Topic 3.1: Chemical Elements and Water
... Covalent Bond: These bonds are the strongest of the bonds. They are formed by the sharing of electrons. There are several subsets of covalent bonding: a). Nonpolar: Here the electrons are shared equally, thus eliminating a positive and negative end on the molecule. ...
... Covalent Bond: These bonds are the strongest of the bonds. They are formed by the sharing of electrons. There are several subsets of covalent bonding: a). Nonpolar: Here the electrons are shared equally, thus eliminating a positive and negative end on the molecule. ...
Ideas To Implementation
... produce other materials of suitable purity: At first, germanium was widely used as a semi-conductor because it was easier to purify than other known semi-conductors, such as silicon Silicon eventually replaced the germanium as semi-conducting material of choice in transistors because: o it is th ...
... produce other materials of suitable purity: At first, germanium was widely used as a semi-conductor because it was easier to purify than other known semi-conductors, such as silicon Silicon eventually replaced the germanium as semi-conducting material of choice in transistors because: o it is th ...
MEMS Micro Electro Mechanical Systems.doc
... manufacturing technology that enables the development of electromechanical systems using batch fabrication techniques similar to those used in integrated circuit (IC) design. They can range in size from micrometers to millimeters MEMS integrate mechanical elements, sensors, actuators and electronics ...
... manufacturing technology that enables the development of electromechanical systems using batch fabrication techniques similar to those used in integrated circuit (IC) design. They can range in size from micrometers to millimeters MEMS integrate mechanical elements, sensors, actuators and electronics ...
Synthesis, Crystal Growth, Structural, Optical, Thermal and
... X-ray diffraction (HRXRD) rocking curve measurements. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic studies were also performed for the identification of different vibrational modes of the fundamental groups present in the compound. The UV–vis transmission spectrum was recorded in the range 200–10 ...
... X-ray diffraction (HRXRD) rocking curve measurements. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic studies were also performed for the identification of different vibrational modes of the fundamental groups present in the compound. The UV–vis transmission spectrum was recorded in the range 200–10 ...
Chemistry 2202 Background Information – Chapter 1 (pg
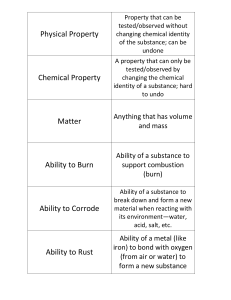
... into something new. Ex. Iron is a strong metal with a shiny surface Qualitative (cannot be measured) Quantitative (can be represented with measurable numbers) Chemical properties – those which you observed when one kind of matter is changed into a different kind of matter. Ex. Iron reactions wit ...
... into something new. Ex. Iron is a strong metal with a shiny surface Qualitative (cannot be measured) Quantitative (can be represented with measurable numbers) Chemical properties – those which you observed when one kind of matter is changed into a different kind of matter. Ex. Iron reactions wit ...
Basic Physical Chemistry 3
... 3CU Description: This course provides a systematic treatment of classical thermodynamics with an emphasis on applications of the first and second laws to chemical and physical changes. Applications are made to chemical equilibrium, electrochemical cells, and other spontaneous processes. Course Objec ...
... 3CU Description: This course provides a systematic treatment of classical thermodynamics with an emphasis on applications of the first and second laws to chemical and physical changes. Applications are made to chemical equilibrium, electrochemical cells, and other spontaneous processes. Course Objec ...
Solid

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass).The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties of solids. Solid-state chemistry is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.