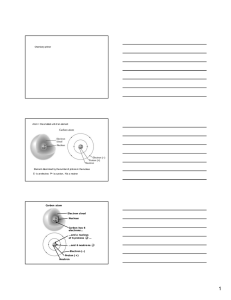
Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element
... Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the composition (chemical formula) but it can also be affected by impurities. This is why color is a poor mineral identifier. Fracture: How a mineral breaks across cleavage planes. Relate ...
... Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the composition (chemical formula) but it can also be affected by impurities. This is why color is a poor mineral identifier. Fracture: How a mineral breaks across cleavage planes. Relate ...
word - University of Guelph
... chemicals and organic solvents in glas apparatus, often under reflux conditions with continous water cooling and under inert gas atmosphere or vacuum on a scale of 10 to 1000 mL total volume. Typical maximum heating temperatures are below 200 °C. Occasionally reactions will be carried out in 50 to 5 ...
... chemicals and organic solvents in glas apparatus, often under reflux conditions with continous water cooling and under inert gas atmosphere or vacuum on a scale of 10 to 1000 mL total volume. Typical maximum heating temperatures are below 200 °C. Occasionally reactions will be carried out in 50 to 5 ...
FCE Reading- Part 6 –Gapped text - E
... If we (6)………………... bias the junction, that is, place a potential across it so that the n-type section is positive with respect to the p-type section, any (7)………………... in the p-type region cross back over the junction into the n-type region, where all the electrons are drawn (8)………………... from the jun ...
... If we (6)………………... bias the junction, that is, place a potential across it so that the n-type section is positive with respect to the p-type section, any (7)………………... in the p-type region cross back over the junction into the n-type region, where all the electrons are drawn (8)………………... from the jun ...
Chapter 1 Chemistry: The Study of Matter
... definite volume but an indefinite shape. A liquid assumes the shape of its container. The particles that make up the liquid are packed close together but can move past one another. ...
... definite volume but an indefinite shape. A liquid assumes the shape of its container. The particles that make up the liquid are packed close together but can move past one another. ...
Concepts of stress and strain
... To minimize deformation, select a material with a large elastic modulus (E or G). • Plastic behavior: This permanent deformation behavior occurs when the tensile (or compressive) uniaxial stress reaches σy. • Toughness: The energy needed to break a unit volume of material. • Ductility: The plastic s ...
... To minimize deformation, select a material with a large elastic modulus (E or G). • Plastic behavior: This permanent deformation behavior occurs when the tensile (or compressive) uniaxial stress reaches σy. • Toughness: The energy needed to break a unit volume of material. • Ductility: The plastic s ...
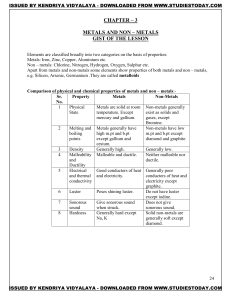
Properties of Ionic and Covalent Substances
... If an atom gains electrons it forms a negative ion (anion), and if it loses electrons it forms a positive ion (cation). Negative and positive ions attract each other and form “ionic bonds”. Ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals when electrons are transferred. All ionic compounds have a solid ...
... If an atom gains electrons it forms a negative ion (anion), and if it loses electrons it forms a positive ion (cation). Negative and positive ions attract each other and form “ionic bonds”. Ionic bonds form between metals and nonmetals when electrons are transferred. All ionic compounds have a solid ...
Solid

Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice) or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass).The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties of solids. Solid-state chemistry is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.