Bacteria and Algae - Hatboro
... • Reproduce asexually via binary fission • 3 forms – Chemosynthetic – Photosynthetic – Heterotrophic ...
... • Reproduce asexually via binary fission • 3 forms – Chemosynthetic – Photosynthetic – Heterotrophic ...
characterization of procaryotic cells inner structures in bacteria
... plants, to use carbon dioxide as the main source of carbon. – Energy is obtained in these microorganims by the oxidation of anorganic compounds or from sunlight. ...
... plants, to use carbon dioxide as the main source of carbon. – Energy is obtained in these microorganims by the oxidation of anorganic compounds or from sunlight. ...
characterization of procaryotic cells inner structures in bacteria
... The majority of bacterial and fungal species of medical importance grow in artificial media in the ...
... The majority of bacterial and fungal species of medical importance grow in artificial media in the ...
013368718X_CH20_313-324.indd
... The Importance of Prokaryotes 13. How do decomposers help the ecosystem recycle nutrients when a tree dies? ...
... The Importance of Prokaryotes 13. How do decomposers help the ecosystem recycle nutrients when a tree dies? ...
Bacteria - Hobbs High School
... • Prokaryote – lack nucleus and various organelles (do have ribosomes) – Oldest and most simplest forms of life ...
... • Prokaryote – lack nucleus and various organelles (do have ribosomes) – Oldest and most simplest forms of life ...
Kingdom Monera
... Kingdom Monera: The Prokaryotes BACTERIA - single-celled prokaryotes - among the simplest forms of living things - w/ few organelles or specialized cell structures - believed to be the most abundant organism on earth ...
... Kingdom Monera: The Prokaryotes BACTERIA - single-celled prokaryotes - among the simplest forms of living things - w/ few organelles or specialized cell structures - believed to be the most abundant organism on earth ...
Prokaryotes
... peptidoglycan = polysaccharides + amino acid chains lipopolysaccharides = lipids + polysaccharides Gram-negative bacteria ...
... peptidoglycan = polysaccharides + amino acid chains lipopolysaccharides = lipids + polysaccharides Gram-negative bacteria ...
TGT- Questions
... They are all archaebacteria. They live in different environments (thermoacidophiles live where it’s hot and acidic, halophiles live where it is salty). 21. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells to each other. What structures do the cell types have in common? What structures does one cell type hav ...
... They are all archaebacteria. They live in different environments (thermoacidophiles live where it’s hot and acidic, halophiles live where it is salty). 21. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells to each other. What structures do the cell types have in common? What structures does one cell type hav ...
Prokaryotes
... Methanogens – archaea bacteria that live in anaerobic conditions and produce methane gas ...
... Methanogens – archaea bacteria that live in anaerobic conditions and produce methane gas ...
Abstract Actinobacteria are important members of the soil
... Actinobacteria are important members of the soil ecosystems, where they are involved in organic matter decomposition. It is worth mentioning that their secondary metabolism allows them to produce a variety of different compounds. These compounds include antibiotics, among them aminoglycosides have a ...
... Actinobacteria are important members of the soil ecosystems, where they are involved in organic matter decomposition. It is worth mentioning that their secondary metabolism allows them to produce a variety of different compounds. These compounds include antibiotics, among them aminoglycosides have a ...
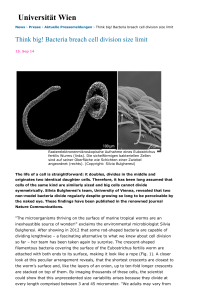
Think big! - Division of Archaea Biology and Ecogenomics
... But what about the tiny little friends of the closely related E. dianeae worm? Here, the filamentous bacteria are attached to the worm host with only one end, as if to form a fur (Fig. 2). How long can one bacterium, that is a fur hair be? Over a tenth of a millimeter, roughly the human vision lower ...
... But what about the tiny little friends of the closely related E. dianeae worm? Here, the filamentous bacteria are attached to the worm host with only one end, as if to form a fur (Fig. 2). How long can one bacterium, that is a fur hair be? Over a tenth of a millimeter, roughly the human vision lower ...
Electric polarization properties of single bacteria measured with electrostatic force microscopy
... Something similar happened with the two shell model, where small objects can be approximated by an analytical formula because the electrical field generated by the probe is approximately homogeneous in the part that mostly contributes to the force. It is something that does not happen i ...
... Something similar happened with the two shell model, where small objects can be approximated by an analytical formula because the electrical field generated by the probe is approximately homogeneous in the part that mostly contributes to the force. It is something that does not happen i ...
Bacteria and the body
... have a higher chance of developing asthma and allergies. This is not to say beneficial bacteria can't also be dangerous. Usually, helpful bacteria and harmful bacteria are mutually exclusive, Maczulak said. But there is overlap, notably in the bacteria that inhabit the body. "Staph bacteria is a goo ...
... have a higher chance of developing asthma and allergies. This is not to say beneficial bacteria can't also be dangerous. Usually, helpful bacteria and harmful bacteria are mutually exclusive, Maczulak said. But there is overlap, notably in the bacteria that inhabit the body. "Staph bacteria is a goo ...
the evolution of the cell
... characteristics, mtDNA has provided important clues about evolutionary history. For example, differences in mtDNA are examined to estimate how closely related one species is to another. ...
... characteristics, mtDNA has provided important clues about evolutionary history. For example, differences in mtDNA are examined to estimate how closely related one species is to another. ...
Gram positive - Cloudfront.net
... – Chromosome & plasmids float freely in cytoplasm • Ribosomes: create proteins • Flagella: used in movement pili • Pili: act as anchors plasma membrance • Capsule: outer coating chromosome • Endospore: “cocoon” to protect DNA in harsh timescell wall plasmid ...
... – Chromosome & plasmids float freely in cytoplasm • Ribosomes: create proteins • Flagella: used in movement pili • Pili: act as anchors plasma membrance • Capsule: outer coating chromosome • Endospore: “cocoon” to protect DNA in harsh timescell wall plasmid ...
Prokaryotes- most numerous living organism group
... • Transformation- bacteria takes up DNA from environment • Conjugation- 2 bacterial cell join and transfer genetic material- plasmids • Transduction- when viruses (bacteriophage) infect bacteria with their genes. ...
... • Transformation- bacteria takes up DNA from environment • Conjugation- 2 bacterial cell join and transfer genetic material- plasmids • Transduction- when viruses (bacteriophage) infect bacteria with their genes. ...
Bacteria

Bacteria (/bækˈtɪəriə/; singular: bacterium) constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a number of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals. Bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep portions of Earth's crust. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationships with plants and animals. They are also known to have flourished in manned spacecraft.There are typically 40 million bacterial cells in a gram of soil and a million bacterial cells in a millilitre of fresh water. There are approximately 5×1030 bacteria on Earth, forming a biomass which exceeds that of all plants and animals. Bacteria are vital in recycling nutrients, with many of the stages in nutrient cycles dependent on these organisms, such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere and putrefaction. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. On 17 March 2013, researchers reported data that suggested bacterial life forms thrive in the Mariana Trench, which with a depth of up to 11 kilometres is the deepest part of the Earth's oceans. Other researchers reported related studies that microbes thrive inside rocks up to 580 metres below the sea floor under 2.6 kilometres of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States. According to one of the researchers, ""You can find microbes everywhere — they're extremely adaptable to conditions, and survive wherever they are.""Most bacteria have not been characterized, and only about half of the phyla of bacteria have species that can be grown in the laboratory. The study of bacteria is known as bacteriology, a branch of microbiology.There are approximately ten times as many bacterial cells in the human flora as there are human cells in the body, with the largest number of the human flora being in the gut flora, and a large number on the skin. The vast majority of the bacteria in the body are rendered harmless by the protective effects of the immune system, and some are beneficial. However, several species of bacteria are pathogenic and cause infectious diseases, including cholera, syphilis, anthrax, leprosy, and bubonic plague. The most common fatal bacterial diseases are respiratory infections, with tuberculosis alone killing about 2 million people per year, mostly in sub-Saharan Africa. In developed countries, antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections and are also used in farming, making antibiotic resistance a growing problem. In industry, bacteria are important in sewage treatment and the breakdown of oil spills, the production of cheese and yogurt through fermentation, and the recovery of gold, palladium, copper and other metals in the mining sector, as well as in biotechnology, and the manufacture of antibiotics and other chemicals.Once regarded as plants constituting the class Schizomycetes, bacteria are now classified as prokaryotes. Unlike cells of animals and other eukaryotes, bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus and rarely harbour membrane-bound organelles. Although the term bacteria traditionally included all prokaryotes, the scientific classification changed after the discovery in the 1990s that prokaryotes consist of two very different groups of organisms that evolved from an ancient common ancestor. These evolutionary domains are called Bacteria and Archaea.