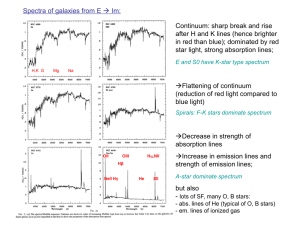
Our Universe
... •Our Sun has around 5 Billion years remaining. It is predicted to only exist for 10 Billion total years. ...
... •Our Sun has around 5 Billion years remaining. It is predicted to only exist for 10 Billion total years. ...
5X_Measuring_galaxy_redshifts
... wavelength’, such that the Doppler shift is the same for all channels. Largescale variations are then filtered out (i.e. only spectral lines left). The spectrum is then ‘slid’ against a template prepared from a known bright galaxy or star, and a correlation function derived. The peaks in the functio ...
... wavelength’, such that the Doppler shift is the same for all channels. Largescale variations are then filtered out (i.e. only spectral lines left). The spectrum is then ‘slid’ against a template prepared from a known bright galaxy or star, and a correlation function derived. The peaks in the functio ...
Quasars - Ann Arbor Earth Science
... emission lines. On closer inspection it is a galaxy, usually a spiral or disturbed system, whose strong emission lines are too broad and of ionization too high to be produced by the galaxy's stellar population. In type 1 Seyferts, some of the emission lines, those that can be produced at high densit ...
... emission lines. On closer inspection it is a galaxy, usually a spiral or disturbed system, whose strong emission lines are too broad and of ionization too high to be produced by the galaxy's stellar population. In type 1 Seyferts, some of the emission lines, those that can be produced at high densit ...
U7 Review WS KEY
... b. because every chemical element has a characteristic spectrum c. because chemical elements do not have characteristic spectra d. because colors and lines in the spectrum of stars are all the same How bright a star appears as seen from Earth is called _absolute magnitude_ . Astronomers use _lig ...
... b. because every chemical element has a characteristic spectrum c. because chemical elements do not have characteristic spectra d. because colors and lines in the spectrum of stars are all the same How bright a star appears as seen from Earth is called _absolute magnitude_ . Astronomers use _lig ...
Stars and Galaxies - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... scale up and use meters and kilometers for large numbers. ...
... scale up and use meters and kilometers for large numbers. ...
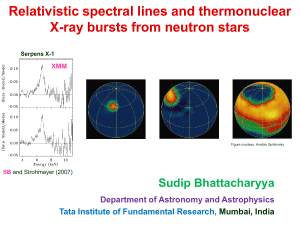
Broad Relativistic Iron Lines from Neutron Star LMXBs
... (2) Full LAXPC area is important to increase the signal-to-noise for both burst oscillations and X-ray spectrum. Note that RXTE-PCA operated with much lesser area during most of its lifetime. (3) Most promising sources are known from RXTE observations. (4) Astrosat will model the burst and non-burst ...
... (2) Full LAXPC area is important to increase the signal-to-noise for both burst oscillations and X-ray spectrum. Note that RXTE-PCA operated with much lesser area during most of its lifetime. (3) Most promising sources are known from RXTE observations. (4) Astrosat will model the burst and non-burst ...
r*=13.6 km MPA1 EOS
... Denis A. Leahy, Sharon M. Morsink and Yi Chou The accreting millisecond pulsar XTE J1807-294 is studied through a pulse-shape modeling analysis. The model includes blackbody and Comptonized emission from the one visible hot spot and makes use of the Oblate Schwarzschild approximation for ray-tracing ...
... Denis A. Leahy, Sharon M. Morsink and Yi Chou The accreting millisecond pulsar XTE J1807-294 is studied through a pulse-shape modeling analysis. The model includes blackbody and Comptonized emission from the one visible hot spot and makes use of the Oblate Schwarzschild approximation for ray-tracing ...
Wavelength
... • 2. Elliptical: oldest & largest galaxies, smooth & oval shaped • 3. Irregular: don’t have a distinct shape, may be young galaxies that haven’t formed or 2 gal. colliding ...
... • 2. Elliptical: oldest & largest galaxies, smooth & oval shaped • 3. Irregular: don’t have a distinct shape, may be young galaxies that haven’t formed or 2 gal. colliding ...
The Milky Way – A Classic Galaxy
... telescope in the 1920’s to image The Andromeda Nebula • Could see the brightest individual stars. Among them, variables of the right color and light variation to show them as Cepheids • Therefore, this was not a nearby nebula around a new star, it was an entire galaxy. • Herschel’s map then could be ...
... telescope in the 1920’s to image The Andromeda Nebula • Could see the brightest individual stars. Among them, variables of the right color and light variation to show them as Cepheids • Therefore, this was not a nearby nebula around a new star, it was an entire galaxy. • Herschel’s map then could be ...
Ch 3 Sec 1 Tools of modern astronomy
... dwarf. It’s called a neutron star. May be 3X as massive as our sum, but only 20 km across D. The biggest stars, more than 40X the sun, leave behind a black hole 1. There is no hole – it just looks like one 2. The star is so massive that its gravity is extremely high and nothing, not even light, can ...
... dwarf. It’s called a neutron star. May be 3X as massive as our sum, but only 20 km across D. The biggest stars, more than 40X the sun, leave behind a black hole 1. There is no hole – it just looks like one 2. The star is so massive that its gravity is extremely high and nothing, not even light, can ...
Chapter14- Our Galaxy - SFA Physics and Astronomy
... The Milky Way’s Rotation Curve is flat, indicating that the Milky Way’s mass is not concentrated in the center bulge This implies the existence of “Dark Matter” ...
... The Milky Way’s Rotation Curve is flat, indicating that the Milky Way’s mass is not concentrated in the center bulge This implies the existence of “Dark Matter” ...
A-105 Homework 1
... Ch. 11 - Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes - 31 points 1. (4 pts.) You learned about white dwarfs in Ch. 10. Compare the masses and radii of white dwarfs and neutron stars and state what supports each from further collapse. ...
... Ch. 11 - Neutron Stars, Pulsars, and Black Holes - 31 points 1. (4 pts.) You learned about white dwarfs in Ch. 10. Compare the masses and radii of white dwarfs and neutron stars and state what supports each from further collapse. ...
ppt
... Spectra does not seem to be identical to the identified pulsars High galactic diffuse background make analysis difficult ...
... Spectra does not seem to be identical to the identified pulsars High galactic diffuse background make analysis difficult ...
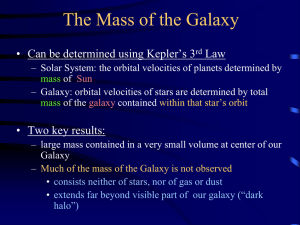
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
... – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
Space ppt
... Types of Galaxies • Galaxies are classified by their shape. • Developed by Edwin Hubble • 3 Types of Galaxies – A. Spiral – B. Elliptical – C. Irregular ...
... Types of Galaxies • Galaxies are classified by their shape. • Developed by Edwin Hubble • 3 Types of Galaxies – A. Spiral – B. Elliptical – C. Irregular ...
Practice Questions for Final
... B. A spaceship passing near a 10 solar mass black hole is much more likely to be destroyed than a spaceship passing at the same distance from the center of a 10 solar mass mainsequence star. C. If you watch someone else fall into a black hole, you will never see them cross the event horizon. However ...
... B. A spaceship passing near a 10 solar mass black hole is much more likely to be destroyed than a spaceship passing at the same distance from the center of a 10 solar mass mainsequence star. C. If you watch someone else fall into a black hole, you will never see them cross the event horizon. However ...
6th Grade Science Chapter 19 Jeopardy Game
... they are very similar to early galaxies. b. Distant galaxies share many characteristics with early galaxies. c. Distant galaxies have not changed as much as close galaxies, so they are most similar to early galaxies. d. Because it takes a long time for light to travel through space, looking at dista ...
... they are very similar to early galaxies. b. Distant galaxies share many characteristics with early galaxies. c. Distant galaxies have not changed as much as close galaxies, so they are most similar to early galaxies. d. Because it takes a long time for light to travel through space, looking at dista ...
Due: January 15, 2014 Name
... c. the influence of their intense gravitational field on atoms and molecules that are emitting light from the event horizons of the black holes. d. their gravitational influence on nearby matter, particularly companion stars. 13. The physical properties of a black hole that allow it to interact with ...
... c. the influence of their intense gravitational field on atoms and molecules that are emitting light from the event horizons of the black holes. d. their gravitational influence on nearby matter, particularly companion stars. 13. The physical properties of a black hole that allow it to interact with ...
What is the net result of the proton-proton chain? a. 2 protons make
... What are the two most important intrinsic properties used to classify stars: a. Mass and age b. Luminosity and surface temperature c. Distance and luminosity d. Distance and surface temperature e. Distance and color Stars that have masses similar to the Sun and sizes similar to the Earth are: a. Mai ...
... What are the two most important intrinsic properties used to classify stars: a. Mass and age b. Luminosity and surface temperature c. Distance and luminosity d. Distance and surface temperature e. Distance and color Stars that have masses similar to the Sun and sizes similar to the Earth are: a. Mai ...
Multi-wavelength Astronomy Multi
... But modern astrophysics requires studying an object across the whole EM spectrum Different physical processes can be studied at different wavelengths X-ray, gamma ray and radio astronomers need to identify their sources with optical counterparts ...
... But modern astrophysics requires studying an object across the whole EM spectrum Different physical processes can be studied at different wavelengths X-ray, gamma ray and radio astronomers need to identify their sources with optical counterparts ...
X Ray Astronomy
... • As the detectors can tell when each photon hit, it is trivial to see if a sources' emission is varying in time. In the case of a stellar X-ray source, an X-ray binary for example, or the emission from an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN), this is useful to show the orbital period of the source (or par ...
... • As the detectors can tell when each photon hit, it is trivial to see if a sources' emission is varying in time. In the case of a stellar X-ray source, an X-ray binary for example, or the emission from an Active Galactic Nucleus (AGN), this is useful to show the orbital period of the source (or par ...
After Dark M S
... and a second exploding in the Pinwheel Galaxy, M101, toward the end of August. Though both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of a massive star. The supernova in M101 may mark the death of a white dwarf star in a binar ...
... and a second exploding in the Pinwheel Galaxy, M101, toward the end of August. Though both are supernovas, the natures of these two exploding stars are very different. The supernova in M51 may mark the death of a massive star. The supernova in M101 may mark the death of a white dwarf star in a binar ...
The Death of Stars
... Supernova 1987A (Type II) • Nearby! Only 170,000 light years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud (a small “satellite” galaxy of the Milky Way). • It initially was a 20 Msun star (but blue supergiant, NOT red -- this is a mystery, is it because of the low metallicity? Perhaps it was two stars merging ...
... Supernova 1987A (Type II) • Nearby! Only 170,000 light years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud (a small “satellite” galaxy of the Milky Way). • It initially was a 20 Msun star (but blue supergiant, NOT red -- this is a mystery, is it because of the low metallicity? Perhaps it was two stars merging ...
Extragalactic AO Science
... reduce throughput further making it difficult to observe faint extended sources. Normal galaxy disks only achieve a maximum SB of K~16 mag/sq arcsec and this fades as (1+z)4. This means all normal disks are fainter than 22.5 mag within 0.05x0.05”. ...
... reduce throughput further making it difficult to observe faint extended sources. Normal galaxy disks only achieve a maximum SB of K~16 mag/sq arcsec and this fades as (1+z)4. This means all normal disks are fainter than 22.5 mag within 0.05x0.05”. ...
Gamma-ray burst

Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are flashes of gamma rays associated with extremely energetic explosions that have been observed in distant galaxies. They are the brightest electromagnetic events known to occur in the universe. Bursts can last from ten milliseconds to several hours. The initial burst is usually followed by a longer-lived ""afterglow"" emitted at longer wavelengths (X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, infrared, microwave and radio).Most observed GRBs are believed to consist of a narrow beam of intense radiation released during a supernova or hypernova as a rapidly rotating, high-mass star collapses to form a neutron star, quark star, or black hole. A subclass of GRBs (the ""short"" bursts) appear to originate from a different process – this may be due to the merger of binary neutron stars. The cause of the precursor burst observed in some of these short events may be due to the development of a resonance between the crust and core of such stars as a result of the massive tidal forces experienced in the seconds leading up to their collision, causing the entire crust of the star to shatter.The sources of most GRBs are billions of light years away from Earth, implying that the explosions are both extremely energetic (a typical burst releases as much energy in a few seconds as the Sun will in its entire 10-billion-year lifetime) and extremely rare (a few per galaxy per million years). All observed GRBs have originated from outside the Milky Way galaxy, although a related class of phenomena, soft gamma repeater flares, are associated with magnetars within the Milky Way. It has been hypothesized that a gamma-ray burst in the Milky Way, pointing directly towards the Earth, could cause a mass extinction event.GRBs were first detected in 1967 by the Vela satellites, a series of satellites designed to detect covert nuclear weapons tests. Hundreds of theoretical models were proposed to explain these bursts in the years following their discovery, such as collisions between comets and neutron stars. Little information was available to verify these models until the 1997 detection of the first X-ray and optical afterglows and direct measurement of their redshifts using optical spectroscopy, and thus their distances and energy outputs. These discoveries, and subsequent studies of the galaxies and supernovae associated with the bursts, clarified the distance and luminosity of GRBs. These facts definitively placed them in distant galaxies and also connected long GRBs with the explosion of massive stars, the only possible source for the energy outputs observed.