They are classify organisms into Three domains(are the cell types
... unicellular prokaryotes(ancient bacteria) ,scientists, discovered these unique organisms(extremophiles) living in areas of extreme conditions some archaea found in hot spring and are called thermophiles(heat loving) other founds in very salt conditions called halophiles(salt loving) or low pH . This ...
... unicellular prokaryotes(ancient bacteria) ,scientists, discovered these unique organisms(extremophiles) living in areas of extreme conditions some archaea found in hot spring and are called thermophiles(heat loving) other founds in very salt conditions called halophiles(salt loving) or low pH . This ...
Reverting Antibiotic Resistance in Multi
... Associate Professor Eric Yap, LKCMedicine Project Description ...
... Associate Professor Eric Yap, LKCMedicine Project Description ...
221_exam_1_2003
... Describe how thioglycolate medium is used to determine the relationship of an organism to oxygen. Explain the function of the various key ingredients of the thioglycolate medium. Describe the growth pattern you would expect to observe for a strict aerobe, strict anaerobe, facultative and microaerop ...
... Describe how thioglycolate medium is used to determine the relationship of an organism to oxygen. Explain the function of the various key ingredients of the thioglycolate medium. Describe the growth pattern you would expect to observe for a strict aerobe, strict anaerobe, facultative and microaerop ...
Chapter 18 Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
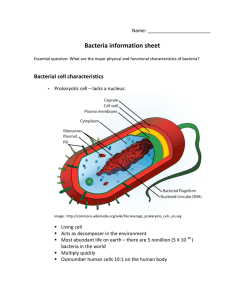
... • Cytoplasm – semi-fluid material inside the cell’s plasma membrane • Ribosome – organelle that helps to manufacture proteins • DNA - stores and communicates genetic information for the cell ...
... • Cytoplasm – semi-fluid material inside the cell’s plasma membrane • Ribosome – organelle that helps to manufacture proteins • DNA - stores and communicates genetic information for the cell ...
Structure of Bacteria
... • Most numerous organisms on Earth • Include all bacteria • Earliest fossils date 2.5 billion years old ...
... • Most numerous organisms on Earth • Include all bacteria • Earliest fossils date 2.5 billion years old ...
Bacterial cell characteristics
... • Bacterial cells have three basic shapes: o Cocci (round) o Spirilla (spiral) o Bacilli (oval) ...
... • Bacterial cells have three basic shapes: o Cocci (round) o Spirilla (spiral) o Bacilli (oval) ...
Prokaryotes
... Bacteria occur in many shapes and sizes. Most bacteria have one of three basic shapes: rod-shaped, sphere-shaped, or spiral-shaped. Spiral shaped bacteria in the form of spirilla (singular, spirillum) or vibrio (comma like). Sphere-shaped bacteria are called cocci (singular, coccus). An examp ...
... Bacteria occur in many shapes and sizes. Most bacteria have one of three basic shapes: rod-shaped, sphere-shaped, or spiral-shaped. Spiral shaped bacteria in the form of spirilla (singular, spirillum) or vibrio (comma like). Sphere-shaped bacteria are called cocci (singular, coccus). An examp ...
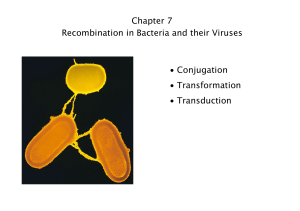
Chapter 7 Recombination in Bacteria and their Viruses
... • Bacteriophages can transduce bacterial genes from one cell to another. • In transformation, DNA from the environment can enter bacterial cells and integrate into the chromosome. • These methods of gene transfer generate partial diploids that allow study of genes. ...
... • Bacteriophages can transduce bacterial genes from one cell to another. • In transformation, DNA from the environment can enter bacterial cells and integrate into the chromosome. • These methods of gene transfer generate partial diploids that allow study of genes. ...
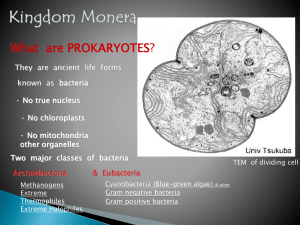
Vocabulary Chapter 11 Prokaryotes Monera Another name given to
... A more advanced group of bacteria often referred to as “true bacteria” Example: Pneumonia is caused by eubacteria living in human cells mycoplasmas A membrane that surrounds some types of bacteria Example: Eubacteria cells are surrounded by mycoplasmas composed of fatty compounds. cyanobacteria The ...
... A more advanced group of bacteria often referred to as “true bacteria” Example: Pneumonia is caused by eubacteria living in human cells mycoplasmas A membrane that surrounds some types of bacteria Example: Eubacteria cells are surrounded by mycoplasmas composed of fatty compounds. cyanobacteria The ...
Chapter 20 Viruses, Bacteria, and Archaea
... •Gram-positive bacteria stain purple, whereas Gram-negative bacteria stain pink. •This difference is dependent on the thick or thin (respectively) peptidoglycan cell wall. ...
... •Gram-positive bacteria stain purple, whereas Gram-negative bacteria stain pink. •This difference is dependent on the thick or thin (respectively) peptidoglycan cell wall. ...
B 1_1 Bacteria - Philip Rogers Elementary School
... Some types of bacteria live in extreme environments where few other organisms can survive. Bacteria normally have three basic shapes— spheres, rods, and spirals. Sphere-shaped bacteria are called cocci (KAHK si), rod-shaped bacteria are called bacilli (bah SIH li), and spiral-shaped bacteria are cal ...
... Some types of bacteria live in extreme environments where few other organisms can survive. Bacteria normally have three basic shapes— spheres, rods, and spirals. Sphere-shaped bacteria are called cocci (KAHK si), rod-shaped bacteria are called bacilli (bah SIH li), and spiral-shaped bacteria are cal ...
Antibiotics, Viruses, and Prions
... • Serious infections get multiple antibiotics at the same time • Bacteria that are immune to one probably aren’t immune to the others ...
... • Serious infections get multiple antibiotics at the same time • Bacteria that are immune to one probably aren’t immune to the others ...
4 The dominant form of life on Earth
... The total volume of the Earth’s oceans is 1.4 × 1018 m3 . The total number of bacteria is therefore 1012 bacteria m−3 × 1.4 × 1018 m3 = 1.4 × 1030 bacteria. What is the mass of a single bacterium? A typical bacterium is 1µm (10−6 m) in size or 1µm3 (10−18 m3 ) in volume. Being made mostly of water, ...
... The total volume of the Earth’s oceans is 1.4 × 1018 m3 . The total number of bacteria is therefore 1012 bacteria m−3 × 1.4 × 1018 m3 = 1.4 × 1030 bacteria. What is the mass of a single bacterium? A typical bacterium is 1µm (10−6 m) in size or 1µm3 (10−18 m3 ) in volume. Being made mostly of water, ...
Introductory slides - first couple of lectures
... Place the cell into a cubic swimming pool 1 cm on each side, then expand the entire system so that the cell is now 2 m long (equivalent to a tall [6’6”] human): Swimming pool is just over 6 miles on a side!! ...
... Place the cell into a cubic swimming pool 1 cm on each side, then expand the entire system so that the cell is now 2 m long (equivalent to a tall [6’6”] human): Swimming pool is just over 6 miles on a side!! ...
Prokaryotic organisms
... need only CO2 as a carbon source, obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic ...
... need only CO2 as a carbon source, obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic ...
A virus, or virion, is a tiny particle consisting of a DNA or RNA
... obtain nourishment from dead organic matter. 2. Autotrophs may be photoautotrophs (photosynthetic autotrophs) that obtain energy from light or chemoautotrophs (chemosynthetic autotrophs) that obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic chemical's. 3. Most bacteria are aerobic; some are facultative anaerobe ...
... obtain nourishment from dead organic matter. 2. Autotrophs may be photoautotrophs (photosynthetic autotrophs) that obtain energy from light or chemoautotrophs (chemosynthetic autotrophs) that obtain energy by oxidizing inorganic chemical's. 3. Most bacteria are aerobic; some are facultative anaerobe ...
sprulina - Ethio Celebrities
... • Some have formed millions of years old stromatolites as living structures ...
... • Some have formed millions of years old stromatolites as living structures ...
The bacterial world
... Bacteria in the living world Bacteria = one of the three groups of organisms on Earth ...
... Bacteria in the living world Bacteria = one of the three groups of organisms on Earth ...
Test 1 Review
... 10. The number of bacteria in a culture is given by the function n(t) 975e0.4t where t is measured in hours. a. What is the relative growth rate of this bacterium population? b. What is the initial population of the culture? c. How many bacteria will the culture contain at time t = 5? 11. At the b ...
... 10. The number of bacteria in a culture is given by the function n(t) 975e0.4t where t is measured in hours. a. What is the relative growth rate of this bacterium population? b. What is the initial population of the culture? c. How many bacteria will the culture contain at time t = 5? 11. At the b ...
Bell Ringer - Effingham County Schools
... 4. Alana conducted an experiment to see which type of coffee cup kept coffee the hottest for the longest period of time. She put 200ml of boiling water (125o Celsius) in each of the following cups: a Styrofoam cup, a paper cup, and a ceramic cup. Every five minutes she measured the temperature of ea ...
... 4. Alana conducted an experiment to see which type of coffee cup kept coffee the hottest for the longest period of time. She put 200ml of boiling water (125o Celsius) in each of the following cups: a Styrofoam cup, a paper cup, and a ceramic cup. Every five minutes she measured the temperature of ea ...
Quiz Answers
... reproduction. Resistance can happen through a mutation in a gene that causes the enzyme structure to change so that the antibiotic can no longer bind and the bacteria can reproduce in the presence of the antibiotic. - Destruction/Inactivation: Resistance can happen through the production of enzymes ...
... reproduction. Resistance can happen through a mutation in a gene that causes the enzyme structure to change so that the antibiotic can no longer bind and the bacteria can reproduce in the presence of the antibiotic. - Destruction/Inactivation: Resistance can happen through the production of enzymes ...
Bacteria
... they useful to us? [They play a role in making yogurt, cheese, and other foods. Bacteria also aid in digestion.] ...
... they useful to us? [They play a role in making yogurt, cheese, and other foods. Bacteria also aid in digestion.] ...
Bacteria

Bacteria (/bækˈtɪəriə/; singular: bacterium) constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals. Bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep portions of Earth's crust. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships with plants and animals. They are also known to have flourished in manned spacecraft.There are typically 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil and a million bacterial cells in a millilitre of fresh water. There are approximately 5×1030 bacteria on Earth, forming a biomass which exceeds that of all plants and animals. Bacteria are vital in recycling nutrients, with many of the stages in nutrient cycles dependent on these organisms, such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere and putrefaction. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. On 17 March 2013, researchers reported data that suggested bacterial life forms thrive in the Mariana Trench, which with a depth of up to 11 kilometres is the deepest part of the Earth's oceans. Other researchers reported related studies that microbes thrive inside rocks up to 580 metres below the sea floor under 2.6 kilometres of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States. According to one of the researchers, ""You can find microbes everywhere — they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are.""Most bacteria have not been characterized, and only about half of the phyla of bacteria have species that can be grown in the laboratory. The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology.There are approximately ten times as many bacterial cells in the human flora as there are human cells in the body, with the largest number of the human flora being in the gut flora, and a large number on the skin. The vast majority of the bacteria in the body are rendered harmless by the protective effects of the immune system, and some are beneficial. However, several species of bacteria are pathogenic and cause infectious diseases, including cholera, syphilis, anthrax, leprosy, and bubonic plague. The most common fatal bacterial diseases are respiratory infections, with tuberculosis alone killing about 2 million people per year, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. In developed countries, antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections and are also used in farming, making antibiotic resistance a growing problem. In industry, bacteria are important in sewage treatment and the breakdown of oil spills, the production of cheese and yogurt through fermentation, and the recovery of gold, palladium, copper and other metals in the mining sector, as well as in biotechnology, and the manufacture of antibiotics and other chemicals.Once regarded as plants constituting the class Schizomycetes, bacteria are now classified as prokaryotes. Unlike cells of animals and other eukaryotes, bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus and rarely harbour membrane-bound organelles. Although the term bacteria traditionally included all prokaryotes, the scientific classification changed after the discovery in the 1990s that prokaryotes consist of two very different groups of organisms that evolved from an ancient common ancestor. These evolutionary domains are called Bacteria and Archaea.