Chapter 8, Lesson 5, pdf
... • The heated gases of stars produce light. • As light passes through a star’s outer atmosphere, some of the light is absorbed by the stars atmosphere. • When scientists look at a spectrum of this starlight, they see that the absorbed light has “dropped out” of the spectrum, forming dark lines calle ...
... • The heated gases of stars produce light. • As light passes through a star’s outer atmosphere, some of the light is absorbed by the stars atmosphere. • When scientists look at a spectrum of this starlight, they see that the absorbed light has “dropped out” of the spectrum, forming dark lines calle ...
Post-class version
... Your report will be due at the final exam, Wednesday, April 30. Not required if you have already been to Brooks this semester & written a report. As before, take elevator to 5th floor of this building, walk up to 6th floor. Bring your blue ticket with your name and my name (Nancy Morrison) written o ...
... Your report will be due at the final exam, Wednesday, April 30. Not required if you have already been to Brooks this semester & written a report. As before, take elevator to 5th floor of this building, walk up to 6th floor. Bring your blue ticket with your name and my name (Nancy Morrison) written o ...
Name
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun C) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun C) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
Name - MIT
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun C) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun C) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
Name
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere C) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
... A) The rate that visible light from the Sun is being absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere B) The rate that gamma rays are hitting the Earth’s atmosphere C) The rate that hydrogen is being fused into helium in the Sun D) The rate that white dwarfs are being formed in the galaxy E) The rate that stars f ...
Core-collapse supernovae and their massive progenitors
... constrain the explosion models and determine if there is any link between the explosion mechanism and mass of the star. There are peculiar Type II-P SNe that have distinctly lower luminosities and kinetic energies (measured by the expansion velocity of the ejecta) than normal (Pastorello et al. 2004 ...
... constrain the explosion models and determine if there is any link between the explosion mechanism and mass of the star. There are peculiar Type II-P SNe that have distinctly lower luminosities and kinetic energies (measured by the expansion velocity of the ejecta) than normal (Pastorello et al. 2004 ...
Where do you find yourself now??
... -from which the spiral arm gets its name. All of these stars are bright giant and supergiant -stars, thousands of times more luminous than the Sun. The most luminous star on the map -is Rho Cassiopeia - to us 4000 light years away, it is a dim naked eye star, but in reality -it is a huge supergiant ...
... -from which the spiral arm gets its name. All of these stars are bright giant and supergiant -stars, thousands of times more luminous than the Sun. The most luminous star on the map -is Rho Cassiopeia - to us 4000 light years away, it is a dim naked eye star, but in reality -it is a huge supergiant ...
Document
... • Gravitational tides pull matter off big low density objects towards small high density objects. ...
... • Gravitational tides pull matter off big low density objects towards small high density objects. ...
talk - University of Southampton
... For the perfectly conducting case with insignificant inertia of plasma the magnetosphere is described by Magnetodynamics (MD -- inertia-free ...
... For the perfectly conducting case with insignificant inertia of plasma the magnetosphere is described by Magnetodynamics (MD -- inertia-free ...
3A8d
... (that can include the Milky Way), which provide empirical support for the hierarchical assembly of galaxies. Exclude the obvious one, i.e. the observation of occasional instances of galaxies merging at the present time. In each case explain why the same observations are not as readily understood in ...
... (that can include the Milky Way), which provide empirical support for the hierarchical assembly of galaxies. Exclude the obvious one, i.e. the observation of occasional instances of galaxies merging at the present time. In each case explain why the same observations are not as readily understood in ...
$doc.title
... much of the nature of the visible universe. Nuclear fusion is the engine of stars; it produces the energy that stabilizes them against gravitaBonal collapse and makes them shine. Spectacular stellar ex ...
... much of the nature of the visible universe. Nuclear fusion is the engine of stars; it produces the energy that stabilizes them against gravitaBonal collapse and makes them shine. Spectacular stellar ex ...
SWFAS Apr 16 Newsletter - Southwest Florida Astronomical Society
... Great Comet of 1811. Hale–Bopp was discovered on July 23, 1995, at a great distance from the Sun, raising expectations that the comet would brighten considerably by the time it passed close to Earth. Although predicting the brightness of comets with any degree of accuracy is very difficult, Hale–Bop ...
... Great Comet of 1811. Hale–Bopp was discovered on July 23, 1995, at a great distance from the Sun, raising expectations that the comet would brighten considerably by the time it passed close to Earth. Although predicting the brightness of comets with any degree of accuracy is very difficult, Hale–Bop ...
School Supplies - Rowan County Schools
... According to Hubble’s Law, galaxies are moving _____ from one another. ...
... According to Hubble’s Law, galaxies are moving _____ from one another. ...
ppt
... Some Facts of Our Milky Way Galaxy • Distance from Sun to galactic center = 8 kpc ± 1 kpc • Disk of our galaxy = 50 kpc diameter, 0.6 kpc thick, with a central bar-shaped bulge • Central bulge is 2 kpc in diameter(has both Pop I and Pop II stars) • Sun orbits center of galaxy at 790,000 km/hr, take ...
... Some Facts of Our Milky Way Galaxy • Distance from Sun to galactic center = 8 kpc ± 1 kpc • Disk of our galaxy = 50 kpc diameter, 0.6 kpc thick, with a central bar-shaped bulge • Central bulge is 2 kpc in diameter(has both Pop I and Pop II stars) • Sun orbits center of galaxy at 790,000 km/hr, take ...
universe.pps - Prophet Muhammad For All
... -from which the spiral arm gets its name. All of these stars are bright giant and supergiant -stars, thousands of times more luminous than the Sun. The most luminous star on the map -is Rho Cassiopeia - to us 4000 light years away, it is a dim naked eye star, but in reality -it is a huge supergiant ...
... -from which the spiral arm gets its name. All of these stars are bright giant and supergiant -stars, thousands of times more luminous than the Sun. The most luminous star on the map -is Rho Cassiopeia - to us 4000 light years away, it is a dim naked eye star, but in reality -it is a huge supergiant ...
9. Fascinating observations. But how much is well understood?
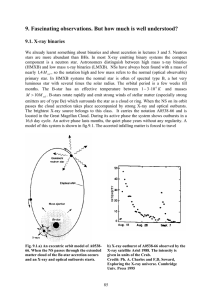
... sources which undergo repeted bursting of subsecond duration. Sometimes they exhibit luminous superflares lasting some 100 seconds but their repetition has not yet been observed. The other class of high field objects are the Anomalous X-ray Pulsars (AXP).They were discovered as pulsating X-ray sourc ...
... sources which undergo repeted bursting of subsecond duration. Sometimes they exhibit luminous superflares lasting some 100 seconds but their repetition has not yet been observed. The other class of high field objects are the Anomalous X-ray Pulsars (AXP).They were discovered as pulsating X-ray sourc ...
HighRedshiftGalaxies
... young and old stellar populations emphasizes the relatively weak connection between stellar mass and light and implies there may be significant uncertainties in the estimation of integrated luminosity densities for star-forming populations. Clearly a major uncertainty in any transformation based o ...
... young and old stellar populations emphasizes the relatively weak connection between stellar mass and light and implies there may be significant uncertainties in the estimation of integrated luminosity densities for star-forming populations. Clearly a major uncertainty in any transformation based o ...
Stars_Galaxies_Introduction - Etiwanda E
... question to each group Project may still include typical science assignments/routines Incorporates technology at many different levels Students are able to differentiate within the project by choice of assignment ...
... question to each group Project may still include typical science assignments/routines Incorporates technology at many different levels Students are able to differentiate within the project by choice of assignment ...
What does X-ray light show us?
... Gamma-ray astronomy presents unique opportunities to explore these exotic objects. By exploring the universe at these high energies, scientists can search for new physics, testing theories and performing experiments which are not possible in earthbound laboratories. ...
... Gamma-ray astronomy presents unique opportunities to explore these exotic objects. By exploring the universe at these high energies, scientists can search for new physics, testing theories and performing experiments which are not possible in earthbound laboratories. ...
Multi-Wavelength Observations of Known, and Searches
... HMXBs containing neutron stars may begin as gamma-ray binaries with furiously rotating neutron stars before spinning down. ...
... HMXBs containing neutron stars may begin as gamma-ray binaries with furiously rotating neutron stars before spinning down. ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.