1.1 Stars in the Broader Context of Modern Astro
... by a gamma-ray burst (GRB) at redshift z ∼ 9.4. A gamma-ray burst is thought to mark the end of a massive and rapidly rotating star, when its core collapses directly into a black hole and two extremely energetic jets of plasma are emitted from its rotational poles at nearly the speed of light (see F ...
... by a gamma-ray burst (GRB) at redshift z ∼ 9.4. A gamma-ray burst is thought to mark the end of a massive and rapidly rotating star, when its core collapses directly into a black hole and two extremely energetic jets of plasma are emitted from its rotational poles at nearly the speed of light (see F ...
Chapter 7 Review Answers
... 13. It is unlikely that we will travel across even our own galaxy because it is 100,000 ly across, meaning that it would take 100,000 years travelling at the speed of light to get across the galaxy. 14.All galaxies with a high rate of production of stars have lots of dust and gas, which are the birt ...
... 13. It is unlikely that we will travel across even our own galaxy because it is 100,000 ly across, meaning that it would take 100,000 years travelling at the speed of light to get across the galaxy. 14.All galaxies with a high rate of production of stars have lots of dust and gas, which are the birt ...
Groups of Stars
... MOVING TOWARDS THE MILKY WAY, THEY WILL EVENTUALLY COLLIDE!!! This event will occur in about 5 billion years…) ...
... MOVING TOWARDS THE MILKY WAY, THEY WILL EVENTUALLY COLLIDE!!! This event will occur in about 5 billion years…) ...
Ch 28 Vocab cnp
... gravitational field so intense that not even light can escape A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky A distant neutron star that emits rapid pulses of light and radio waves instead of steady radiation The theory holding that the universe originated from the instant expansion of an ...
... gravitational field so intense that not even light can escape A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky A distant neutron star that emits rapid pulses of light and radio waves instead of steady radiation The theory holding that the universe originated from the instant expansion of an ...
Slide 1
... the Big Bang theory. For example, we tend to imagine a giant explosion. Experts however say that there was no explosion; there was (and continues to be) an expansion. Rather than imagining a balloon popping and releasing its contents, imagine a balloon expanding: an infinitesimally small balloon exp ...
... the Big Bang theory. For example, we tend to imagine a giant explosion. Experts however say that there was no explosion; there was (and continues to be) an expansion. Rather than imagining a balloon popping and releasing its contents, imagine a balloon expanding: an infinitesimally small balloon exp ...
Version presented at conference - DCC
... and numerical models predict nova-like transients from double neutron star and black hole/neutron star mergers [2]. GRB afterglows and supernovas are both well-studied phenomenon associated with gravitational radiation [3,4]. While GW and EM signals are expected to travel at the same speed, a common ...
... and numerical models predict nova-like transients from double neutron star and black hole/neutron star mergers [2]. GRB afterglows and supernovas are both well-studied phenomenon associated with gravitational radiation [3,4]. While GW and EM signals are expected to travel at the same speed, a common ...
Review Quiz No. 22
... the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a white dwarf. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a neutron star. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a black hole. a neutron star is tidally disrupted by a ...
... the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a white dwarf. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a neutron star. the iron core of a very massive star collapses to form a black hole. a neutron star is tidally disrupted by a ...
The Assembly of M31`s Halo from Dwarf Galaxy Building Blocks
... Studies of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation allow us to probe the properties of the Universe all the way back to Big Bang ...
... Studies of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation allow us to probe the properties of the Universe all the way back to Big Bang ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... Stars, Galaxies, and Constellations Stars = objects in space, made of gases, which produce their own light and heat. Earth’s nearest star is the sun (149,600,000 km away) The next nearest star is Proxima Centauri (4.24 light years away) Light year = the distance light travels in 1 year • Light trave ...
... Stars, Galaxies, and Constellations Stars = objects in space, made of gases, which produce their own light and heat. Earth’s nearest star is the sun (149,600,000 km away) The next nearest star is Proxima Centauri (4.24 light years away) Light year = the distance light travels in 1 year • Light trave ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... Some white dwarfs do not just cool and die. They will have one or more large explosions and become a nova A supernova is a star that has such a tremendous explosion that it blows itself apart. Before a supernova all of the stars elements will be fused into iron ...
... Some white dwarfs do not just cool and die. They will have one or more large explosions and become a nova A supernova is a star that has such a tremendous explosion that it blows itself apart. Before a supernova all of the stars elements will be fused into iron ...
Document
... The production of these jets is intricately linked to the rotation of the black hole and its surrounding accretion disk - the disk of material surrounding the black hole. Previous work has studied these systems where these two rotations were aligned. However, these simplified models cannot account f ...
... The production of these jets is intricately linked to the rotation of the black hole and its surrounding accretion disk - the disk of material surrounding the black hole. Previous work has studied these systems where these two rotations were aligned. However, these simplified models cannot account f ...
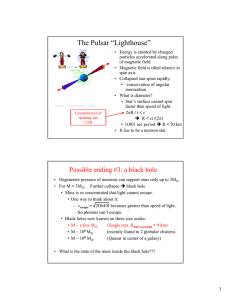
The Pulsar “Lighthouse”
... Hubble images of Planetary Nebulae These are former Red Giants, blowing away outer 25% of their mass because of intense energy production in middle layers of star. ...
... Hubble images of Planetary Nebulae These are former Red Giants, blowing away outer 25% of their mass because of intense energy production in middle layers of star. ...
Poster VLF GRBs - INFN-LNF
... This is ideal number, the real one is less than 10 due to occassional nonavailability of transmitters and other technical and observational issues. ...
... This is ideal number, the real one is less than 10 due to occassional nonavailability of transmitters and other technical and observational issues. ...
PARTS OF THE UNIVERSE
... v Parallax: apparent shift in the position of an object when view from two different locations. v Parallax Example v Can be used to measure the distance of stars from Earth that are relatively close. v Proxima Centauri: closest star to earth v (4.3 light years away – 40 trillion km) ...
... v Parallax: apparent shift in the position of an object when view from two different locations. v Parallax Example v Can be used to measure the distance of stars from Earth that are relatively close. v Proxima Centauri: closest star to earth v (4.3 light years away – 40 trillion km) ...
2014 Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. 1 Astro 113 Final Exam Review 1. What
... 25. An object at room temperature (T = 300 degrees Kelvin) emits blackbody radiation at primarily what wavelength? An object at T = 106 degrees Kelvin? 26. Are galaxies distributed evenly through sp ...
... 25. An object at room temperature (T = 300 degrees Kelvin) emits blackbody radiation at primarily what wavelength? An object at T = 106 degrees Kelvin? 26. Are galaxies distributed evenly through sp ...
PPT - LSC
... • 100,000 mass of neutron stars and black holes • Direct measurement of the acceleration of the universe • Background gravitational waves • Other sources such as IMBH……. • The angular position and the time of the coalescence a week before with 10arcsec and 0.01 sec accuracy • Point all possible dete ...
... • 100,000 mass of neutron stars and black holes • Direct measurement of the acceleration of the universe • Background gravitational waves • Other sources such as IMBH……. • The angular position and the time of the coalescence a week before with 10arcsec and 0.01 sec accuracy • Point all possible dete ...
Gravitational Wave Astronomy using 0.1Hz space laser interferometer
... • 100,000 mass of neutron stars and black holes • Direct measurement of the acceleration of the universe • Background gravitational waves • Other sources such as IMBH……. • The angular position and the time of the coalescence a week before with 10arcsec and 0.01 sec accuracy • Point all possible dete ...
... • 100,000 mass of neutron stars and black holes • Direct measurement of the acceleration of the universe • Background gravitational waves • Other sources such as IMBH……. • The angular position and the time of the coalescence a week before with 10arcsec and 0.01 sec accuracy • Point all possible dete ...
Neutron Stars
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) ...
... If initial star mass < 8 MSun or so. (and remember: Maximum WD mass is 1.4 MSun , radius is about that of the Earth) ...
15.4 Star Systems and Galaxies
... I. Star Systems and Planets A. Star system-groups of two or more stars 1. Binary stars - two stars or double stars a. Eclipsing binary-a system in which one star blocks the light from another II. Planets Around Other Stars A. Astronomers study gravitational effects on stars to see if there is a pla ...
... I. Star Systems and Planets A. Star system-groups of two or more stars 1. Binary stars - two stars or double stars a. Eclipsing binary-a system in which one star blocks the light from another II. Planets Around Other Stars A. Astronomers study gravitational effects on stars to see if there is a pla ...
Watch the episode titled “The Milky Way” from the series “The
... our galaxy? What do astronomers think came first, the galaxy or the black hole? Besides being sucked into the black hole, what else is happening at the edges of a black hole? Once formed at the edge of a black hole, what is likely to happen to that star? About how many times has our solar system bee ...
... our galaxy? What do astronomers think came first, the galaxy or the black hole? Besides being sucked into the black hole, what else is happening at the edges of a black hole? Once formed at the edge of a black hole, what is likely to happen to that star? About how many times has our solar system bee ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.