18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotics
... Some bacteria cause disease. • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making toxins. • A toxin is a poison released by an organism. ...
... Some bacteria cause disease. • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making toxins. • A toxin is a poison released by an organism. ...
Chapter 27
... Oxygen relationships: obligate aerobes; facultative anaerobes; obligate anaerobes ...
... Oxygen relationships: obligate aerobes; facultative anaerobes; obligate anaerobes ...
Bacteria - LiveText
... - may be used to make yogurt, pickles, and buttermilk - or to make medicines using biotechnology Ex. Strep throat ; staph infections; tuberculosis ...
... - may be used to make yogurt, pickles, and buttermilk - or to make medicines using biotechnology Ex. Strep throat ; staph infections; tuberculosis ...
Bacteria - Dickinson ISD
... 1) Eubacteria (Domain Bacteria) – Largest bacterial kingdom – Cell walls contain peptidoglycan ...
... 1) Eubacteria (Domain Bacteria) – Largest bacterial kingdom – Cell walls contain peptidoglycan ...
Ch. 15.4
... a. Multicellular organisms b. Photosynthetic organisms c. Eukaryotes d. Prokaryotes 11. Organisms in the domains Bacteria and Archaea were previously grouped in a kingdom called: a. Animalia b. Fungi c. Monera d. Eukarya 12. Bacteria and archaea differ in: a. The presence of a membrane-bound nucleus ...
... a. Multicellular organisms b. Photosynthetic organisms c. Eukaryotes d. Prokaryotes 11. Organisms in the domains Bacteria and Archaea were previously grouped in a kingdom called: a. Animalia b. Fungi c. Monera d. Eukarya 12. Bacteria and archaea differ in: a. The presence of a membrane-bound nucleus ...
Bacteria Poster Questions
... 2. (a) What is the difference in shape between cocci, diplococci, and streptococci? (b) Draw each of the bacteria shapes. (c) Give one example of each type of bacteria. 3. Some bacteria are said to be Gram negative (G-), and others are said to be Gram positive (G+). (a) Is there a difference in colo ...
... 2. (a) What is the difference in shape between cocci, diplococci, and streptococci? (b) Draw each of the bacteria shapes. (c) Give one example of each type of bacteria. 3. Some bacteria are said to be Gram negative (G-), and others are said to be Gram positive (G+). (a) Is there a difference in colo ...
bacterial chromosome cell membrane
... Because this structure allows some substances to diffuse across its barrier, while keeping other substances out, it is known as being semi-permeable. Constructed primarily of a double layer of lipids that contain a phosphate group, this structure is described as a phospholipid bilayer. There are als ...
... Because this structure allows some substances to diffuse across its barrier, while keeping other substances out, it is known as being semi-permeable. Constructed primarily of a double layer of lipids that contain a phosphate group, this structure is described as a phospholipid bilayer. There are als ...
Kingdom – Monera
... This connection allows one of the cells to __pass__ __DNA__ to the other cell. Some bacteria have small circles of DNA called ___plasmid___. 6.) __Eschirichia coli__, __staphylococcus__, and __clostridium__ are examples of bacteria. Many of the bacteria are helpful. Some live in the soil and help pl ...
... This connection allows one of the cells to __pass__ __DNA__ to the other cell. Some bacteria have small circles of DNA called ___plasmid___. 6.) __Eschirichia coli__, __staphylococcus__, and __clostridium__ are examples of bacteria. Many of the bacteria are helpful. Some live in the soil and help pl ...
Fungi and Bacteria - Singapore Asia Publishers
... • Fungi and bacteria are living things. • Fungi s come in different shapes and sizes, s feed on plants and animals, and s reproduce by spores. • Bacteria (and other microorganisms) are so small that they can only be seen under a microscope. Living things Fungi ...
... • Fungi and bacteria are living things. • Fungi s come in different shapes and sizes, s feed on plants and animals, and s reproduce by spores. • Bacteria (and other microorganisms) are so small that they can only be seen under a microscope. Living things Fungi ...
EVE 290 Introduction to Environmental Engineering HW #8 1. A
... 1. A radioactive nuclide is reduced by 90% in 12 minutes. What is its half-life? Hint: What is the “order” of the reaction process that is associated with radioactivity? (Ans: 3.6 minutes) 2. A radioactive waste from a clinical laboratory contains 0.2 microcuries of calcium-45 (45Ca) per liter. The ...
... 1. A radioactive nuclide is reduced by 90% in 12 minutes. What is its half-life? Hint: What is the “order” of the reaction process that is associated with radioactivity? (Ans: 3.6 minutes) 2. A radioactive waste from a clinical laboratory contains 0.2 microcuries of calcium-45 (45Ca) per liter. The ...
Bacteria - Humble ISD
... – Eubacteria has cells walls made of peptidoglycan – One single, double stranded circular DNA ...
... – Eubacteria has cells walls made of peptidoglycan – One single, double stranded circular DNA ...
v. taxonomy of the prokaryotes
... a) Cell-wall-less bacteria that inhabit body fluids of plants and animals 9. Actinomycetes a) Produce many useful antibiotics (1) Especially the genus Streptomyces VI. ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY A. Important in demineralization 1. Breaking down of organic molecules into inorganic molecules 2. If a c ...
... a) Cell-wall-less bacteria that inhabit body fluids of plants and animals 9. Actinomycetes a) Produce many useful antibiotics (1) Especially the genus Streptomyces VI. ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY A. Important in demineralization 1. Breaking down of organic molecules into inorganic molecules 2. If a c ...
Prokaryotes
... peptidoglycan while Gram negative bacteria have ____________ peptidoglycan. 5. Gram-___________ bacteria have lipopolysaccharides on their cell wall, meaning they are ___________ resistant to antibiotics, which prevent peptidoglycan cross-linking. a. Negative…more b. Negative…less c. Positive…less d ...
... peptidoglycan while Gram negative bacteria have ____________ peptidoglycan. 5. Gram-___________ bacteria have lipopolysaccharides on their cell wall, meaning they are ___________ resistant to antibiotics, which prevent peptidoglycan cross-linking. a. Negative…more b. Negative…less c. Positive…less d ...
Bacteria Prokaryotes Eubacteria Archaebacteria
... · includes Bacteria (eubacteria) and Archaea · most abundant type of organism · evolution has yielded hundreds of thousands of bacteria that are adapted to places no other organisms can live ...
... · includes Bacteria (eubacteria) and Archaea · most abundant type of organism · evolution has yielded hundreds of thousands of bacteria that are adapted to places no other organisms can live ...
diplo - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate pairing of cells
... with the shape name to indicate pairing of cells. strepto - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate filaments. staphylo - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate clusters. ...
... with the shape name to indicate pairing of cells. strepto - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate filaments. staphylo - a prefix used with the shape name to indicate clusters. ...
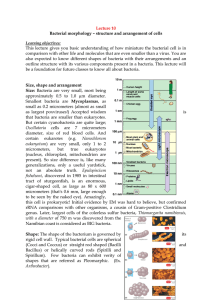
Lecture 10 Bacterial morphology – structure and arrangement of
... eukaryotum) are very small, only 1 to 2 micrometers, but true eukaryotes (nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondrion are present). So size difference is, like many generalizations, only a useful yardstick, not an absolute truth. Epulopiscium fishelsoni, discovered in 1985 in intestinal tract of sturgeonfis ...
... eukaryotum) are very small, only 1 to 2 micrometers, but true eukaryotes (nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondrion are present). So size difference is, like many generalizations, only a useful yardstick, not an absolute truth. Epulopiscium fishelsoni, discovered in 1985 in intestinal tract of sturgeonfis ...
Lecture 1 Thursday Jan. 4, 2001
... Filamentous Gram+; abundant in soil; odour of fresh soil = geosmin; some cause plant diseases, many very important in producing antibiotics, including antassociates; Frankia is a root-associate with many boreal shrubs, N2-fixing; ...
... Filamentous Gram+; abundant in soil; odour of fresh soil = geosmin; some cause plant diseases, many very important in producing antibiotics, including antassociates; Frankia is a root-associate with many boreal shrubs, N2-fixing; ...
Scientific American, February 2010, p
... killers. Tuberculosis alone takes nearly two million lives every year, and Yersinia pestis, infamous for causing bubonic plague, killed approximately one third of Europe’s population in the 14th century. Investigators have made considerable progress over the past 100 years in taming some species wit ...
... killers. Tuberculosis alone takes nearly two million lives every year, and Yersinia pestis, infamous for causing bubonic plague, killed approximately one third of Europe’s population in the 14th century. Investigators have made considerable progress over the past 100 years in taming some species wit ...
Exam Questions for Lesson 1
... Describe how each of the following parts of the body is protected to prevent microorganisms entering living cells. (i) ...
... Describe how each of the following parts of the body is protected to prevent microorganisms entering living cells. (i) ...
Bacteria

Bacteria (/bækˈtɪəriə/; singular: bacterium) constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals. Bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep portions of Earth's crust. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships with plants and animals. They are also known to have flourished in manned spacecraft.There are typically 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil and a million bacterial cells in a millilitre of fresh water. There are approximately 5×1030 bacteria on Earth, forming a biomass which exceeds that of all plants and animals. Bacteria are vital in recycling nutrients, with many of the stages in nutrient cycles dependent on these organisms, such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere and putrefaction. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. On 17 March 2013, researchers reported data that suggested bacterial life forms thrive in the Mariana Trench, which with a depth of up to 11 kilometres is the deepest part of the Earth's oceans. Other researchers reported related studies that microbes thrive inside rocks up to 580 metres below the sea floor under 2.6 kilometres of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States. According to one of the researchers, ""You can find microbes everywhere — they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are.""Most bacteria have not been characterized, and only about half of the phyla of bacteria have species that can be grown in the laboratory. The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology.There are approximately ten times as many bacterial cells in the human flora as there are human cells in the body, with the largest number of the human flora being in the gut flora, and a large number on the skin. The vast majority of the bacteria in the body are rendered harmless by the protective effects of the immune system, and some are beneficial. However, several species of bacteria are pathogenic and cause infectious diseases, including cholera, syphilis, anthrax, leprosy, and bubonic plague. The most common fatal bacterial diseases are respiratory infections, with tuberculosis alone killing about 2 million people per year, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. In developed countries, antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections and are also used in farming, making antibiotic resistance a growing problem. In industry, bacteria are important in sewage treatment and the breakdown of oil spills, the production of cheese and yogurt through fermentation, and the recovery of gold, palladium, copper and other metals in the mining sector, as well as in biotechnology, and the manufacture of antibiotics and other chemicals.Once regarded as plants constituting the class Schizomycetes, bacteria are now classified as prokaryotes. Unlike cells of animals and other eukaryotes, bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus and rarely harbour membrane-bound organelles. Although the term bacteria traditionally included all prokaryotes, the scientific classification changed after the discovery in the 1990s that prokaryotes consist of two very different groups of organisms that evolved from an ancient common ancestor. These evolutionary domains are called Bacteria and Archaea.