Slide 1
... Control of plaque forming bacteria such as Streptococcus mutans, St. sunguis and St. sobrinus and Lactobacillus acidophilus by addition of bacteriophages to toothpaste, chewing gum and sweets Control of biofilm forming bacteria like listeria, Escherichia and Pseudomonas sp. in different industries ( ...
... Control of plaque forming bacteria such as Streptococcus mutans, St. sunguis and St. sobrinus and Lactobacillus acidophilus by addition of bacteriophages to toothpaste, chewing gum and sweets Control of biofilm forming bacteria like listeria, Escherichia and Pseudomonas sp. in different industries ( ...
Microbiology of Environmental Engineering Systems
... The cultivation of microorganisms is performed under suitable conditions, usually at optimal temperature, pH, osmotic pressure and concentration of gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen), on a semi-solid or liquid medium, containing all necessary substances for the growth of the strain. The elemen ...
... The cultivation of microorganisms is performed under suitable conditions, usually at optimal temperature, pH, osmotic pressure and concentration of gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen), on a semi-solid or liquid medium, containing all necessary substances for the growth of the strain. The elemen ...
2/5.DMD – theory
... (chemical components of the bacterial cell, various requirements of nutrients); temperature (psychrophilic bacteria, mesophiles, and thermophiles); - gaseous requirements of bacteria (strictly aerobic bacteria, facultative anaerobic bacteria, strictly anaerobic bacteria, microaerophilic bacteria, ca ...
... (chemical components of the bacterial cell, various requirements of nutrients); temperature (psychrophilic bacteria, mesophiles, and thermophiles); - gaseous requirements of bacteria (strictly aerobic bacteria, facultative anaerobic bacteria, strictly anaerobic bacteria, microaerophilic bacteria, ca ...
Applied Environmental Microbiology
... Julio Martínez, Marco Antonio Rogel, Ernesto Ormeño-Orrillo, Esperanza Martínez-Romero Genomic Sciences Center, UNAM, Cuernavaca, Morelos, Mexico ...
... Julio Martínez, Marco Antonio Rogel, Ernesto Ormeño-Orrillo, Esperanza Martínez-Romero Genomic Sciences Center, UNAM, Cuernavaca, Morelos, Mexico ...
Biology - Dux Private Tutoring
... The pathogen that caused malaria is transmitted via a vector, the Anopheles mosquito. In summary, when the mosquito bites an infected person, it sucks up infected blood, consuming gametocytes of the Plasmodium protozoan. Soon after, oocysts develop in the gut wall of the mosquito, which eventually d ...
... The pathogen that caused malaria is transmitted via a vector, the Anopheles mosquito. In summary, when the mosquito bites an infected person, it sucks up infected blood, consuming gametocytes of the Plasmodium protozoan. Soon after, oocysts develop in the gut wall of the mosquito, which eventually d ...
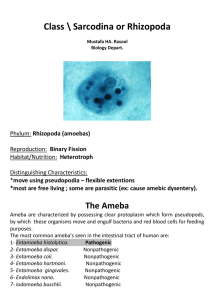
Entamoeba histolytica
... Cysts remain viable in faces for few days, in water for longer periods. Cysts are killed by dryness, heat (over 55ºC) and by chlorine. ...
... Cysts remain viable in faces for few days, in water for longer periods. Cysts are killed by dryness, heat (over 55ºC) and by chlorine. ...
Bacteria - HCC Learning Web
... shape, provides physical protection, and prevents the cell from bursting in a hypotonic environment • Eukaryote cell walls are made of cellulose or chitin • Bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan, a network of sugar polymers cross-linked by polypeptides ...
... shape, provides physical protection, and prevents the cell from bursting in a hypotonic environment • Eukaryote cell walls are made of cellulose or chitin • Bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan, a network of sugar polymers cross-linked by polypeptides ...
Antibiotic Stewardship - Surgical Infection Society
... What is antibiotic stewardship? Antibiotic stewardship refers to coordinated interventions to promote appropriate antibiotic use. The goals of antibiotic stewardship include: (1) improving health outcomes related to the treatment of infections, (2) preventing adverse effects, (3) reducing antibiotic ...
... What is antibiotic stewardship? Antibiotic stewardship refers to coordinated interventions to promote appropriate antibiotic use. The goals of antibiotic stewardship include: (1) improving health outcomes related to the treatment of infections, (2) preventing adverse effects, (3) reducing antibiotic ...
DENS 521 3rd S
... Decreased penetration through the outer membrane prevents the drug from reaching the target PBP In G+ve bacteria, the peptidoglycan polymer is very near the cell surface, thus the small b-lactam antibiotic molecules can penetrate easily to the PBPs, where the final stages of the synthesis of the ...
... Decreased penetration through the outer membrane prevents the drug from reaching the target PBP In G+ve bacteria, the peptidoglycan polymer is very near the cell surface, thus the small b-lactam antibiotic molecules can penetrate easily to the PBPs, where the final stages of the synthesis of the ...
The interaction between the mucosal immune system and the
... potentially pathogenic and pathogenic bacteria and therewith prevent infections 13. The human colon harbors about 1011 bacteria per gram contents. It is important to realise that over 99.9% of the colonic microflora consists of a stable ecosystem of possibly as many as 400 different species of anaer ...
... potentially pathogenic and pathogenic bacteria and therewith prevent infections 13. The human colon harbors about 1011 bacteria per gram contents. It is important to realise that over 99.9% of the colonic microflora consists of a stable ecosystem of possibly as many as 400 different species of anaer ...
Allies and Enemies: How the World Depends on Bacteria
... survival. Unlike any other type of cell in biology, bacteria do these things using the simplest cell in biology. What about viruses, which are often described as the simplest biological beings in existence? The science of microbiology has adopted viruses mainly because viruses are microscopic and bi ...
... survival. Unlike any other type of cell in biology, bacteria do these things using the simplest cell in biology. What about viruses, which are often described as the simplest biological beings in existence? The science of microbiology has adopted viruses mainly because viruses are microscopic and bi ...
Corporation>
... meningitis Bacterial meningitis is one of the most potentially serious infection ,in infants and older children . Associated with a high rate of acute complications and risk of long-term morbidity. The etiology of meningitis in the neonate and the treatment are generally distinct from in olde ...
... meningitis Bacterial meningitis is one of the most potentially serious infection ,in infants and older children . Associated with a high rate of acute complications and risk of long-term morbidity. The etiology of meningitis in the neonate and the treatment are generally distinct from in olde ...
VCLab 5 Spore stain and acid fast stain
... (There are other bacteria that are aerotolerant aerobes; if they are exposed to air, they won’t die, but they won’t grow, either.) Why make endospores? To resist adverse environmental conditions: changes in temperature, pressure, pH, oxygen, and moisture. When we inoculate media and place it in the ...
... (There are other bacteria that are aerotolerant aerobes; if they are exposed to air, they won’t die, but they won’t grow, either.) Why make endospores? To resist adverse environmental conditions: changes in temperature, pressure, pH, oxygen, and moisture. When we inoculate media and place it in the ...
Effects of the application of biofertilizers on the microflora and yield
... fresh organic residues, synthesis and mineralization of humus (Govedarica and Jarak, 1995). The number of fungi in the variant with biofertilizer was slightly lower than in the control variant and was 16.93 x 104, while the number of fungi in the control variant contributed 20.81 x 104. In the varia ...
... fresh organic residues, synthesis and mineralization of humus (Govedarica and Jarak, 1995). The number of fungi in the variant with biofertilizer was slightly lower than in the control variant and was 16.93 x 104, while the number of fungi in the control variant contributed 20.81 x 104. In the varia ...
rumen microbiology-2012
... the animals to digest difficult components of their diet particularly cellulose. Intestinal symbionts may be commensals or benefit the animal through vitamin production and protection against pathogens. The endozoic algae of coral polyps and other invertebrates supply a major part of the animal’s nu ...
... the animals to digest difficult components of their diet particularly cellulose. Intestinal symbionts may be commensals or benefit the animal through vitamin production and protection against pathogens. The endozoic algae of coral polyps and other invertebrates supply a major part of the animal’s nu ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiology
... Small-subunit rDNA clone libraries. 16S rRNA gene clone libraries were generated from total communities of DNAs isolated from the rhizosphere and endosphere (shoot-associated DNA). Rhizosphere 16S rRNA genes were amplified by PCR with the primers 8f and pH by using the conditions described above, wh ...
... Small-subunit rDNA clone libraries. 16S rRNA gene clone libraries were generated from total communities of DNAs isolated from the rhizosphere and endosphere (shoot-associated DNA). Rhizosphere 16S rRNA genes were amplified by PCR with the primers 8f and pH by using the conditions described above, wh ...
Full Text PDF - Jaypee Journals
... as therapeutic agents. They are self-replicating as well as self-limiting. They continue to multiply and penetrate deeper as long as local infection is present. This is sharp contrast to antibiotics which decrease in concentration below the site of infection. Phages are lytic against specific bacter ...
... as therapeutic agents. They are self-replicating as well as self-limiting. They continue to multiply and penetrate deeper as long as local infection is present. This is sharp contrast to antibiotics which decrease in concentration below the site of infection. Phages are lytic against specific bacter ...
w ie v
... Flow cytometry is now an established method for the direct numeration of individual cell numbers, cell size distribution and cell complexity (biochemical and physiological) in aquatic and environmental microbiology. To date the flow cytometry has been applied to phytoplankton and bacterioplankton st ...
... Flow cytometry is now an established method for the direct numeration of individual cell numbers, cell size distribution and cell complexity (biochemical and physiological) in aquatic and environmental microbiology. To date the flow cytometry has been applied to phytoplankton and bacterioplankton st ...
PDF - Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science
... plants have evoked interest as source of natural products. They have been screened for their potential uses as alternative remedies for the treatment of many infectious diseases (Tepe et al., 2004).The present work aims at the isolation and identification of bacteria infecting urinary tract and test ...
... plants have evoked interest as source of natural products. They have been screened for their potential uses as alternative remedies for the treatment of many infectious diseases (Tepe et al., 2004).The present work aims at the isolation and identification of bacteria infecting urinary tract and test ...
Antimicrobial Evaluation of Leaf and Stem Extract of Cordia macleodii
... and content was optimized for the maximum amount of extraction with varying time of 6 and 12 h. The extracts were tested for their antimicrobial activities against gram-positive bacteria (B. sutilis), gram-negative bacteria (E. coli) and fungi (A. niger). The extracts were found to be more active ag ...
... and content was optimized for the maximum amount of extraction with varying time of 6 and 12 h. The extracts were tested for their antimicrobial activities against gram-positive bacteria (B. sutilis), gram-negative bacteria (E. coli) and fungi (A. niger). The extracts were found to be more active ag ...
Will Koning`s Summer Project
... If each cell of Tony Blair were represented in a proportional system, bacteria would hold a huge majority controlling 90% of the house. Tony is not the only cultured individual, as each person is built with about 1013 cells but carries around about 1014 bacteria on internal and external body surface ...
... If each cell of Tony Blair were represented in a proportional system, bacteria would hold a huge majority controlling 90% of the house. Tony is not the only cultured individual, as each person is built with about 1013 cells but carries around about 1014 bacteria on internal and external body surface ...
Conjunctivitis - Wellness Practices of America
... The conjunctiva is exposed to bacteria and other irritants. Tears help protect the conjunctiva by washing away bacteria. Tears also contain enzymes and antibodies that kill bacteria. There are many causes of conjunctivitis. Viruses are the most common cause. Other causes include bacteria, Chlamydia, ...
... The conjunctiva is exposed to bacteria and other irritants. Tears help protect the conjunctiva by washing away bacteria. Tears also contain enzymes and antibodies that kill bacteria. There are many causes of conjunctivitis. Viruses are the most common cause. Other causes include bacteria, Chlamydia, ...
Hilury_Ha_Case_1_Q2_Individual
... Trypticase soy agar with 5% sheep blood (Gera & McIver, 2012). In particular, ideal growth media would be those that contain neo peptone extracts, glucose, and all amino acids (Gera & McIver, 2012). When viewed under a light microscope, we would expect to see S. pyogenes colonies in one plane direct ...
... Trypticase soy agar with 5% sheep blood (Gera & McIver, 2012). In particular, ideal growth media would be those that contain neo peptone extracts, glucose, and all amino acids (Gera & McIver, 2012). When viewed under a light microscope, we would expect to see S. pyogenes colonies in one plane direct ...
2c Types of Stains
... The first step in preparing a slide for staining is to “fix” the slide. This is done by passing the slide through a flame a few times. The purpose of this is to attach the cells (or the bacteria) to the slide and kill the microbes. This procedure shrinks the cells and causes the proteins in the cell ...
... The first step in preparing a slide for staining is to “fix” the slide. This is done by passing the slide through a flame a few times. The purpose of this is to attach the cells (or the bacteria) to the slide and kill the microbes. This procedure shrinks the cells and causes the proteins in the cell ...
Bacterial Profile Associated with Appendicitis
... of Bacteriodes and the ability to produce Beta-lactamase which inactivates the antibiotics23. Other gram-negative bacteria represented by K. pneumon, C. frundii, S. typhi, P. mirabilis and E. aerogeneswere also detected to implicate in appendicitis although in low frequencies compared with other mem ...
... of Bacteriodes and the ability to produce Beta-lactamase which inactivates the antibiotics23. Other gram-negative bacteria represented by K. pneumon, C. frundii, S. typhi, P. mirabilis and E. aerogeneswere also detected to implicate in appendicitis although in low frequencies compared with other mem ...
Bacteria

Bacteria (/bækˈtɪəriə/; singular: bacterium) constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals. Bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep portions of Earth's crust. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships with plants and animals. They are also known to have flourished in manned spacecraft.There are typically 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil and a million bacterial cells in a millilitre of fresh water. There are approximately 5×1030 bacteria on Earth, forming a biomass which exceeds that of all plants and animals. Bacteria are vital in recycling nutrients, with many of the stages in nutrient cycles dependent on these organisms, such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere and putrefaction. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. On 17 March 2013, researchers reported data that suggested bacterial life forms thrive in the Mariana Trench, which with a depth of up to 11 kilometres is the deepest part of the Earth's oceans. Other researchers reported related studies that microbes thrive inside rocks up to 580 metres below the sea floor under 2.6 kilometres of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States. According to one of the researchers, ""You can find microbes everywhere — they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are.""Most bacteria have not been characterized, and only about half of the phyla of bacteria have species that can be grown in the laboratory. The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology.There are approximately ten times as many bacterial cells in the human flora as there are human cells in the body, with the largest number of the human flora being in the gut flora, and a large number on the skin. The vast majority of the bacteria in the body are rendered harmless by the protective effects of the immune system, and some are beneficial. However, several species of bacteria are pathogenic and cause infectious diseases, including cholera, syphilis, anthrax, leprosy, and bubonic plague. The most common fatal bacterial diseases are respiratory infections, with tuberculosis alone killing about 2 million people per year, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. In developed countries, antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections and are also used in farming, making antibiotic resistance a growing problem. In industry, bacteria are important in sewage treatment and the breakdown of oil spills, the production of cheese and yogurt through fermentation, and the recovery of gold, palladium, copper and other metals in the mining sector, as well as in biotechnology, and the manufacture of antibiotics and other chemicals.Once regarded as plants constituting the class Schizomycetes, bacteria are now classified as prokaryotes. Unlike cells of animals and other eukaryotes, bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus and rarely harbour membrane-bound organelles. Although the term bacteria traditionally included all prokaryotes, the scientific classification changed after the discovery in the 1990s that prokaryotes consist of two very different groups of organisms that evolved from an ancient common ancestor. These evolutionary domains are called Bacteria and Archaea.