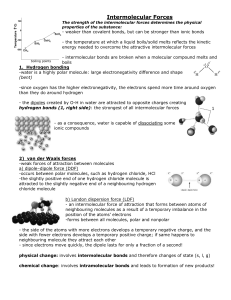
OBJECTIVES
... small to see the different parts Can occur between any state of matter: gas in gas; liquid in gas; gas in liquid; solid in liquid; solid in solid (alloys), etc. Thus, based on the distribution of their components, mixtures are called homogeneous or heterogeneous. ...
... small to see the different parts Can occur between any state of matter: gas in gas; liquid in gas; gas in liquid; solid in liquid; solid in solid (alloys), etc. Thus, based on the distribution of their components, mixtures are called homogeneous or heterogeneous. ...
Elements – (Metals)
... 1) Electrical and thermal conduction Electrical and thermal conduction because of movement of free electrons while metals cations remain fixed 2) Luster Electrons are excited to higher energy state by light all wavelengths. Electrons fall back to lower levels and re-emit light so metals have shiny s ...
... 1) Electrical and thermal conduction Electrical and thermal conduction because of movement of free electrons while metals cations remain fixed 2) Luster Electrons are excited to higher energy state by light all wavelengths. Electrons fall back to lower levels and re-emit light so metals have shiny s ...
title of article in english
... A variety of ceramic materials such as alumina (Al2O3), zirconia (ZrO2), magnesia (MgO), silicon carbide (SiC), and silicon nitride (Si3N4) are widely used in microelectronics, automotive, medical and biotechnological applications. Despite superior mechanical and physical properties, these materials ...
... A variety of ceramic materials such as alumina (Al2O3), zirconia (ZrO2), magnesia (MgO), silicon carbide (SiC), and silicon nitride (Si3N4) are widely used in microelectronics, automotive, medical and biotechnological applications. Despite superior mechanical and physical properties, these materials ...
Annealing Stages
... • Mention some factors that may affect the actual cooling rate of an air cooled specimen. • What effects do the alloying additives have on the microstructure and mechanical properties of air cooled (normalized) steel specimens? • What effects do the alloying additives have on the microstructure and ...
... • Mention some factors that may affect the actual cooling rate of an air cooled specimen. • What effects do the alloying additives have on the microstructure and mechanical properties of air cooled (normalized) steel specimens? • What effects do the alloying additives have on the microstructure and ...
Plasmonic Periodic Structures Composed by 2D Materials
... Abstract Two-dimensional (2D) media, such as Graphene, can give to the host material electromagnetic properties which are not found in nature. From these fascinating effective behaviors, the Epsilon-Near-Zero (ENZ) effect and accordingly the appearance of Dirac Point (DP) is the objective of this wo ...
... Abstract Two-dimensional (2D) media, such as Graphene, can give to the host material electromagnetic properties which are not found in nature. From these fascinating effective behaviors, the Epsilon-Near-Zero (ENZ) effect and accordingly the appearance of Dirac Point (DP) is the objective of this wo ...
Solid

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass).The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties of solids. Solid-state chemistry is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.