- ZORA - Universität Zürich
... available) from the human oral cavity were found to belong to one of 11 phyla and within these largest subdivisions of the domain Bacteria, to one of 18 classes. Earlier studies from this laboratory on the composition and diversity of human subgingival and supragingival plaques could never identify ...
... available) from the human oral cavity were found to belong to one of 11 phyla and within these largest subdivisions of the domain Bacteria, to one of 18 classes. Earlier studies from this laboratory on the composition and diversity of human subgingival and supragingival plaques could never identify ...
Molecular identification of bacteria associated with canine
... associated with canine gingivitis and periodontitis and to compare this with the normal oral flora. Swabs were obtained from the gingival margin of three dogs with gingivitis and three orally healthy controls, and subgingival plaque was collected from three dogs with periodontitis. Samples were subj ...
... associated with canine gingivitis and periodontitis and to compare this with the normal oral flora. Swabs were obtained from the gingival margin of three dogs with gingivitis and three orally healthy controls, and subgingival plaque was collected from three dogs with periodontitis. Samples were subj ...
Drug resistant anaerobic infections: Are they complicating
... Metronidazole, Penicillin, Clindamycin respectively. ...
... Metronidazole, Penicillin, Clindamycin respectively. ...
Isolation and Identification of Bacterial Organisms that are
... This research work was carried out to examine the bacterial organisms that are associated with the spoilage of African breadfruits (Treculia africana) (Ukwa). Samples of the spoilt breadfruits were analyzed using five fold serial dilution method and the last three test tubes were used for the inocul ...
... This research work was carried out to examine the bacterial organisms that are associated with the spoilage of African breadfruits (Treculia africana) (Ukwa). Samples of the spoilt breadfruits were analyzed using five fold serial dilution method and the last three test tubes were used for the inocul ...
Transcript 2
... managing the patient’s medical conditions, but you have to know about the condition in case you’re giving them an antibiotic that may have an adverse effect on their condition. There may be contraindications. Some drugs can only be given parenterally (IV); they are not good for outpatient use. In or ...
... managing the patient’s medical conditions, but you have to know about the condition in case you’re giving them an antibiotic that may have an adverse effect on their condition. There may be contraindications. Some drugs can only be given parenterally (IV); they are not good for outpatient use. In or ...
Microfluidics Expanding the Frontiers of Microbial Ecology
... responses to more complex gradients), without needing to tether cells to surfaces as was traditionally done. One downside of this approach is the potential for fluid flow through the test section, as precise pressure equalization is challenging. The same principle can be applied with considerably more ...
... responses to more complex gradients), without needing to tether cells to surfaces as was traditionally done. One downside of this approach is the potential for fluid flow through the test section, as precise pressure equalization is challenging. The same principle can be applied with considerably more ...
Dental plaque biofilm
... Facilitate processing and uptake of nutrients, cross-feeding, removal of harmful metabolic products Development of an appropriate physico-chemical environment ...
... Facilitate processing and uptake of nutrients, cross-feeding, removal of harmful metabolic products Development of an appropriate physico-chemical environment ...
Biological Degradation of Naphthalene: A New Era
... Although many naphthalene-degrading bacteria have been isolated, these bacteria may thrive in one environment but may not be able to compete with other micro-organisms in another environment, as environmental conditions impose a selection pressure on specific types of bacteria. PAH are soluble in no ...
... Although many naphthalene-degrading bacteria have been isolated, these bacteria may thrive in one environment but may not be able to compete with other micro-organisms in another environment, as environmental conditions impose a selection pressure on specific types of bacteria. PAH are soluble in no ...
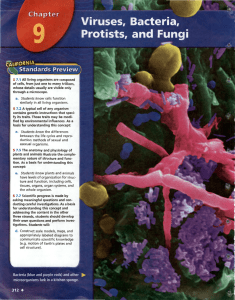
MS-SCI-LS-Unit 3 -- Chapter 9
... shaped like rods, bricks, threads, or bullets. There are even viruses that have complex, robot-like shapes, such as the bacteriophage in Figure 1. A bacteriophage (bak TEER ee oh fayj) is a virus that infects bacteria. In fact, its name means "bacteria eater." Although viruses may look different fro ...
... shaped like rods, bricks, threads, or bullets. There are even viruses that have complex, robot-like shapes, such as the bacteriophage in Figure 1. A bacteriophage (bak TEER ee oh fayj) is a virus that infects bacteria. In fact, its name means "bacteria eater." Although viruses may look different fro ...
Lab 1
... 1. Collect environmental samples. 2. Realize the wide distribution of microorganisms in the environment. 3. Realize the wide diversity of microorganisms in the environment. Introduction As a group bacteria have three fundamental properties: (1) they are small single cell organisms (typically about o ...
... 1. Collect environmental samples. 2. Realize the wide distribution of microorganisms in the environment. 3. Realize the wide diversity of microorganisms in the environment. Introduction As a group bacteria have three fundamental properties: (1) they are small single cell organisms (typically about o ...
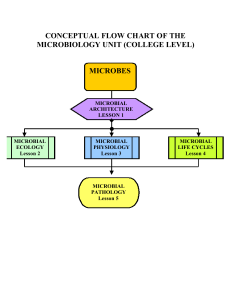
conceptual flow chart of the microbiology unit (college level) microbes
... bodies). Microbiology can be therefore be defined as the study of microbes which are all small organisms that require the use of a microscope to see. There are many different species of microorganisms that have been classified or put into similar groups based on the possession of certain characteris ...
... bodies). Microbiology can be therefore be defined as the study of microbes which are all small organisms that require the use of a microscope to see. There are many different species of microorganisms that have been classified or put into similar groups based on the possession of certain characteris ...
Antibiotics that affect the ribosome
... antibiotics in commensal and pathogenic bacteria resulting from the acquisition of tet genes. Two mechanisms are involved in tetracycline resistance. The first is due to efflux proteins, including Tet(A), Tet(B), Tet(C), Tet(D), Tet(E), Tet(G), Tet(H) and Tet(Z), which reduce the intracellular drug ...
... antibiotics in commensal and pathogenic bacteria resulting from the acquisition of tet genes. Two mechanisms are involved in tetracycline resistance. The first is due to efflux proteins, including Tet(A), Tet(B), Tet(C), Tet(D), Tet(E), Tet(G), Tet(H) and Tet(Z), which reduce the intracellular drug ...
Relationships between common water bacteria
... and responding to the presence of neighbouring microbial populations. The process is related to the synthesis of low-molecular-mass signalling molecules, the concentration of which results from the population density of the producing organisms. The most common signalling molecules found in Gram-nega ...
... and responding to the presence of neighbouring microbial populations. The process is related to the synthesis of low-molecular-mass signalling molecules, the concentration of which results from the population density of the producing organisms. The most common signalling molecules found in Gram-nega ...
Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in the Microbial
... Phenotypic drug resistance refers to the fact that when the bacteria are not growing, they can become unsusceptible to antibiotics. Then, when the bacteria are sub-cultured into a fresh media, and they begin to grow again, they regain their antibiotic susceptibility. This complex mechanism has been ...
... Phenotypic drug resistance refers to the fact that when the bacteria are not growing, they can become unsusceptible to antibiotics. Then, when the bacteria are sub-cultured into a fresh media, and they begin to grow again, they regain their antibiotic susceptibility. This complex mechanism has been ...
Ecological and physiological studies on large intestinal bacteria in
... species for synthesis of hydrolytic and reductive enzymes associated with genotoxicity Twenty intestinal isolates, belonging to six different anaerobic and facultative bacterial genera, were tested for their abilities to produce GN, GS, NR,AR and AS. The activities of these enzymes varied considerab ...
... species for synthesis of hydrolytic and reductive enzymes associated with genotoxicity Twenty intestinal isolates, belonging to six different anaerobic and facultative bacterial genera, were tested for their abilities to produce GN, GS, NR,AR and AS. The activities of these enzymes varied considerab ...
Ecological and physiological studies on large intestinal bacteria in
... species for synthesis of hydrolytic and reductive enzymes associated with genotoxicity Twenty intestinal isolates, belonging to six different anaerobic and facultative bacterial genera, were tested for their abilities to produce GN, GS, NR,AR and AS. The activities of these enzymes varied considerab ...
... species for synthesis of hydrolytic and reductive enzymes associated with genotoxicity Twenty intestinal isolates, belonging to six different anaerobic and facultative bacterial genera, were tested for their abilities to produce GN, GS, NR,AR and AS. The activities of these enzymes varied considerab ...
Antimicrobial action of tea tree oil
... tree oil and that Quad 10 would have the clearest zone of inhibition but we were incorrect in this prediction. Tea tree oil was not predicted to control all the bacteria tested, nor be superior to Quad 10 or Listerine. The results indicated that the other products showed no or little zone of inhibit ...
... tree oil and that Quad 10 would have the clearest zone of inhibition but we were incorrect in this prediction. Tea tree oil was not predicted to control all the bacteria tested, nor be superior to Quad 10 or Listerine. The results indicated that the other products showed no or little zone of inhibit ...
Lecture 13-14 Dental plaque and caries
... Waals’ forces – reversible (can washed off with water flush) ...
... Waals’ forces – reversible (can washed off with water flush) ...
25 Microbial ecology
... The microflora of soil includes hundreds of species of bacteria, viruses, protozoa, actinomyces and fungi. It is various species of putrefactiving, nitrifying, denitrifying, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The most often inhabitants of soil are the representatives of genus Azotobacter, Nocardia, and Clos ...
... The microflora of soil includes hundreds of species of bacteria, viruses, protozoa, actinomyces and fungi. It is various species of putrefactiving, nitrifying, denitrifying, nitrogen-fixing bacteria. The most often inhabitants of soil are the representatives of genus Azotobacter, Nocardia, and Clos ...
review
... direct short-range cell–cell communication between microorganisms and presumably in the differentiation of cells within multicellular communities. However, microorganisms also have the ability to emit and to receive various long-range signals that can mutually influence their behaviour. Such signals ...
... direct short-range cell–cell communication between microorganisms and presumably in the differentiation of cells within multicellular communities. However, microorganisms also have the ability to emit and to receive various long-range signals that can mutually influence their behaviour. Such signals ...
Procedure:
... Most bacteria are difficult to see under the bright field microscope. Bacteria are almost colorless and therefore show little contrast with the broth in which they are suspended. To visualize bacteria, either dyes or stains, are used. Since staining of bacterial cells is relatively fast, inexpensive ...
... Most bacteria are difficult to see under the bright field microscope. Bacteria are almost colorless and therefore show little contrast with the broth in which they are suspended. To visualize bacteria, either dyes or stains, are used. Since staining of bacterial cells is relatively fast, inexpensive ...
Microbiology
... components to go outside and cause diseases to the humans body. Ribosome: the synthesis of protein take place in ribosome. Chromosome: it contain DNA (Deoxy Ribose Nucleic Acid) as a genetic natural. Plasma: it is an extrachronosomal circular DNA which contains ß-lactamase enzyme provide to some ant ...
... components to go outside and cause diseases to the humans body. Ribosome: the synthesis of protein take place in ribosome. Chromosome: it contain DNA (Deoxy Ribose Nucleic Acid) as a genetic natural. Plasma: it is an extrachronosomal circular DNA which contains ß-lactamase enzyme provide to some ant ...
Why Carbohydrates - Tehran University of Medical Sciences
... Polysaccharides/ Peptidoglycanes Gram Negative bacteria ...
... Polysaccharides/ Peptidoglycanes Gram Negative bacteria ...
Prokaryotes
... 44. You Describe! Describe the color of these stained bacteria. 45. These bacteria are red. They’re referred to as gram-negative. 46. Prokaryotes have a wide variety of physical characteristics. Some prokaryotes, for example, have flagella that act like propellers, pushing the cell through the wa ...
... 44. You Describe! Describe the color of these stained bacteria. 45. These bacteria are red. They’re referred to as gram-negative. 46. Prokaryotes have a wide variety of physical characteristics. Some prokaryotes, for example, have flagella that act like propellers, pushing the cell through the wa ...
Dr. Scott Taylor University of Waterloo Department of Chemistry
... pneumonia due to inhibition by pulmonary surfactant. Over the last several years, Dap-resistant bacteria have emerged. This has caused considerable alarm in the medical community as Dap is often used as a last defence against serious infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( ...
... pneumonia due to inhibition by pulmonary surfactant. Over the last several years, Dap-resistant bacteria have emerged. This has caused considerable alarm in the medical community as Dap is often used as a last defence against serious infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( ...
Bacteria

Bacteria (/bækˈtɪəriə/; singular: bacterium) constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals. Bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep portions of Earth's crust. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships with plants and animals. They are also known to have flourished in manned spacecraft.There are typically 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil and a million bacterial cells in a millilitre of fresh water. There are approximately 5×1030 bacteria on Earth, forming a biomass which exceeds that of all plants and animals. Bacteria are vital in recycling nutrients, with many of the stages in nutrient cycles dependent on these organisms, such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere and putrefaction. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. On 17 March 2013, researchers reported data that suggested bacterial life forms thrive in the Mariana Trench, which with a depth of up to 11 kilometres is the deepest part of the Earth's oceans. Other researchers reported related studies that microbes thrive inside rocks up to 580 metres below the sea floor under 2.6 kilometres of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States. According to one of the researchers, ""You can find microbes everywhere — they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are.""Most bacteria have not been characterized, and only about half of the phyla of bacteria have species that can be grown in the laboratory. The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology.There are approximately ten times as many bacterial cells in the human flora as there are human cells in the body, with the largest number of the human flora being in the gut flora, and a large number on the skin. The vast majority of the bacteria in the body are rendered harmless by the protective effects of the immune system, and some are beneficial. However, several species of bacteria are pathogenic and cause infectious diseases, including cholera, syphilis, anthrax, leprosy, and bubonic plague. The most common fatal bacterial diseases are respiratory infections, with tuberculosis alone killing about 2 million people per year, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. In developed countries, antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections and are also used in farming, making antibiotic resistance a growing problem. In industry, bacteria are important in sewage treatment and the breakdown of oil spills, the production of cheese and yogurt through fermentation, and the recovery of gold, palladium, copper and other metals in the mining sector, as well as in biotechnology, and the manufacture of antibiotics and other chemicals.Once regarded as plants constituting the class Schizomycetes, bacteria are now classified as prokaryotes. Unlike cells of animals and other eukaryotes, bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus and rarely harbour membrane-bound organelles. Although the term bacteria traditionally included all prokaryotes, the scientific classification changed after the discovery in the 1990s that prokaryotes consist of two very different groups of organisms that evolved from an ancient common ancestor. These evolutionary domains are called Bacteria and Archaea.