods are highly controversial as a result of stochastic effects which complicate the data analysis interpretation process. However, LCN typing techniques may be avoided or reduced by improved processes prior to amplification of purified DNA such as improved sample storage, DNA colle ...
Answers-to-examination-in-Gene-technology_20121020
... Reverse primer: 5’-TCAAAGGTCCCTGTCCTGCAGGGC-3’ d) Change in the DNA sequence that do not cause any change in the amino acid sequence. e) A palindromic sequence: CTTTGA change to 5’-CTATAG-3’ or 5’-TTATAA-5 3’-GATATC-5’ 3’-AATATT-3’ f) The advantage is the possibility to regulate the transcription of ...
... Reverse primer: 5’-TCAAAGGTCCCTGTCCTGCAGGGC-3’ d) Change in the DNA sequence that do not cause any change in the amino acid sequence. e) A palindromic sequence: CTTTGA change to 5’-CTATAG-3’ or 5’-TTATAA-5 3’-GATATC-5’ 3’-AATATT-3’ f) The advantage is the possibility to regulate the transcription of ...
DNA-Polymerase
... solution. (roughly 40 seconds-CAUTION: It bubbles quickly so do 10 second intervals) 5. Add 2.5 ml of 10x TAE buffer, then add 20 ml ethidium bromide (EtBr). 6. Gently pour solution into gel tray, remove bubbles and let it sit for 20 minutes. ...
... solution. (roughly 40 seconds-CAUTION: It bubbles quickly so do 10 second intervals) 5. Add 2.5 ml of 10x TAE buffer, then add 20 ml ethidium bromide (EtBr). 6. Gently pour solution into gel tray, remove bubbles and let it sit for 20 minutes. ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... RNA polymerase complex binds to “promoter” region of DNA and opens helix Promoter region is upstream for a specific gene. Promoter region contains two specific sets of nucleotide sequences. P252 Fig. 6.6 For each gene only ONE strand of the double-stranded DNA molecule is transcribed-this is c ...
... RNA polymerase complex binds to “promoter” region of DNA and opens helix Promoter region is upstream for a specific gene. Promoter region contains two specific sets of nucleotide sequences. P252 Fig. 6.6 For each gene only ONE strand of the double-stranded DNA molecule is transcribed-this is c ...
Safety - Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering
... A. R. van der Krol, L. A. Mur, M. Beld, JNM. Mol and A. R. Stuitje THE PLANT CELL, Vol 2, Issue 4 291-299, 1990 ...
... A. R. van der Krol, L. A. Mur, M. Beld, JNM. Mol and A. R. Stuitje THE PLANT CELL, Vol 2, Issue 4 291-299, 1990 ...
Gene Expression/Transcription & Translation Practice PowerPoint
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
... In 1917 the biologist Thomas Hunt Morgan conducted studies in which he kept some caterpillars in the dark and placed other under red, green, or blue lights. Exposure to red light produced butterflies with brightly colored wings. Exposure to green light resulted in dark-colored wings. Exposure to bl ...
Real-time polymerase chain reaction

A real-time polymerase chain reaction is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR, i.e. in real-time, and not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively (Quantitative real-time PCR), semi-quantitatively, i.e. above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules (Semi quantitative real-time PCR) or qualitatively (Qualitative real-time PCR).Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are: (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA, and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence.The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines propose that the abbreviation qPCR be used for quantitative real-time PCR and that RT-qPCR be used for reverse transcription–qPCR [1]. The acronym ""RT-PCR"" commonly denotes reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and not real-time PCR, but not all authors adhere to this convention.