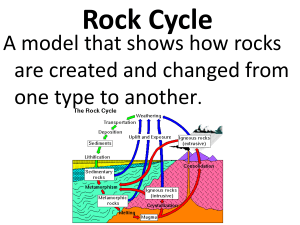
The Rock Cycle
... deposition, compaction and lithification of sediment. Can be melted to form magma. Can be eroded to form sediment. ...
... deposition, compaction and lithification of sediment. Can be melted to form magma. Can be eroded to form sediment. ...
Science Chapter 4 Study Guide Vocabulary
... Sedimentary Rocks—rocks made of sand or sediment and is pressed into layers. This would be a good place to find a fossil. (ex. Sandstone, shale) Igneous Rocks—made from melted rock from a volcano that has cooled (ex. granite) Metamorphic Rocks—made through the process of heating or squeezing (ex. sl ...
... Sedimentary Rocks—rocks made of sand or sediment and is pressed into layers. This would be a good place to find a fossil. (ex. Sandstone, shale) Igneous Rocks—made from melted rock from a volcano that has cooled (ex. granite) Metamorphic Rocks—made through the process of heating or squeezing (ex. sl ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... How are rocks different from minerals? Definition of Mineral: 1. Naturally occurring 2. Solid substance 3. Orderly crystalline structure ...
... How are rocks different from minerals? Definition of Mineral: 1. Naturally occurring 2. Solid substance 3. Orderly crystalline structure ...
Researchers find oldest rocks on Earth
... composition of the rare earth elements neodymium and samarium in the rocks, O'Neil and Carlson determined that the rock samples range from 3.8 to 4.28 billion years old. The oldest dates came from rocks termed "faux amphibolite," which the researchers interpret to be ancient volcanic ...
... composition of the rare earth elements neodymium and samarium in the rocks, O'Neil and Carlson determined that the rock samples range from 3.8 to 4.28 billion years old. The oldest dates came from rocks termed "faux amphibolite," which the researchers interpret to be ancient volcanic ...
Hadean plate tectonics
... MORB and suggest a pure solar component in the lower mantle (Earth is chondritic not solar). Solution of this paradox lies in accumulation of solar wind exposed regolith on a long-lived basaltic crust eventually tranferred to an isolated (?) deep mantle reservoir . ...
... MORB and suggest a pure solar component in the lower mantle (Earth is chondritic not solar). Solution of this paradox lies in accumulation of solar wind exposed regolith on a long-lived basaltic crust eventually tranferred to an isolated (?) deep mantle reservoir . ...
Heat From the outer core causes convection currents in the semi
... Heat From the outer core causes convection currents in the semi-liquid mantle. These currents cause the crust, floating on top of the mantle, to move. ...
... Heat From the outer core causes convection currents in the semi-liquid mantle. These currents cause the crust, floating on top of the mantle, to move. ...
Rock Cycle
... weight and takes up space. (noun) Examples of products of the rock cycle: Magma Sedimentary rock ...
... weight and takes up space. (noun) Examples of products of the rock cycle: Magma Sedimentary rock ...
Section 7.3 Student note
... -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock -figur ...
... -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock -figur ...
ROCKS AND MINERALS
... COLOR - INHERENT OR EXOTIC STREAK - AFTER RUBBING MINERAL ACROSS A PORCELAIN PLATE THE LEFTOVER POWDER RESIDUE ...
... COLOR - INHERENT OR EXOTIC STREAK - AFTER RUBBING MINERAL ACROSS A PORCELAIN PLATE THE LEFTOVER POWDER RESIDUE ...
Directed Reading C14.1 and C14.2
... What is formed when oceanic plates move away from one another and magma rises from the cracks? ...
... What is formed when oceanic plates move away from one another and magma rises from the cracks? ...
Geology of Planet Earth
... 17. Describe the mineral composition and grain size of these three igneous rocks : granite, gabbro, diorite. ...
... 17. Describe the mineral composition and grain size of these three igneous rocks : granite, gabbro, diorite. ...
Week 11 – SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
... iii. Organic debris: Broken up shells or decaying plant matter b. Sediment is produced by the UPLIFT, WEATHERING & EROSION of other rocks (yellow arrows in diagram above). c. The type and size of the sediment controls the texture of the rock. ...
... iii. Organic debris: Broken up shells or decaying plant matter b. Sediment is produced by the UPLIFT, WEATHERING & EROSION of other rocks (yellow arrows in diagram above). c. The type and size of the sediment controls the texture of the rock. ...
ROCKS AND MINERALS
... COLOR - INHERENT OR EXOTIC STREAK - AFTER RUBBING MINERAL ACROSS A PORCELAIN PLATE THE LEFTOVER POWDER RESIDUE ...
... COLOR - INHERENT OR EXOTIC STREAK - AFTER RUBBING MINERAL ACROSS A PORCELAIN PLATE THE LEFTOVER POWDER RESIDUE ...
Minerals, Rocks and Resources
... • Minerals can be tested by scratching the unknown mineral with the edge or point of other materials of known harness ...
... • Minerals can be tested by scratching the unknown mineral with the edge or point of other materials of known harness ...
Science Project – October – OUR PLANET
... Students will demonstrate their knowledge of these three scientific concepts by developing a presentation which demonstrates the integration of how these three concepts work together on our planet. With all projects during the year the “format” or “display” is up to the individual student. All stude ...
... Students will demonstrate their knowledge of these three scientific concepts by developing a presentation which demonstrates the integration of how these three concepts work together on our planet. With all projects during the year the “format” or “display” is up to the individual student. All stude ...
Earth and atmosphere Topic Checklist
... structure of the earth consists of the crust, mantle and core surrounded by the atmosphere The crust is a thin layer of rock The lithosphere, the crust and upper mantle, consists of separates pieces called tectonic plates. Rocks in the Earth’s crust provide many useful substances. The atmosphere is ...
... structure of the earth consists of the crust, mantle and core surrounded by the atmosphere The crust is a thin layer of rock The lithosphere, the crust and upper mantle, consists of separates pieces called tectonic plates. Rocks in the Earth’s crust provide many useful substances. The atmosphere is ...
ROCKS AND MINERALS STUDY GUIDE Classification of Rocks
... ROCKS AND MINERALS STUDY GUIDE 3 Types of Rocks 1. Igneous rocks are formed from lava and magma that has cooled. Lava is outside the earth. Magma is inside the earth. 2. Metamorphic rocks are formed from HEAT and pressure. a. Igneous and Sedimentary rocks can change into metamorphic rocks. 3. Sedim ...
... ROCKS AND MINERALS STUDY GUIDE 3 Types of Rocks 1. Igneous rocks are formed from lava and magma that has cooled. Lava is outside the earth. Magma is inside the earth. 2. Metamorphic rocks are formed from HEAT and pressure. a. Igneous and Sedimentary rocks can change into metamorphic rocks. 3. Sedim ...
Pre-lithification tectonic foliation development in a clastic
... in sedimentary rocks is that it postdates lithification of those rocks. It is well established that fabric development under these circumstances is achieved by a combination of grain rigid body rotation, crystal-plastic deformation and pressure solution. The latter is believed to be the primary mech ...
... in sedimentary rocks is that it postdates lithification of those rocks. It is well established that fabric development under these circumstances is achieved by a combination of grain rigid body rotation, crystal-plastic deformation and pressure solution. The latter is believed to be the primary mech ...
metamorphic rocks 6-2
... Classification of Metamorphic Rocks Only 2 choices: • Foliate – Similar to layers – Also called “banding” ...
... Classification of Metamorphic Rocks Only 2 choices: • Foliate – Similar to layers – Also called “banding” ...
Minerals
... pressure change size, shape, texture and even mineral content due to chemical reactions. ...
... pressure change size, shape, texture and even mineral content due to chemical reactions. ...
Dual Credit Major Topics for Studying
... Earth’s structure: Layers and properties (i.e. crust, mantle core) Names of plates Continental Drift Types of volcanoes; magma types (felsic and maffic) Features of volcanoes Lava types Seismic waves, earthquakes liquefaction 2004 tsunami Rocks and Minerals Types of rocks and roc ...
... Earth’s structure: Layers and properties (i.e. crust, mantle core) Names of plates Continental Drift Types of volcanoes; magma types (felsic and maffic) Features of volcanoes Lava types Seismic waves, earthquakes liquefaction 2004 tsunami Rocks and Minerals Types of rocks and roc ...
how the rock was formed
... some contain several different minerals About 20 minerals make up most of the Earth’s crust; these minerals are known as rockforming minerals ...
... some contain several different minerals About 20 minerals make up most of the Earth’s crust; these minerals are known as rockforming minerals ...
Provenance (geology)

Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the history of sediments movements over time. The Earth is not a static but a dynamic planet, all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types, which are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks (the rock cycle). Rocks exposed to the surface, sooner or later, are broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosion history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.