2nd 6 week test review 2015-2016 ppt
... of the Earth's crust and the shape of the continents. The tectonic plates comprise the bottom of the crust and the top of the Earth's mantle. ...
... of the Earth's crust and the shape of the continents. The tectonic plates comprise the bottom of the crust and the top of the Earth's mantle. ...
Study Guide Exam #4
... How do glaciers shape the landscape? (Chapter 17) How has the size of glaciers changed in the last century? What are moraine, erratic, glacial striations, till & are they formed by deposition or erosion? Sedimentary Rocks: Chemical vs. Detrital. (Chapter 6) What is the difference between chemical & ...
... How do glaciers shape the landscape? (Chapter 17) How has the size of glaciers changed in the last century? What are moraine, erratic, glacial striations, till & are they formed by deposition or erosion? Sedimentary Rocks: Chemical vs. Detrital. (Chapter 6) What is the difference between chemical & ...
The liquid area that surrounds the Earth`s center is the outer core
... Review Notes – Semester One – Earth Science The liquid area that surrounds the Earth’s center is the outer core. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur most frequently at the boundaries of two plates. A mineral that contains something useful and can be sold is an ore. The solid area of the Earth’s core is ...
... Review Notes – Semester One – Earth Science The liquid area that surrounds the Earth’s center is the outer core. Earthquakes and volcanoes occur most frequently at the boundaries of two plates. A mineral that contains something useful and can be sold is an ore. The solid area of the Earth’s core is ...
Igneous Rocks
... Lustre can be earthy (dull), vitreous (glassy), brilliant (shiny), pearly (shiny but not glossy), metallic (like a shiny metal) Streak The colour of the powdered mineral Scratch the mineral on a tile and observe the colour left on the tile Cleavage and Fracture This is how the mineral breaks. Fractu ...
... Lustre can be earthy (dull), vitreous (glassy), brilliant (shiny), pearly (shiny but not glossy), metallic (like a shiny metal) Streak The colour of the powdered mineral Scratch the mineral on a tile and observe the colour left on the tile Cleavage and Fracture This is how the mineral breaks. Fractu ...
There are 4 main layers – the crust, the mantle, the outer core, and
... •Think about it...the deeper you go into the center of the earth, the more stuff is going to be pressing in on you. In the case of the inner core, you have 81% of the Earth's mass pressing in on you! ...
... •Think about it...the deeper you go into the center of the earth, the more stuff is going to be pressing in on you. In the case of the inner core, you have 81% of the Earth's mass pressing in on you! ...
Earth Processes Part 1: Lithosphere
... ROCK CYCLE - All rocks go through a cycle, constantly changing shape due to weathering, erosion, heat, pressure, hardening and cooling. They can change from one type of rock to another. (For example, a sedimentary rock will not always be a sedimentary rock.) Weathering-the breaking down of rocks by ...
... ROCK CYCLE - All rocks go through a cycle, constantly changing shape due to weathering, erosion, heat, pressure, hardening and cooling. They can change from one type of rock to another. (For example, a sedimentary rock will not always be a sedimentary rock.) Weathering-the breaking down of rocks by ...
Review and Study Sheet BRING TO EXAM
... How does CO2 and water interact in atmosphere and geologic cycle ? Why is marble (or limestone) more susceptible to chemical weathering compared to quartz ? What type of stone material would you want for your gravestone ? What climates produce the most mechanical weathering ? What climates produce t ...
... How does CO2 and water interact in atmosphere and geologic cycle ? Why is marble (or limestone) more susceptible to chemical weathering compared to quartz ? What type of stone material would you want for your gravestone ? What climates produce the most mechanical weathering ? What climates produce t ...
Fieldwork, cruise and follow up laboratory studies on different
... Island coast, where as low salinity mangroves (Sonneratia) were present in the landward part. The shore parallel bar near the Bakkhali coast might have been formed by disposition and redistribution of offshore sediment load by long shore current. The sediments in this part of inner shelf are mostly ...
... Island coast, where as low salinity mangroves (Sonneratia) were present in the landward part. The shore parallel bar near the Bakkhali coast might have been formed by disposition and redistribution of offshore sediment load by long shore current. The sediments in this part of inner shelf are mostly ...
The Appalachian Story sheet
... NFLD - ideal for herds of _______________________. 5. Rocks of this area are similar to specific groups found in ______________________ and _______________________. 6. There are rocks called ______________________________ that are unique to the region of northwest ______________________. 7. Nova Sco ...
... NFLD - ideal for herds of _______________________. 5. Rocks of this area are similar to specific groups found in ______________________ and _______________________. 6. There are rocks called ______________________________ that are unique to the region of northwest ______________________. 7. Nova Sco ...
Chapter 6 Vocabulary
... sediment grains or the same mineral grows between and over the grains Clastic (p. 122)- Describes rock and mineral fragments produced by weathering and erosion and classified according to particle size and shape Cross-bedding (p. 126)- Depositional feature of sedimentary rock that forms as inclined ...
... sediment grains or the same mineral grows between and over the grains Clastic (p. 122)- Describes rock and mineral fragments produced by weathering and erosion and classified according to particle size and shape Cross-bedding (p. 126)- Depositional feature of sedimentary rock that forms as inclined ...
Geology 208 History of Earth System Midterm Topics 1 Topics
... Transgressive – Regressive sequences and Sloss Foreland basin and clastic wedge (flysch and molasse) Cyclothems Relative Age Principles of relative age dating and block diagram The nature of unconformities – what is implied Fossil succession and extinction events Biostratigraphy o Defi ...
... Transgressive – Regressive sequences and Sloss Foreland basin and clastic wedge (flysch and molasse) Cyclothems Relative Age Principles of relative age dating and block diagram The nature of unconformities – what is implied Fossil succession and extinction events Biostratigraphy o Defi ...
Time - Research School of Earth Sciences
... to many others who make their research and teaching material available online; sometimes even a single figure or an idea about how to present a subject is a valuable resource. Please note that this PowerPoint presentation is not a complete lecture; it is ...
... to many others who make their research and teaching material available online; sometimes even a single figure or an idea about how to present a subject is a valuable resource. Please note that this PowerPoint presentation is not a complete lecture; it is ...
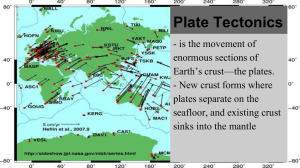
Plate Tectonics
... that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. ...
... that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. ...
Chapter 3 - Igneous Rocks
... Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships Inclusions Unconformities - angular unconformities, Correlation: Using relative dating techniques to date a sequence of sedimentary strata and structures. Relative dating problem, e.g. #21 from Ch. 18 Absolute Dating with Radioactivity Radioactivi ...
... Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships Inclusions Unconformities - angular unconformities, Correlation: Using relative dating techniques to date a sequence of sedimentary strata and structures. Relative dating problem, e.g. #21 from Ch. 18 Absolute Dating with Radioactivity Radioactivi ...
103-04-RocksIntrod-2006(Lesson08)
... • Sedimentary Rocks come from sediments • Sediments: – Abundant on the seafloor (veneer the basalt layer of crust below) – Mostly loose grains (eroded from previously existing rocks) – May be skeletal debris (shells, etc.), plant materials (coal) – May be chemical precipitates from seawater (salts) ...
... • Sedimentary Rocks come from sediments • Sediments: – Abundant on the seafloor (veneer the basalt layer of crust below) – Mostly loose grains (eroded from previously existing rocks) – May be skeletal debris (shells, etc.), plant materials (coal) – May be chemical precipitates from seawater (salts) ...
Sedimentary rocks
... such as those in the upper photograph (A) may someday become a rock like the sandstone in the lower photograph (B). This sandstone was part of a beach over 200 million years ago in the Triassic period. ...
... such as those in the upper photograph (A) may someday become a rock like the sandstone in the lower photograph (B). This sandstone was part of a beach over 200 million years ago in the Triassic period. ...
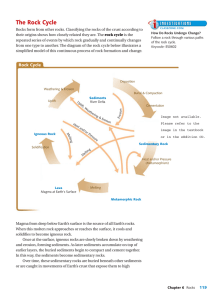
The Rock Cycle
... Magma from deep below Earth’s surface is the source of all Earth’s rocks. When this molten rock approaches or reaches the surface, it cools and solidifies to become igneous rock. Once at the surface, igneous rocks are slowly broken down by weathering and erosion, forming sediments. As later sediment ...
... Magma from deep below Earth’s surface is the source of all Earth’s rocks. When this molten rock approaches or reaches the surface, it cools and solidifies to become igneous rock. Once at the surface, igneous rocks are slowly broken down by weathering and erosion, forming sediments. As later sediment ...
Chapter 15
... formation of lithostratigraphic units that cut across time lines is almost inevitable (see Figure 15.2C for example). As described in the section entitled “Gaps in the Record” we need to forget the concept that the stratigraphic record is like a tape recording that provides us with a sequential reco ...
... formation of lithostratigraphic units that cut across time lines is almost inevitable (see Figure 15.2C for example). As described in the section entitled “Gaps in the Record” we need to forget the concept that the stratigraphic record is like a tape recording that provides us with a sequential reco ...
Teacher Pre-assessment
... d. determine the mineral’s chemical reactivity 30. What property of a rock determines if it will float or sink? a. Its mass b. Its volume c. Its color d. Its density 31. Which of these is most likely formed when a continental and oceanic plate collide? a. An alpine glacier b. A rain shadow desert c. ...
... d. determine the mineral’s chemical reactivity 30. What property of a rock determines if it will float or sink? a. Its mass b. Its volume c. Its color d. Its density 31. Which of these is most likely formed when a continental and oceanic plate collide? a. An alpine glacier b. A rain shadow desert c. ...
Rocks
... Granite is a coarse-grained igneous rock composed mostly of light-colored, light-density, nonferromagnesian minerals. The earth's continental areas are dominated by granite and by rocks with the same mineral composition of granite. ...
... Granite is a coarse-grained igneous rock composed mostly of light-colored, light-density, nonferromagnesian minerals. The earth's continental areas are dominated by granite and by rocks with the same mineral composition of granite. ...
notes
... Granite is a coarse-grained igneous rock composed mostly of light-colored, light-density, nonferromagnesian minerals. The earth's continental areas are dominated by granite and by rocks with the same mineral composition of granite. ...
... Granite is a coarse-grained igneous rock composed mostly of light-colored, light-density, nonferromagnesian minerals. The earth's continental areas are dominated by granite and by rocks with the same mineral composition of granite. ...
Yr 7 Rocks and Fossils Unit Overview
... An understanding that sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic rocks contain minerals and are formed by processes that occur within Earth over a variety of timescales. In this unit students will Understand that the earth is made of layers Explain how volcanoes are formed, lava flows and types of roc ...
... An understanding that sedimentary, igneous and metamorphic rocks contain minerals and are formed by processes that occur within Earth over a variety of timescales. In this unit students will Understand that the earth is made of layers Explain how volcanoes are formed, lava flows and types of roc ...
Earth History – Study Guide Investigations: Sedimentary Rocks +
... Sedimentary Rocks: 1. Give two examples of sedimentary rocks. 2. What are the three main processes that cause Earth’s surface to wear down? 3. What is physical weathering? 4. Name and describe three types of physical weathering. 5. What is chemical weathering? 6. Name and describe three types of che ...
... Sedimentary Rocks: 1. Give two examples of sedimentary rocks. 2. What are the three main processes that cause Earth’s surface to wear down? 3. What is physical weathering? 4. Name and describe three types of physical weathering. 5. What is chemical weathering? 6. Name and describe three types of che ...
Provenance (geology)

Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the history of sediments movements over time. The Earth is not a static but a dynamic planet, all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types, which are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks (the rock cycle). Rocks exposed to the surface, sooner or later, are broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosion history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.