Place in Space
... distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So, this distance is 1 lightyear. ...
... distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So, this distance is 1 lightyear. ...
doc - IAC
... Massive stars are much heavier than the Sun. They can be up to 10 or 100 times more massive. They stand out because of their high luminosity. These stars can become a million times brighter than the Sun. Their masses can be measured dynamically, in the same way as planetary masses are measured. The ...
... Massive stars are much heavier than the Sun. They can be up to 10 or 100 times more massive. They stand out because of their high luminosity. These stars can become a million times brighter than the Sun. Their masses can be measured dynamically, in the same way as planetary masses are measured. The ...
supernova!
... For every 90 Hydrogen atoms (a total mass of 90), there are 9 Heliums (with a total mass of 9x4 = 36); and so on for the other elements. Thus Hydrogen is about 70% of the total mass, the rest (~25% or so) being mostly Helium. This justifies my earlier statements that the universe is ~2/3-3/4 Hydroge ...
... For every 90 Hydrogen atoms (a total mass of 90), there are 9 Heliums (with a total mass of 9x4 = 36); and so on for the other elements. Thus Hydrogen is about 70% of the total mass, the rest (~25% or so) being mostly Helium. This justifies my earlier statements that the universe is ~2/3-3/4 Hydroge ...
Explosive sources of the highest energy radiation
... front formed from the interacaverage once a year. Remarktion of the pulsar wind with the stellar wind of the Be companion. ably, there is no sign of simultaneous While the detection of gamma-ray emission variability at any other wavelengths despite by Fermi was anticipated, the highly variable numer ...
... front formed from the interacaverage once a year. Remarktion of the pulsar wind with the stellar wind of the Be companion. ably, there is no sign of simultaneous While the detection of gamma-ray emission variability at any other wavelengths despite by Fermi was anticipated, the highly variable numer ...
Evidence of the Big Bang and Structure of the Universe
... original Big Bang using sensitive receivers The use of the Hubble Space Telescope and other instruments have led to the predicted age of the universe: 13.7 billion years ...
... original Big Bang using sensitive receivers The use of the Hubble Space Telescope and other instruments have led to the predicted age of the universe: 13.7 billion years ...
Galaxies and Stars
... Galaxy – a large system of stars held together by the same gravitational pull and separated from other large systems. ...
... Galaxy – a large system of stars held together by the same gravitational pull and separated from other large systems. ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • No two electrons can occupy the same quantum state ...
... • No two electrons can occupy the same quantum state ...
Unit 1
... electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and “bounce” • The “bounced material collides with the remaining infalling gas, raising temperatures high enough to set ...
... electrons merge into neutrons, taking energy away from the core • The core collapses, and the layers above fall rapidly toward the center, where they collide with the core material and “bounce” • The “bounced material collides with the remaining infalling gas, raising temperatures high enough to set ...
Chapter 1 Vocabulary – The Puzzled of Matter
... 1. Open cluster – has disorganized or loose appearance and contains no more than a few thousand stars that are well spread out. 2. Associations – are temporary groupings of bright, young stars. In time 3. Globular Cluster – a large spherical-shaped group of older stars that usually lacks sufficient ...
... 1. Open cluster – has disorganized or loose appearance and contains no more than a few thousand stars that are well spread out. 2. Associations – are temporary groupings of bright, young stars. In time 3. Globular Cluster – a large spherical-shaped group of older stars that usually lacks sufficient ...
chapter 28 pages 747-752
... • 1. nebula- cloud of gas and dust • 2. Rotation causes formation of protostar • 3. Once it is hot enough for H to fuse into He, main sequence stage occurs • This is the longest stage of a stars life. • 4. In medium sized stars, once all H has been fused into He, He then starts to fuse into C during ...
... • 1. nebula- cloud of gas and dust • 2. Rotation causes formation of protostar • 3. Once it is hot enough for H to fuse into He, main sequence stage occurs • This is the longest stage of a stars life. • 4. In medium sized stars, once all H has been fused into He, He then starts to fuse into C during ...
PHYSICS 015
... encountered, no exotic or extraordinary circumstances. No one tells the material that a special new behaviour has to rise up to save the day. ….but it’s already too late; gravity ...
... encountered, no exotic or extraordinary circumstances. No one tells the material that a special new behaviour has to rise up to save the day. ….but it’s already too late; gravity ...
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... gravitational pull. The core becomes so small and dense that its gravitational pull is so strong, not even light can escape. ...
... gravitational pull. The core becomes so small and dense that its gravitational pull is so strong, not even light can escape. ...
Astronomy Campus Assessment
... Scientists measure the movement of distant galaxies to learn more about the origin of the universe. You researched scientific data that showed that light from a distant galaxy is red-shifted. How would you evaluate the data? A. It indicates that the expansion of the universe has stopped, and so it d ...
... Scientists measure the movement of distant galaxies to learn more about the origin of the universe. You researched scientific data that showed that light from a distant galaxy is red-shifted. How would you evaluate the data? A. It indicates that the expansion of the universe has stopped, and so it d ...
Review Questions for Chp 2
... 43. What is the function of a telescope? 44. Identify two types of telescopes that must be placed in outer space. 45. What size wavelength of light creates the most damage to living things and what type of electromagnetic radiation is it? 46. Define circumpolar stars and give one example of a circum ...
... 43. What is the function of a telescope? 44. Identify two types of telescopes that must be placed in outer space. 45. What size wavelength of light creates the most damage to living things and what type of electromagnetic radiation is it? 46. Define circumpolar stars and give one example of a circum ...
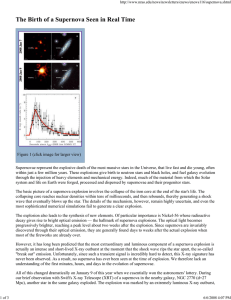
The Birth of a Supernova Seen in Real Time
... kinetic energy of the explosion. As a result, this explosion bares no resemblance to the extraordinary energetics and velocities inferred for GRBs and XRFs. The radio emission thus points to an ordinary core-collapse supernova in which only a tiny fraction of the explosion energy is coupled to fast ...
... kinetic energy of the explosion. As a result, this explosion bares no resemblance to the extraordinary energetics and velocities inferred for GRBs and XRFs. The radio emission thus points to an ordinary core-collapse supernova in which only a tiny fraction of the explosion energy is coupled to fast ...
A Search for Optical Signatures of Gamma
... MOTIVATION No.3: B. Paczynski’s prediction: “Optical flashes preceding GRBs” [ ! ] (astro-ph/0108522): “A search for optical flashes independent of GRB triggers would provide important diagnostics for the GRBs and their ...
... MOTIVATION No.3: B. Paczynski’s prediction: “Optical flashes preceding GRBs” [ ! ] (astro-ph/0108522): “A search for optical flashes independent of GRB triggers would provide important diagnostics for the GRBs and their ...
vdHorst_liverpool2012
... Radio calorimetry • Late-time evolution: no relativistic complications • Blast wave spherical? Progenitor constraints • Very low frequencies and/or very late times GRB 970508 & GRB 980703 (Berger et al. ...
... Radio calorimetry • Late-time evolution: no relativistic complications • Blast wave spherical? Progenitor constraints • Very low frequencies and/or very late times GRB 970508 & GRB 980703 (Berger et al. ...
Document
... USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. ...
... USING KEY TERMS The statements below are false. For each statement, replace the underlined term to make a true statement. ...
Black Holes: Edge of Infinity Jonathan McKinney
... Horizon or Schwarzschild radius: Inside rH, objects must fall Singularity: Near, physics breaks down (need quantum gravity), reached in finite time ...
... Horizon or Schwarzschild radius: Inside rH, objects must fall Singularity: Near, physics breaks down (need quantum gravity), reached in finite time ...
THE BIG BANG - Dublin City Schools
... He noticed that the light, when it was emitted, would have shorter wavelengths. But, he observed longer wavelengths…this is because….expansion of space over the years that the light was traveling to us! This redshift appeared to have a larger displacement for faint, presumably further, galaxies. Hen ...
... He noticed that the light, when it was emitted, would have shorter wavelengths. But, he observed longer wavelengths…this is because….expansion of space over the years that the light was traveling to us! This redshift appeared to have a larger displacement for faint, presumably further, galaxies. Hen ...
kashiwa
... SUBARU has a good location to observe it. <- Pass through near the zenith. Wide band pulsed emission. <- Extend above 10GeV ? Below ten GeV, Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) revealed high energy phenomena, and over 100GeV, Ground-based detectors using Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope are ...
... SUBARU has a good location to observe it. <- Pass through near the zenith. Wide band pulsed emission. <- Extend above 10GeV ? Below ten GeV, Compton Gamma Ray Observatory (CGRO) revealed high energy phenomena, and over 100GeV, Ground-based detectors using Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope are ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... by the same team. The authors used over 150 separate Chandra observations spread over 13 years to obtain these results. These are stellar-mass black hole candidates, which are formed by the collapse of a massive star and typically have masses between five and 10 times that of the Sun. New techni ...
... by the same team. The authors used over 150 separate Chandra observations spread over 13 years to obtain these results. These are stellar-mass black hole candidates, which are formed by the collapse of a massive star and typically have masses between five and 10 times that of the Sun. New techni ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.