Motor proteins of the kinesin superfamily
... (60–70 kDa). Electron microscopy, protease sensitivity and primary sequence analysis showed that the kinesin heavy chain is composed of three domains [2,3]. As shown in Figure 1(a), the globular N-terminal head domain (residues 1–325) contains the ATPase activity as well as a microtubule-binding sit ...
... (60–70 kDa). Electron microscopy, protease sensitivity and primary sequence analysis showed that the kinesin heavy chain is composed of three domains [2,3]. As shown in Figure 1(a), the globular N-terminal head domain (residues 1–325) contains the ATPase activity as well as a microtubule-binding sit ...
Glycolytic Enzymes Associate Dynamically with
... addition of KCN, an inhibitor of complex IV of the mitochondrial respiratory chain (Villani and Attardi, 2007), or increased by the addition of carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP), a proton ionophore that uncouples mitochondrial electron transport from ATP synthesis (Felle and Bentrup, 1 ...
... addition of KCN, an inhibitor of complex IV of the mitochondrial respiratory chain (Villani and Attardi, 2007), or increased by the addition of carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP), a proton ionophore that uncouples mitochondrial electron transport from ATP synthesis (Felle and Bentrup, 1 ...
REVIEWS Structural insights into the function of the
... in e-GDI (orange), which form part of the GDI-CHM consensus domain (GCD) region. The coordinates CxC or CC acceptor residues of H-ras (PDB 4q21) were taken from the Brookhaven databank. (b) The location of residues involved efficiently inhibit prenylation in FAD binding to flavoproteins. The structu ...
... in e-GDI (orange), which form part of the GDI-CHM consensus domain (GCD) region. The coordinates CxC or CC acceptor residues of H-ras (PDB 4q21) were taken from the Brookhaven databank. (b) The location of residues involved efficiently inhibit prenylation in FAD binding to flavoproteins. The structu ...
SKIP controls lysosome positioning using a composite kinesin
... terminally citrulline (mCit, a GFP derivative) tagged KHC (Cai et al., 2007) and HA-KLC2, or as a control GFP and HA-KLC2. Co-transfection of mCit-KHC with HA-KLC2 resulted in an increase in HA-KLC2 expression compared to co-transfection with GFP (Figure 5A, compare lanes 1,2). Cit-KHC was bound (l ...
... terminally citrulline (mCit, a GFP derivative) tagged KHC (Cai et al., 2007) and HA-KLC2, or as a control GFP and HA-KLC2. Co-transfection of mCit-KHC with HA-KLC2 resulted in an increase in HA-KLC2 expression compared to co-transfection with GFP (Figure 5A, compare lanes 1,2). Cit-KHC was bound (l ...
manipulation of respiratory burst of neutrophils using c1
... Figure 2-2 NADPH oxidase complex and where it can be found. Taken from Fig. 1 in Dahlgren et al, 1999. ........................................................................................................... 11 Figure 2-3 Conversion of molecular oxygen, O2 to superoxide, O2- by NADPH oxidase comp ...
... Figure 2-2 NADPH oxidase complex and where it can be found. Taken from Fig. 1 in Dahlgren et al, 1999. ........................................................................................................... 11 Figure 2-3 Conversion of molecular oxygen, O2 to superoxide, O2- by NADPH oxidase comp ...
Extracellular ATP signaling in plants
... Animal purinergic receptors are of two types, P2X ion channels and P2Y G-protein-coupled seven-transmembrane receptors [3]. Extensive efforts to identify plant homologs of these animal receptors by sequence and structural comparison algorithms failed to identify canonical P2 receptors [34,35]. Recen ...
... Animal purinergic receptors are of two types, P2X ion channels and P2Y G-protein-coupled seven-transmembrane receptors [3]. Extensive efforts to identify plant homologs of these animal receptors by sequence and structural comparison algorithms failed to identify canonical P2 receptors [34,35]. Recen ...
Mitochondrial Dynamics
... Mitochondrial division is a highly coordinated process that involves the formation of two or more daughter organelles by scission of a single mitochondrion. To an extent the mechanisms that carry out mitochondrial fission reflect the evolutionary history of the organelle. Mitochondria are descended ...
... Mitochondrial division is a highly coordinated process that involves the formation of two or more daughter organelles by scission of a single mitochondrion. To an extent the mechanisms that carry out mitochondrial fission reflect the evolutionary history of the organelle. Mitochondria are descended ...
Isoprenoid biosynthesis in bacterial pathogens
... (HMGR) is present in all four sequenced Vibrio species (V. cholerae, Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio fischeri). Gophna et al. (2006) examined the evolutionary history of hmgR within these species, and their data suggest that hmgR was acquired by an ancestral Vibrio in a single ...
... (HMGR) is present in all four sequenced Vibrio species (V. cholerae, Vibrio vulnificus, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio fischeri). Gophna et al. (2006) examined the evolutionary history of hmgR within these species, and their data suggest that hmgR was acquired by an ancestral Vibrio in a single ...
Cryptic O2 –-generating NADPH oxidase in
... DCs generate a substantial amount of O2– in the presence of PMA following preincubation with pro-inflammatory ligands such as lipopolysaccharide and pansorbin, and to a lesser extent with anti-CD40 or polyinosinic polycytidylic acid. We found that the virtual lack of the oxidase response to PMA alon ...
... DCs generate a substantial amount of O2– in the presence of PMA following preincubation with pro-inflammatory ligands such as lipopolysaccharide and pansorbin, and to a lesser extent with anti-CD40 or polyinosinic polycytidylic acid. We found that the virtual lack of the oxidase response to PMA alon ...
The variability of autophagy and cell death susceptibility
... mitochondria.2 BECN1 and PIK3C3/VPS34, for example, are pivotal in the formation of a lipid kinase complex, which in turn allows the recruitment and shuttling of ATG proteins that contribute to the generation of the phagophore, the initial sequestering compartment. Next, the ubiquitin-like conjugat ...
... mitochondria.2 BECN1 and PIK3C3/VPS34, for example, are pivotal in the formation of a lipid kinase complex, which in turn allows the recruitment and shuttling of ATG proteins that contribute to the generation of the phagophore, the initial sequestering compartment. Next, the ubiquitin-like conjugat ...
PowerPoint Template
... and conducted into the cell via cascades of coupled reactions. The first steps of signal transmission often take place in close association with the membrane, before the signal is conducted into the cell interior. The cell uses mainly two mechanisms for transmission of signals at the cytosolic side ...
... and conducted into the cell via cascades of coupled reactions. The first steps of signal transmission often take place in close association with the membrane, before the signal is conducted into the cell interior. The cell uses mainly two mechanisms for transmission of signals at the cytosolic side ...
The LIR motif – crucial for selective autophagy
... (Macro)autophagy is a fundamental degradation process for macromolecules and organelles of vital importance for cell and tissue homeostasis. Autophagy research has gained a strong momentum in recent years because of its relevance to cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, muscular dystrophy, lipid stora ...
... (Macro)autophagy is a fundamental degradation process for macromolecules and organelles of vital importance for cell and tissue homeostasis. Autophagy research has gained a strong momentum in recent years because of its relevance to cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, muscular dystrophy, lipid stora ...
Divergent Functional Properties of the Ribosome
... several Hsp70s have been solved (Flaherty et al., 1990; Harrison et al., 1997; Sriram et al., 1997). These structures resemble that of actin and hexokinase, consisting of two lobes with a deep cleft between them in which nucleotide binds. More recently, the structure of the 18-kDa peptide-binding do ...
... several Hsp70s have been solved (Flaherty et al., 1990; Harrison et al., 1997; Sriram et al., 1997). These structures resemble that of actin and hexokinase, consisting of two lobes with a deep cleft between them in which nucleotide binds. More recently, the structure of the 18-kDa peptide-binding do ...
The tumor suppressor Scrib interacts with the zyxin
... Correct processing of these signals allows appropriate cellular growth, differentiation, and tissue morphogenesis, but malfunctions often lie at the basis of pathologies such as tumor growth and metastasis. At sites of cell adhesion, more and more proteins are being identified that not only play a r ...
... Correct processing of these signals allows appropriate cellular growth, differentiation, and tissue morphogenesis, but malfunctions often lie at the basis of pathologies such as tumor growth and metastasis. At sites of cell adhesion, more and more proteins are being identified that not only play a r ...
Supplementary Online Materials
... Figure S1. Comparison of topological determinants of NHB1-CNC factors within membranes. (A) Comparison of the TM1 helices within Nrf1, Nrf3, CncC and Skn-1. The -helices of NHB1-CNC factors were wheeled using the HeliQuest programme. Some of the polar and charged amino acids in the membrane-spannin ...
... Figure S1. Comparison of topological determinants of NHB1-CNC factors within membranes. (A) Comparison of the TM1 helices within Nrf1, Nrf3, CncC and Skn-1. The -helices of NHB1-CNC factors were wheeled using the HeliQuest programme. Some of the polar and charged amino acids in the membrane-spannin ...
Complete atomic model of the bacterial flagellar filament by electron
... The bacterial flagellar filament is a helical propeller for bacterial locomotion. It is a helical assembly of a single protein, flagellin, and its tubular structure is formed by 11 protofilaments in two distinct conformations, L- and R-type, for supercoiling. The X-ray crystal structure of a flagell ...
... The bacterial flagellar filament is a helical propeller for bacterial locomotion. It is a helical assembly of a single protein, flagellin, and its tubular structure is formed by 11 protofilaments in two distinct conformations, L- and R-type, for supercoiling. The X-ray crystal structure of a flagell ...
Extracellular ATP Functions as an
... whereas P2Y receptors are G protein–coupled receptors. Some physiological processes are dependent on the activation of purinoceptors by extracellular ATP to initiate signaling cascades. For example, extracellular ATP binds to P2X7 receptors to activate astrocyte Gln release, which modulates synaptic ...
... whereas P2Y receptors are G protein–coupled receptors. Some physiological processes are dependent on the activation of purinoceptors by extracellular ATP to initiate signaling cascades. For example, extracellular ATP binds to P2X7 receptors to activate astrocyte Gln release, which modulates synaptic ...
Effects of Macromolecular Crowding on Protein Folding
... Protein folding is the process whereby an extended and unstructured polypeptide is converted into a compact folded structure that typically constitutes its functional form. The process has been characterized extensively in-vitro in dilute buffer solutions over the last few decades. However, invivo, ...
... Protein folding is the process whereby an extended and unstructured polypeptide is converted into a compact folded structure that typically constitutes its functional form. The process has been characterized extensively in-vitro in dilute buffer solutions over the last few decades. However, invivo, ...
Tyr130 phosphorylation triggers Syk release
... yk, a 72-kDa cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinase essential to receptor-mediated signaling in B cells, has two N-terminal SH2 domains connected by a 45-residue region (interdomain A). These tandem SH2 domains are separated by a longer, 104-residue region (interdomain B) from a C-terminal kinase domai ...
... yk, a 72-kDa cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinase essential to receptor-mediated signaling in B cells, has two N-terminal SH2 domains connected by a 45-residue region (interdomain A). These tandem SH2 domains are separated by a longer, 104-residue region (interdomain B) from a C-terminal kinase domai ...
Subcellular Trafficking of Mammalian Lysosomal Proteins: An
... M(X)9G and WE motifs mentioned above). This point is further supported when looking at MLN64, a lysosomal protein involved in cholesterol transport, whose sorting depends on a KSASNP motif located in its C-terminal START domain [34]. This motif mediates binding to the cytosolic protein 14-3-3 indepe ...
... M(X)9G and WE motifs mentioned above). This point is further supported when looking at MLN64, a lysosomal protein involved in cholesterol transport, whose sorting depends on a KSASNP motif located in its C-terminal START domain [34]. This motif mediates binding to the cytosolic protein 14-3-3 indepe ...
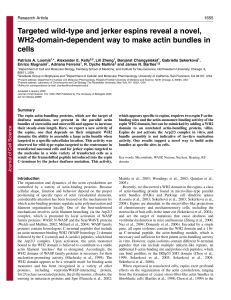
Targeted wild-type and jerker espins reveal a novel, WH2
... (A-C) Isoform and domain dependence for forming the centrosomal actin bundle (CAB) by wild-type espins and the nuclear actin bundle (NAB) by jerker (je) espins. (A) Representatives of the four major espinisoform size classes. ABM, actin-bundling module; AR, ankyrin-like repeat; je, jerker peptide (r ...
... (A-C) Isoform and domain dependence for forming the centrosomal actin bundle (CAB) by wild-type espins and the nuclear actin bundle (NAB) by jerker (je) espins. (A) Representatives of the four major espinisoform size classes. ABM, actin-bundling module; AR, ankyrin-like repeat; je, jerker peptide (r ...
Solid-phase classical complement activation by C
... phylogenetically ancient and highly conserved family of pentraxins, which share a common structure with five identical subunits linked by weak non-covalent bonds and arranged in cyclic symmetry. Due to its dramatic rise within the initial 24 to 72 hours in response to proinflammatory stimuli or tiss ...
... phylogenetically ancient and highly conserved family of pentraxins, which share a common structure with five identical subunits linked by weak non-covalent bonds and arranged in cyclic symmetry. Due to its dramatic rise within the initial 24 to 72 hours in response to proinflammatory stimuli or tiss ...
Lysosomal Function and Dysfunction
... mTORC1 inhibition shortly after nutrient starvation (2 h), longer incubation in these conditions (over 6 h) induces mTORC1 activation, as evidenced by an increase in the phosphorylation of its downstream target S6K (50). More importantly, this effect is dependent on the autophagy regulators Atg5 and ...
... mTORC1 inhibition shortly after nutrient starvation (2 h), longer incubation in these conditions (over 6 h) induces mTORC1 activation, as evidenced by an increase in the phosphorylation of its downstream target S6K (50). More importantly, this effect is dependent on the autophagy regulators Atg5 and ...
Calcium binding chaperones of the endoplasmic reticulum
... Ca2+ store refilling is controlled by the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) (Lipskaia et al. 2009) while the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger and the plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase actively remove Ca2+ from the cells (Rhodes and Sanderson 2009). Taken together, both the ER Ca2+ buffering proteins and t ...
... Ca2+ store refilling is controlled by the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) (Lipskaia et al. 2009) while the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger and the plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase actively remove Ca2+ from the cells (Rhodes and Sanderson 2009). Taken together, both the ER Ca2+ buffering proteins and t ...
Structural studies on lysosomal proteins
... In each of the three domains of life, bacteria, archaea and eukaryota, the cell is the basic unit of life. Eukaryotic cells are distinct in that in all of them, different cellular functions are arranged to distinct compartments called cell organelles. In multicellular organisms, the diversity of cel ...
... In each of the three domains of life, bacteria, archaea and eukaryota, the cell is the basic unit of life. Eukaryotic cells are distinct in that in all of them, different cellular functions are arranged to distinct compartments called cell organelles. In multicellular organisms, the diversity of cel ...
Apoptosome

The apoptosome is a large quaternary protein structure formed in the process of apoptosis. Its formation is triggered by the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria in response to an internal (intrinsic) or external (extrinsic) cell death stimulus. Stimuli can vary from DNA damage and viral infection to developmental cues such as those leading to the degradation of a tadpole's tail.In mammalian cells, once cytochrome c is released, it binds to the cytosolic protein Apaf-1 to facilitate the formation of apoptosome. An early biochemical study suggests a two-to-one ratio of cytochrome c to apaf-1 for apoptosome formation. However, recent structural studies suggest the cytochrome c to apaf-1 ratio is one-to-one. It has also been shown that the nucleotide dATP as third component binds to apaf-1, however its exact role is still debated. The mammalian apoptosome had never been crystallized, but a human APAF-1/cytochrome-c apoptosome has been imaged at lower (2 nm) resolution by cryogenic transmission electron microscopy 10 years ago, revealing a wheel-like particle with 7-fold symmetry. Recently, a medium resolution (9.5 Ångström) structure of human apoptosome was also solved by cryo-electron microscopy, which allows unambiguous inference for positions of all the APAF-1 domains (CARD, NBARC and WD40) and cytochrome c. There is also now a crystal structure of the monomeric, inactive Apaf-1 subunit (PDB 3SFZ). Once formed, the apoptosome can then recruit and activate the inactive pro-caspase-9. Once activated, this initiator caspase can then activate effector caspases and trigger a cascade of events leading to apoptosis.