Unpacking the Standards
... c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosio ...
... c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosio ...
Chapter 13: Introduction to Landform Study
... components of structure and process 4. drainage: movement of water either over Earth’s surface or down into the soil and bedrock V. Internal and External Geomorphic Processes A. internal processes 1. fueled by internal heat 2. result in crustal movements of various kinds 3. constructive, uplifting, ...
... components of structure and process 4. drainage: movement of water either over Earth’s surface or down into the soil and bedrock V. Internal and External Geomorphic Processes A. internal processes 1. fueled by internal heat 2. result in crustal movements of various kinds 3. constructive, uplifting, ...
Chapter 9: Earth`s Changing Surface
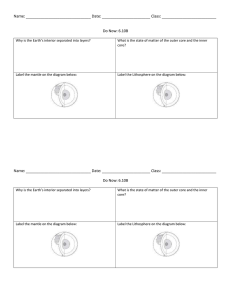
... 1. The inner core is solid and the outer core is liquid. 2. This liquid moves in currents, which make Earth’s magnetic field. Lesson 2: What causes earthquakes and volcanoes? Earth’s Plates a. The lithosphere is broken into small and large sections called plates. 1. All sections meet at plate bounda ...
... 1. The inner core is solid and the outer core is liquid. 2. This liquid moves in currents, which make Earth’s magnetic field. Lesson 2: What causes earthquakes and volcanoes? Earth’s Plates a. The lithosphere is broken into small and large sections called plates. 1. All sections meet at plate bounda ...
Question (1) (25 marks) State whether the following statements are
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
Name: Date: Class: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date: Pod: Name: Date
... 2. In order for a rock to be classified as igneous, what must have happened during its formation? a. Solid rock changing under pressure b. Liquid rock changing its physical state. c. Small rocks becoming cemented together. d. Layered rocks breaking into smaller pieces. 3. Sedimentary rocks often con ...
... 2. In order for a rock to be classified as igneous, what must have happened during its formation? a. Solid rock changing under pressure b. Liquid rock changing its physical state. c. Small rocks becoming cemented together. d. Layered rocks breaking into smaller pieces. 3. Sedimentary rocks often con ...
GEOL 1403 Physical Geology Lecture Topics
... This course is designed to introduce the science of geology, emphasizing plate tectonics, rocks, minerals, geological processes, structural geology, and landforms. The following is a list of topics that should be covered as part of the lecture component of the course. Please refer to the GEOL 1403 P ...
... This course is designed to introduce the science of geology, emphasizing plate tectonics, rocks, minerals, geological processes, structural geology, and landforms. The following is a list of topics that should be covered as part of the lecture component of the course. Please refer to the GEOL 1403 P ...
Essential Questions: February 13-17, 2017 Name: Date: Period
... c. continental drift 4Earthquakes are a sudden motion caused by movement of tectonic plates working against a. friction b. gravity c. magnetic forces 5When an oceanic plate slides under a continental plate, what is usually formed? a. continental drift b. seafloor spreading c. subduction zone 6At wha ...
... c. continental drift 4Earthquakes are a sudden motion caused by movement of tectonic plates working against a. friction b. gravity c. magnetic forces 5When an oceanic plate slides under a continental plate, what is usually formed? a. continental drift b. seafloor spreading c. subduction zone 6At wha ...
Understanding Our Environment
... Slide slowly across earth’s surface. - Ocean basins form where continents crack and pull apart. - Magma forced up through cracks in oceanic crust form mid-oceanic ridges. ...
... Slide slowly across earth’s surface. - Ocean basins form where continents crack and pull apart. - Magma forced up through cracks in oceanic crust form mid-oceanic ridges. ...
GEOLOGY EXAM IS ___Weds. 11/28
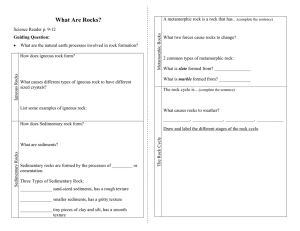
... Answer the following questions. 1. Name the three major groups of rocks. __________________________________________________________________________ 2. What type of rock forms when heat and pressure below Earth’s surface changes rock? __________________________________________________________________ ...
... Answer the following questions. 1. Name the three major groups of rocks. __________________________________________________________________________ 2. What type of rock forms when heat and pressure below Earth’s surface changes rock? __________________________________________________________________ ...
Rock types Soil-forming factor 1: Parent material
... surface conditions and not the underlying bedrock. It should be noted that the general nature of this map means that at a local level, the conditions may be quite different to that shown. Other than the terms alluvium (deposited by water), aeolian (deposited by wind), organic (peat deposits) and col ...
... surface conditions and not the underlying bedrock. It should be noted that the general nature of this map means that at a local level, the conditions may be quite different to that shown. Other than the terms alluvium (deposited by water), aeolian (deposited by wind), organic (peat deposits) and col ...
review list 2013
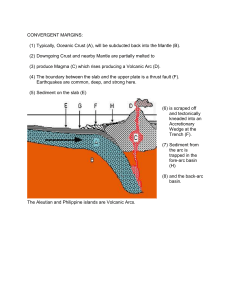
... Current Plate Tectonic Theory includes Alfred Wegener’s original idea of Continental Drift and the modern idea of seafloor spreading. Continental Drift evidence: Correlation of fossils, rock structures and types, continent shapes, and climate (glacial) evidence across continents. Seafloor spre ...
... Current Plate Tectonic Theory includes Alfred Wegener’s original idea of Continental Drift and the modern idea of seafloor spreading. Continental Drift evidence: Correlation of fossils, rock structures and types, continent shapes, and climate (glacial) evidence across continents. Seafloor spre ...
Earth Revealed #10: Geologic Time
... 4. True or False. A slump area becoming a landslide area is an example of the transitional nature of ...
... 4. True or False. A slump area becoming a landslide area is an example of the transitional nature of ...
Mature vs. Immature Sandstone
... Immature sandstone is equipped with diverse, unstable minerals. Its grains are poorlysorted and angular. The sandstone has not been transported far and is close to the source area. Near the source area, the sandstone has varying energy. The composition of immature sandstone mostly quartz, however ha ...
... Immature sandstone is equipped with diverse, unstable minerals. Its grains are poorlysorted and angular. The sandstone has not been transported far and is close to the source area. Near the source area, the sandstone has varying energy. The composition of immature sandstone mostly quartz, however ha ...
Rock Types - Volcanoes Alive!
... igneous rocks, on the other hand, are formed when magma reaches the surface of Earth and cools quickly. Mineral crystals cannot grow very large during this rapid cooling, so the rocks are fine grained. Texture can vary. Examples are pumice and obsidian. Igneous rocks are the most common rocks found ...
... igneous rocks, on the other hand, are formed when magma reaches the surface of Earth and cools quickly. Mineral crystals cannot grow very large during this rapid cooling, so the rocks are fine grained. Texture can vary. Examples are pumice and obsidian. Igneous rocks are the most common rocks found ...
31_Geology
... most common method in the US, and what are two problems with this method? What are some recycling initiatives in the US? What can you do to help reduce the amount of solid ...
... most common method in the US, and what are two problems with this method? What are some recycling initiatives in the US? What can you do to help reduce the amount of solid ...
Chapter 13 Earth`s Interior and Tectonics
... Atoms>>>Elements>>>Minerals>>>Rocks>>>Continents Bedrock: solid rock that underlies the surface material of the Earth. Regolith: the layer above the bedrock, usually composed of weathered down bedrock. Outcrop: exposure of rock at the Earth’s surface. Mineral Classification What does it take to be a ...
... Atoms>>>Elements>>>Minerals>>>Rocks>>>Continents Bedrock: solid rock that underlies the surface material of the Earth. Regolith: the layer above the bedrock, usually composed of weathered down bedrock. Outcrop: exposure of rock at the Earth’s surface. Mineral Classification What does it take to be a ...
8H - UCC Revision
... rocks with small crystals (like basalt). Magma underground cools down much more slowly and forms rocks with bigger crystals, like granite. ...
... rocks with small crystals (like basalt). Magma underground cools down much more slowly and forms rocks with bigger crystals, like granite. ...
This famous round building was made for sports
... Changes the size of the rock but not what it is made of; caused by water, temperature, wind, and plants Breaks down rocks through chemical reactions by creating a new substance (Ex: acid rain, rust) ...
... Changes the size of the rock but not what it is made of; caused by water, temperature, wind, and plants Breaks down rocks through chemical reactions by creating a new substance (Ex: acid rain, rust) ...
What Are Rocks - Lewiston School District
... What causes rocks to weather? ______________, ________________, _______________, ______________ ...
... What causes rocks to weather? ______________, ________________, _______________, ______________ ...
Provenance (geology)

Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the history of sediments movements over time. The Earth is not a static but a dynamic planet, all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types, which are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks (the rock cycle). Rocks exposed to the surface, sooner or later, are broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosion history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.