Antimicrobial natural products
... The efficiency of antibiotics in combating microbial infections was very promising shortly after their introduction. It was even thought that the microbial war was as good as over as declared by the Surgeon General of the United States [25]. However, in his 1945 Nobel Prize speech, Fleming warned th ...
... The efficiency of antibiotics in combating microbial infections was very promising shortly after their introduction. It was even thought that the microbial war was as good as over as declared by the Surgeon General of the United States [25]. However, in his 1945 Nobel Prize speech, Fleming warned th ...
Review - Wound Infection Institute
... aeruginosa and S aureus and tested the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of a range of antibiotics indicated for each type of bacteria.[30] While the MIC values for the planktonic form of each strain were as expected, the minimal biofilm eradication concentrations (MBECs) were generally 100 to ...
... aeruginosa and S aureus and tested the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of a range of antibiotics indicated for each type of bacteria.[30] While the MIC values for the planktonic form of each strain were as expected, the minimal biofilm eradication concentrations (MBECs) were generally 100 to ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... Compare photosynthesis in plants with bacteria: Plants (divided by 6, H2O added to each side) C O2 + 2 H2O C(H2O) + O2 + H2O Photosynthesis in green sulfur bacteria C O2 + 2H2S C(H2O) + 2S + H2O Photosynthesis in purple non-sulfur bacteria C O2 + 2CH3CHOHCH3 C(H2O) + 2CH3COCH3+ H2O isopropanol acet ...
... Compare photosynthesis in plants with bacteria: Plants (divided by 6, H2O added to each side) C O2 + 2 H2O C(H2O) + O2 + H2O Photosynthesis in green sulfur bacteria C O2 + 2H2S C(H2O) + 2S + H2O Photosynthesis in purple non-sulfur bacteria C O2 + 2CH3CHOHCH3 C(H2O) + 2CH3COCH3+ H2O isopropanol acet ...
Microbes and Health Kit: "What Causes Yogurtness?" - Bio-Rad
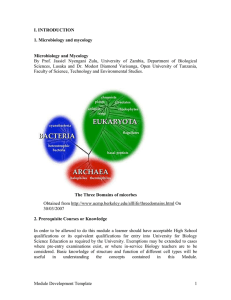
... Bacteria are one of the three great domains of life along with Eukarya (Animals, Plants, and Fungi) and Archaea (ancient bacteria-like organisms classified as a separate domain of life by Carl Woese in 1977). Bacteria and Archaea are classified as prokaryotes, single-celled creatures usually too sma ...
... Bacteria are one of the three great domains of life along with Eukarya (Animals, Plants, and Fungi) and Archaea (ancient bacteria-like organisms classified as a separate domain of life by Carl Woese in 1977). Bacteria and Archaea are classified as prokaryotes, single-celled creatures usually too sma ...
Prokaryote PowerPoint
... • During the 14th century, a bacterial disease known as bubonic plague, spread across Europe and killed about 25% of the human population. • Other types of diseases caused by bacteria include tuberculosis, cholera, many sexually transmissible diseases, and certain types of food poisoning. ...
... • During the 14th century, a bacterial disease known as bubonic plague, spread across Europe and killed about 25% of the human population. • Other types of diseases caused by bacteria include tuberculosis, cholera, many sexually transmissible diseases, and certain types of food poisoning. ...
Chapter 7 PP
... – the cause for the disease called trichinellosis – rarely caused from pork and is more often caused by eating undercooked game meats – killed by cooking pork to an internal temperature of 145 F (63 C) with a three-minute rest – killed in whole cuts and ground game by cooking to an internal temperat ...
... – the cause for the disease called trichinellosis – rarely caused from pork and is more often caused by eating undercooked game meats – killed by cooking pork to an internal temperature of 145 F (63 C) with a three-minute rest – killed in whole cuts and ground game by cooking to an internal temperat ...
Microbiology_Course_Summary
... Targets to Meet Learning Objective #2 Target 1: Differentiate between the Hanging Drop and Wet Mount techniques Target 2: Perform the technique involved in the preparation of a smear from a bacterial culture and one from a pus culture Target 3: Differentiate between simple staining and differe ...
... Targets to Meet Learning Objective #2 Target 1: Differentiate between the Hanging Drop and Wet Mount techniques Target 2: Perform the technique involved in the preparation of a smear from a bacterial culture and one from a pus culture Target 3: Differentiate between simple staining and differe ...
Bacterial Symbioses and the Innate Immune Response of the Model
... I would first like to thank my advisor, Dr. Spencer Nyholm for supervising my research for the past seven years. I am also grateful to the members of my committee, Dr. Joerg Graf, Dr. Daniel Gage, Dr. David Benson and Dr. Steven Geary, who asked held me to a high standard and asked really good quest ...
... I would first like to thank my advisor, Dr. Spencer Nyholm for supervising my research for the past seven years. I am also grateful to the members of my committee, Dr. Joerg Graf, Dr. Daniel Gage, Dr. David Benson and Dr. Steven Geary, who asked held me to a high standard and asked really good quest ...
Automated species and strain identification of bacteria
... margin lines shown on this review document. Return to your MySPIE ToDo list and approve or disapprove this submission. ...
... margin lines shown on this review document. Return to your MySPIE ToDo list and approve or disapprove this submission. ...
meningitis
... illness and the treatment differ depending on the cause. Viral meningitis is generally less severe and clears up without specific treatment. But bacterial meningitis can be quite severe and may result in brain damage, hearing loss, learning disabilities or death. For bacterial meningitis, it is also ...
... illness and the treatment differ depending on the cause. Viral meningitis is generally less severe and clears up without specific treatment. But bacterial meningitis can be quite severe and may result in brain damage, hearing loss, learning disabilities or death. For bacterial meningitis, it is also ...
Ch 23 bacteria notes - Firelands Local Schools
... – Most species of bacteria are classified into two categories based on the structure of their cell walls as determined by a technique called the Gram stain. – Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall, and they appear purple under a microscope after the Gram-stain ...
... – Most species of bacteria are classified into two categories based on the structure of their cell walls as determined by a technique called the Gram stain. – Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall, and they appear purple under a microscope after the Gram-stain ...
MB_23_win
... – Most species of bacteria are classified into two categories based on the structure of their cell walls as determined by a technique called the Gram stain. – Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall, and they appear purple under a microscope after the Gram-stain ...
... – Most species of bacteria are classified into two categories based on the structure of their cell walls as determined by a technique called the Gram stain. – Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall, and they appear purple under a microscope after the Gram-stain ...
MB_23_win
... – Most species of bacteria are classified into two categories based on the structure of their cell walls as determined by a technique called the Gram stain. – Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall, and they appear purple under a microscope after the Gram-stain ...
... – Most species of bacteria are classified into two categories based on the structure of their cell walls as determined by a technique called the Gram stain. – Gram-positive bacteria have a thick layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall, and they appear purple under a microscope after the Gram-stain ...
Lab manual
... EXERCISE 7.0: DEGRADATION OF COMPLEX CARBON SOURCES (Groups of 2) ..................................................83 EXERCISE 7.1: METABOLISM IN PHENOL RED BROTH (Groups of 2) ..................................................................84 EXERCISE 7.2: GROWTH IN TSI (Groups of 2) ........... ...
... EXERCISE 7.0: DEGRADATION OF COMPLEX CARBON SOURCES (Groups of 2) ..................................................83 EXERCISE 7.1: METABOLISM IN PHENOL RED BROTH (Groups of 2) ..................................................................84 EXERCISE 7.2: GROWTH IN TSI (Groups of 2) ........... ...
HUGONIA MYSTAX Research Article ARUMUGAM VIMALAVADY
... Regarding antimicrobial activity, petroleum ether, ethanol and aqueous extracts (cold, boiled and autoclaved) extracts showed maximum zone of inhibition against both gram-positive and gramnegative bacteria while chloroform extract showed maximum zone of inhibition against only gram-negative bacteria ...
... Regarding antimicrobial activity, petroleum ether, ethanol and aqueous extracts (cold, boiled and autoclaved) extracts showed maximum zone of inhibition against both gram-positive and gramnegative bacteria while chloroform extract showed maximum zone of inhibition against only gram-negative bacteria ...
LACTIC ACID BACTERIA AS BIOPROTECTIVE AGENTS AGAINST FOODBORNE PATHOGENS AND SPOILAGE
... There is a growing concern in the microbiological safety of fresh fruit and vegetables. The contamination of these products with plant and human pathogens can cause considerably economic losses for the industry, apart from being the origin of foodborne diseases. Some of the most important contaminan ...
... There is a growing concern in the microbiological safety of fresh fruit and vegetables. The contamination of these products with plant and human pathogens can cause considerably economic losses for the industry, apart from being the origin of foodborne diseases. Some of the most important contaminan ...
The Nitrogen Cycle WS File
... Nitrogen is a crucial element for all living things, forming an essential part of the structure of proteins and nucleic acids. The Earth’s atmosphere is about 80% nitrogen gas (N2), but molecular nitrogen is so stable that is only rarely available directly to organisms and is often in short supply i ...
... Nitrogen is a crucial element for all living things, forming an essential part of the structure of proteins and nucleic acids. The Earth’s atmosphere is about 80% nitrogen gas (N2), but molecular nitrogen is so stable that is only rarely available directly to organisms and is often in short supply i ...
Efflux pumps of Gram-negative bacteria: what they do, how they do it
... as well as the means by which the transporter recognizes structurally unrelated compounds is not yet completely understood. Unlike the ABC transporters, members of resistance nodulation division (RND) family obtain their energy from the PMF established as the result of cellular metabolism. Protons t ...
... as well as the means by which the transporter recognizes structurally unrelated compounds is not yet completely understood. Unlike the ABC transporters, members of resistance nodulation division (RND) family obtain their energy from the PMF established as the result of cellular metabolism. Protons t ...
Microbiology and Mycology.doc
... Title of Learning Activity: Elements of Bacteriology Summary of the Learning Activity: In this activity, you will learn about the history of microbiology and appreciate the discoveries of microbes, microscopes and the development of the sterile culture technique. Microorganisms are quite diverse in ...
... Title of Learning Activity: Elements of Bacteriology Summary of the Learning Activity: In this activity, you will learn about the history of microbiology and appreciate the discoveries of microbes, microscopes and the development of the sterile culture technique. Microorganisms are quite diverse in ...
Antimicrobial activities of silver dressings: an in vitro comparison
... in acute and chronic wound care, such as in diabetic ulcers. Our study confirmed the effectiveness of topical silver against a broad range of bacterial pathogens, and identified differences between these commonly available dressings. With the enhanced bacterial killing effects, there is also concern ...
... in acute and chronic wound care, such as in diabetic ulcers. Our study confirmed the effectiveness of topical silver against a broad range of bacterial pathogens, and identified differences between these commonly available dressings. With the enhanced bacterial killing effects, there is also concern ...
BLOOD AGAR
... Purpose Blood agar is used to determine the ability of an organism to hemolyze erythrocytes (RBCs). Medical Applications The ability to produce hemolysis is associated with virulence. Many pathogenic species of Streptococcus, Staphylococcus and Clostridium demonstrate hemolysis. Streptococcus pyogen ...
... Purpose Blood agar is used to determine the ability of an organism to hemolyze erythrocytes (RBCs). Medical Applications The ability to produce hemolysis is associated with virulence. Many pathogenic species of Streptococcus, Staphylococcus and Clostridium demonstrate hemolysis. Streptococcus pyogen ...
Escherichia Coli
... •Size: E. coli is about one-hundredth the size of a human cell (about a micron long and one-tenth of a micron wide). ...
... •Size: E. coli is about one-hundredth the size of a human cell (about a micron long and one-tenth of a micron wide). ...
The ecology of transfer of mobile genetic elements
... signatures and functions relevant to HGT and the persistence of MGE as they respond to environmental conditions or triggers. Novel methods, such as the reverse transcription-PCR analysis of environmental mRNA followed by hybridization, or DNA-based hybridization using microarrays, should ultimately ...
... signatures and functions relevant to HGT and the persistence of MGE as they respond to environmental conditions or triggers. Novel methods, such as the reverse transcription-PCR analysis of environmental mRNA followed by hybridization, or DNA-based hybridization using microarrays, should ultimately ...
Silogini Thanarajah
... Motile: Moving or having power to move spontaneously. Immotile: Not moving or lacking the ability to move. Agar: A dried hydrophilic, colloidal substance extracted from various species of red algae; used in solid culture media for bacteria and other microorganisms. ...
... Motile: Moving or having power to move spontaneously. Immotile: Not moving or lacking the ability to move. Agar: A dried hydrophilic, colloidal substance extracted from various species of red algae; used in solid culture media for bacteria and other microorganisms. ...
Bacteria

Bacteria (/bækˈtɪəriə/; singular: bacterium) constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals. Bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep portions of Earth's crust. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships with plants and animals. They are also known to have flourished in manned spacecraft.There are typically 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil and a million bacterial cells in a millilitre of fresh water. There are approximately 5×1030 bacteria on Earth, forming a biomass which exceeds that of all plants and animals. Bacteria are vital in recycling nutrients, with many of the stages in nutrient cycles dependent on these organisms, such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere and putrefaction. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. On 17 March 2013, researchers reported data that suggested bacterial life forms thrive in the Mariana Trench, which with a depth of up to 11 kilometres is the deepest part of the Earth's oceans. Other researchers reported related studies that microbes thrive inside rocks up to 580 metres below the sea floor under 2.6 kilometres of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States. According to one of the researchers, ""You can find microbes everywhere — they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are.""Most bacteria have not been characterized, and only about half of the phyla of bacteria have species that can be grown in the laboratory. The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology.There are approximately ten times as many bacterial cells in the human flora as there are human cells in the body, with the largest number of the human flora being in the gut flora, and a large number on the skin. The vast majority of the bacteria in the body are rendered harmless by the protective effects of the immune system, and some are beneficial. However, several species of bacteria are pathogenic and cause infectious diseases, including cholera, syphilis, anthrax, leprosy, and bubonic plague. The most common fatal bacterial diseases are respiratory infections, with tuberculosis alone killing about 2 million people per year, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. In developed countries, antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections and are also used in farming, making antibiotic resistance a growing problem. In industry, bacteria are important in sewage treatment and the breakdown of oil spills, the production of cheese and yogurt through fermentation, and the recovery of gold, palladium, copper and other metals in the mining sector, as well as in biotechnology, and the manufacture of antibiotics and other chemicals.Once regarded as plants constituting the class Schizomycetes, bacteria are now classified as prokaryotes. Unlike cells of animals and other eukaryotes, bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus and rarely harbour membrane-bound organelles. Although the term bacteria traditionally included all prokaryotes, the scientific classification changed after the discovery in the 1990s that prokaryotes consist of two very different groups of organisms that evolved from an ancient common ancestor. These evolutionary domains are called Bacteria and Archaea.