black hole
... Pulsars radiate their energy away quite rapidly; the radiation weakens and stops in a few tens of millions of years, making the neutron star virtually undetectable. Pulsars also will not be visible on Earth if their jets are not pointing our way. ...
... Pulsars radiate their energy away quite rapidly; the radiation weakens and stops in a few tens of millions of years, making the neutron star virtually undetectable. Pulsars also will not be visible on Earth if their jets are not pointing our way. ...
cassiopeia a - Chandra X
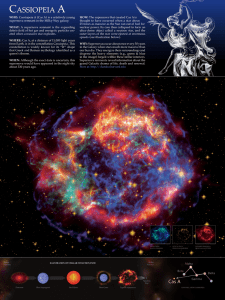
... that Greek and Roman mythology identified as a queen’s throne. WHEN: Although the exact date is uncertain, this supernova would have appeared in the night sky about 330 years ago. ...
... that Greek and Roman mythology identified as a queen’s throne. WHEN: Although the exact date is uncertain, this supernova would have appeared in the night sky about 330 years ago. ...
Big Bang Theory Scientific origin of the Universe
... How are distances in the universe measured? • Light-year – the distance that light travels in one year going at the speed of light • Speed of light – 300,000 km/second • Speed of light – 186, 000 miles/second • 9.5 trillion km in one year • Closest star (other that sun) is Proxima Centauri is 4.3 l ...
... How are distances in the universe measured? • Light-year – the distance that light travels in one year going at the speed of light • Speed of light – 300,000 km/second • Speed of light – 186, 000 miles/second • 9.5 trillion km in one year • Closest star (other that sun) is Proxima Centauri is 4.3 l ...
Scientific Results Summary
... One of the most globally exciting events, especially in the world of astronomy, was NASA’s Deep Impact Mission. Subaru and many other telescopes on Mauna Kea participated in the once-in-a-lifetime spectacle. On July 4th, a space probe impacted comet 9P/Tempel 1 with a huge chunk of copper traveling ...
... One of the most globally exciting events, especially in the world of astronomy, was NASA’s Deep Impact Mission. Subaru and many other telescopes on Mauna Kea participated in the once-in-a-lifetime spectacle. On July 4th, a space probe impacted comet 9P/Tempel 1 with a huge chunk of copper traveling ...
100 Greatest Discoveries in Science
... 10. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (1964) Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson discover cosmic microwave background radiation, which they suspect is the afterglow of the big bang. Their measurements, combined with Edwin Hubble's earlier finding that the galaxies are rushing away, make a strong case ...
... 10. Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (1964) Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson discover cosmic microwave background radiation, which they suspect is the afterglow of the big bang. Their measurements, combined with Edwin Hubble's earlier finding that the galaxies are rushing away, make a strong case ...
White Dwarf Stars - University of California Observatories
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
Unit 11 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 8. What is the relationship between a star’s temperature, luminosity, absolute magnitude and color? 9. How can parallax be used to determine the distance to stars? 10. Be able to use an H-R diagram to plot the temperature, absolute magnitude, and luminosity of a star. Be able to use an H-R diagram t ...
... 8. What is the relationship between a star’s temperature, luminosity, absolute magnitude and color? 9. How can parallax be used to determine the distance to stars? 10. Be able to use an H-R diagram to plot the temperature, absolute magnitude, and luminosity of a star. Be able to use an H-R diagram t ...
The “Big Bang” Theory
... • Our solar system, including the Earth, formed about 4.6 billion years ago. • That is about 10 billion years after the “Big Bang”. • Hominids (early ancestors of man) have only been around for about 3.6 million years and Homo sapiens for only about 200,000 years. ...
... • Our solar system, including the Earth, formed about 4.6 billion years ago. • That is about 10 billion years after the “Big Bang”. • Hominids (early ancestors of man) have only been around for about 3.6 million years and Homo sapiens for only about 200,000 years. ...
Notes: Astronomy and Groups of Stars
... -100’s of billions of stars - it takes 100,000 light years to travel across our galaxy - our galaxy revolves slowly (225 million years) as the stars orbit the center of the galaxy. - galaxies are also in clusters. Our cluster is called the Local Group (30 galaxies) patterns or picture of stars not b ...
... -100’s of billions of stars - it takes 100,000 light years to travel across our galaxy - our galaxy revolves slowly (225 million years) as the stars orbit the center of the galaxy. - galaxies are also in clusters. Our cluster is called the Local Group (30 galaxies) patterns or picture of stars not b ...
ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... Universe - http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/StarChild/universe_level2/universe.html Using the website find the following box and Click on the topics to find your answers: The Milky Way ...
... Universe - http://starchild.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/StarChild/universe_level2/universe.html Using the website find the following box and Click on the topics to find your answers: The Milky Way ...
deep space - altaastronomy
... • If they were stable they still would be very unpleasant to travel through. As you try to pass through the wormhole, you will get fried by X-rays and gamma rays. ...
... • If they were stable they still would be very unpleasant to travel through. As you try to pass through the wormhole, you will get fried by X-rays and gamma rays. ...
Neutron Stars, Relativity and Black Holes
... Einstein’s Theories of Relativity James Clerk Maxwell synthesized empirical formulas of electricity and magnetism into an electromagnetic theory. In 1865, he used his theory to show that light was an electromagnetic wave. In his theory, there was no provision for the speed of light to transform l ...
... Einstein’s Theories of Relativity James Clerk Maxwell synthesized empirical formulas of electricity and magnetism into an electromagnetic theory. In 1865, he used his theory to show that light was an electromagnetic wave. In his theory, there was no provision for the speed of light to transform l ...
Top 5 Optical Telescopes
... Located on La Palma Allowed the study of the nature of black holes, the formation history of stars and galaxies in the early universe, the physics of distant planets around other stars, and the nature of dark matter and dark energy in the universe Primary mirror consists of 36 individual hexag ...
... Located on La Palma Allowed the study of the nature of black holes, the formation history of stars and galaxies in the early universe, the physics of distant planets around other stars, and the nature of dark matter and dark energy in the universe Primary mirror consists of 36 individual hexag ...
combined astro show 2013
... The temperature of the gas, generally the spectral lines of various elements become more prominent at certain temperatures ...
... The temperature of the gas, generally the spectral lines of various elements become more prominent at certain temperatures ...
Ch. 22 (NS & BH
... Distance measurements of some gamma bursts shows them to be very far away – 2 billion parsecs for the first one measured. Occasionally the spectrum of a burst can be measured, allowing distance determination: ...
... Distance measurements of some gamma bursts shows them to be very far away – 2 billion parsecs for the first one measured. Occasionally the spectrum of a burst can be measured, allowing distance determination: ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #20 Key
... 14-3. How did Edwin Hubble prove that the Andromeda “Nebula” is not a nebula within our Milky Way Galaxy? Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared ...
... 14-3. How did Edwin Hubble prove that the Andromeda “Nebula” is not a nebula within our Milky Way Galaxy? Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared ...
Neutron Stars & Black Holes
... Distance measurements of some gamma bursts shows them to be very far away – 2 billion parsecs for the first one measured. Occasionally the spectrum of a burst can be measured, allowing distance determination: ...
... Distance measurements of some gamma bursts shows them to be very far away – 2 billion parsecs for the first one measured. Occasionally the spectrum of a burst can be measured, allowing distance determination: ...
Astronomy 1 Study Guide Key 16
... 7. A galaxy is a collection of stars. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way. 8. It has many solar systems with in its arms. At the center of our spiral galaxy is a black hole, so our galaxy is also called a quasar. Stars Be able to read an H-R diagram. ...
... 7. A galaxy is a collection of stars. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way. 8. It has many solar systems with in its arms. At the center of our spiral galaxy is a black hole, so our galaxy is also called a quasar. Stars Be able to read an H-R diagram. ...
Chapter 13 Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... Distance measurements of some gamma bursts show them to be very far away – 2 billion parsecs for the first one measured. Occasionally the spectrum of a burst can be measured, allowing distance determination: ...
... Distance measurements of some gamma bursts show them to be very far away – 2 billion parsecs for the first one measured. Occasionally the spectrum of a burst can be measured, allowing distance determination: ...
Galaxies and the Big Bang Theory
... A _______________ _________________ is a device used to detect long radio waves from objects in space. A ___________ is a huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity The three different types of galaxies that exist in our universe are: ...
... A _______________ _________________ is a device used to detect long radio waves from objects in space. A ___________ is a huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity The three different types of galaxies that exist in our universe are: ...
STAR SYTEMS AND GALAXIES
... • In a binary system usually one star is much brighter than the other. • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enoug ...
... • In a binary system usually one star is much brighter than the other. • We can detect binary systems easily if one star blocks another, called an eclipsing binary. • We have found planets moving around stars in other systems. We can only detect very large planets because the planets must have enoug ...
Observing: The process of using one or more of your senses to
... Quasar: An enormously bright, distant galaxy with a giant black hole at its center (p 617) Elliptical galaxy: A galaxy shaped like a round or flattened ball, generally containing only old stars (p 618) Binary star: A star system with 2 stars (p 615) Open cluster: A star cluster that has a loose, dis ...
... Quasar: An enormously bright, distant galaxy with a giant black hole at its center (p 617) Elliptical galaxy: A galaxy shaped like a round or flattened ball, generally containing only old stars (p 618) Binary star: A star system with 2 stars (p 615) Open cluster: A star cluster that has a loose, dis ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.