Molten rock that comes to the surface of the earth is called:
... d. determine the mineral’s chemical reactivity 30. What property of a rock determines if it will float or sink? a. Its mass b. Its volume c. Its color d. Its density 31. Which of these is most likely formed when a continental and oceanic plate collide? a. An alpine glacier b. A rain shadow desert c. ...
... d. determine the mineral’s chemical reactivity 30. What property of a rock determines if it will float or sink? a. Its mass b. Its volume c. Its color d. Its density 31. Which of these is most likely formed when a continental and oceanic plate collide? a. An alpine glacier b. A rain shadow desert c. ...
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide
... 1. What is a divide? 2. What does stream load refer to? What are the three methods of transporting stream load? 3. What is discharge? What factors affect discharge? 4. What are meanders? When do they form in a rivers “life cycle?” 5. What is a river that joins another river called? 6. When does depo ...
... 1. What is a divide? 2. What does stream load refer to? What are the three methods of transporting stream load? 3. What is discharge? What factors affect discharge? 4. What are meanders? When do they form in a rivers “life cycle?” 5. What is a river that joins another river called? 6. When does depo ...
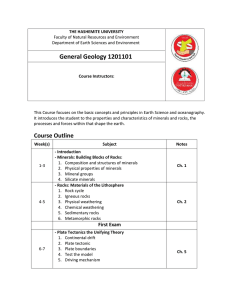
Outline General Geology 2011
... THE HASHEMITE UNIVERSITY Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of Earth Sciences and Environment ...
... THE HASHEMITE UNIVERSITY Faculty of Natural Resources and Environment Department of Earth Sciences and Environment ...
Study Guide 1
... identifiable igneous rocks by crystal size volcanic (crystals too small to see) – basalt plutonic (large crystals) – granite how sediment is lithified common types of sedimentary rocks: shale, sandstone, limestone identifiable sedimentary rocks – sandstone, shell limestone what is metamorphism w ...
... identifiable igneous rocks by crystal size volcanic (crystals too small to see) – basalt plutonic (large crystals) – granite how sediment is lithified common types of sedimentary rocks: shale, sandstone, limestone identifiable sedimentary rocks – sandstone, shell limestone what is metamorphism w ...
Geller PPT Slides
... “Rocks formed from particles or dissolved materials from previously existing rocks.” See Table 19.2 in textbook ...
... “Rocks formed from particles or dissolved materials from previously existing rocks.” See Table 19.2 in textbook ...
Late Paleozoic Mountain Building
... Vertical (“thick-skinned”) block uplifts in the western US created the Ancestral Rockies (eroded away and the sedimentary wedge is all that is left) due to compressio from E, W, and S. Modern Rockies are in similar location, “flatirons” along the front range are formed from the Fountain Fm. (Arkosic ...
... Vertical (“thick-skinned”) block uplifts in the western US created the Ancestral Rockies (eroded away and the sedimentary wedge is all that is left) due to compressio from E, W, and S. Modern Rockies are in similar location, “flatirons” along the front range are formed from the Fountain Fm. (Arkosic ...
Rock Cycle
... 1. Go to www.phschool.com 2. Enter cfp-1056 into the Web Code area on the top left hand side of the web page. 3. Press the yellow circle to the right of the area where you entered the web code. 4. Press the orange start button. 5. Read the description at the top of the page titled “The Rock cycle” a ...
... 1. Go to www.phschool.com 2. Enter cfp-1056 into the Web Code area on the top left hand side of the web page. 3. Press the yellow circle to the right of the area where you entered the web code. 4. Press the orange start button. 5. Read the description at the top of the page titled “The Rock cycle” a ...
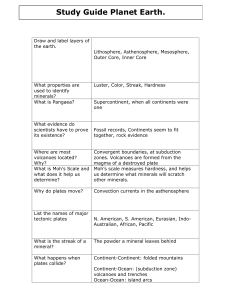
Study Guide for 3rd nine week assessment 2017
... because these provinces contain sediments and most fossils are found in these type of rocks. 15. Erosion and deposition are occurring constantly in the coastal plain 16. When El Nino occurs this causes a reduction in fish because upwelling stops and down welling begins 17. Pyrite is an ore of Iron a ...
... because these provinces contain sediments and most fossils are found in these type of rocks. 15. Erosion and deposition are occurring constantly in the coastal plain 16. When El Nino occurs this causes a reduction in fish because upwelling stops and down welling begins 17. Pyrite is an ore of Iron a ...
GEOLOGY 335 LAB -- SEDIMENTARY PROCESSES
... calcium carbonate (CaCO3), usually calcite; effervesces upon contact with hydrochloric acid ...
... calcium carbonate (CaCO3), usually calcite; effervesces upon contact with hydrochloric acid ...
UNIT TITLE: Readers Theater
... 6. The process of weathering breaks down rocks to form sediment. 7. Erosion is the process that moves sediment. The three agents of erosion are water, wind, and ice (or glaciers). 8. The interior of Earth is hot. Convection currents in the mantle cause tectonic plates to move. This causes earthquak ...
... 6. The process of weathering breaks down rocks to form sediment. 7. Erosion is the process that moves sediment. The three agents of erosion are water, wind, and ice (or glaciers). 8. The interior of Earth is hot. Convection currents in the mantle cause tectonic plates to move. This causes earthquak ...
Exam II
... 56. The splitting of rocks due to the repeated freezing and thawing is known as root wedging. 57. The jumping of sediment grains along the stream bed is known as bedload. 58. The uppermost layer of regolith that can support rooted plants is known as soil. 59. In a soil profile, the B and E layers ar ...
... 56. The splitting of rocks due to the repeated freezing and thawing is known as root wedging. 57. The jumping of sediment grains along the stream bed is known as bedload. 58. The uppermost layer of regolith that can support rooted plants is known as soil. 59. In a soil profile, the B and E layers ar ...
chapter1
... Nebular Hypothesis - dust clouds - consist primarily of hydrogen and helium and "dust" particles attract each other under the influence of gravity Stars ...
... Nebular Hypothesis - dust clouds - consist primarily of hydrogen and helium and "dust" particles attract each other under the influence of gravity Stars ...
Document
... moving depocenter in the direction of thrust motion Piggyback Basin: basins that are on the hanging wall of a thrust fault and move with the hanging wall. Sediments evolve from fine-grained turbidites to shallow water continental seds over time ...
... moving depocenter in the direction of thrust motion Piggyback Basin: basins that are on the hanging wall of a thrust fault and move with the hanging wall. Sediments evolve from fine-grained turbidites to shallow water continental seds over time ...
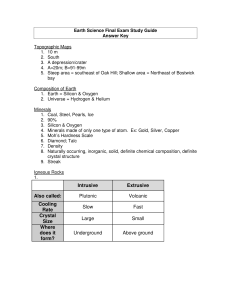
Final Exam Study Guide Answer Key
... 3. What determines the properties of a mineral? (composition) 4. What do minerals in the sulfate group contain (sulfur) 5. What mineral reacts with acid? (calcite) 6. What does inorganic mean? (not living) 7. Why is coal not a mineral? (it came from living things) 8. What determines a rocks texture? ...
... 3. What determines the properties of a mineral? (composition) 4. What do minerals in the sulfate group contain (sulfur) 5. What mineral reacts with acid? (calcite) 6. What does inorganic mean? (not living) 7. Why is coal not a mineral? (it came from living things) 8. What determines a rocks texture? ...
Introduction to Geography
... Introduction to Geography By Arthur Getis Judith Getis Jerome D. Fellmann ...
... Introduction to Geography By Arthur Getis Judith Getis Jerome D. Fellmann ...
ocks in the lithosphere
... Igneous rock is rock formed by the hardening and crystallization of molten material that originates deep within the earth. Two important variables used for the classification of igneous rocks are particle size, which largely depends upon the cooling history, and the ...
... Igneous rock is rock formed by the hardening and crystallization of molten material that originates deep within the earth. Two important variables used for the classification of igneous rocks are particle size, which largely depends upon the cooling history, and the ...
Lesson 4-3 Sedimentary Rocks Outline
... and air can change the physical or chemical properties of rock. ...
... and air can change the physical or chemical properties of rock. ...
EarthScience_Quiz_Ch3
... c) crystal masses with a defined chemical composition d) naturally occurring aggregates of plant fibers and fragments ...
... c) crystal masses with a defined chemical composition d) naturally occurring aggregates of plant fibers and fragments ...
Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary
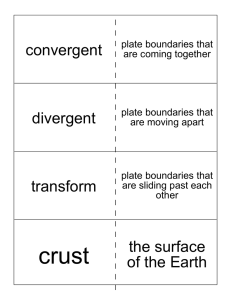
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
Rock Cycle Unit Vocabulary 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
... 1. lithosphere – rigid, top layer of Earth made of the crust and upper mantle - broken into plates that move around on the lower mantle 2. mantle – largest layer of Earth’s interior that lies below the crust - although solid, it flows slowly like putty 3. igneous rock – rock that forms when melted r ...
See Q. “Sampler” on packet, pages 12
... 1) Rock Particles (grains) 2) Intergranular cement (also called matrix) *Their strength and other properties may be different from one another and may affect further weathering, infiltration, water storage, etc. Two Sedimentary Rock Types: 1) Detrital (aka Clastic): with rock fragments/grains and ce ...
... 1) Rock Particles (grains) 2) Intergranular cement (also called matrix) *Their strength and other properties may be different from one another and may affect further weathering, infiltration, water storage, etc. Two Sedimentary Rock Types: 1) Detrital (aka Clastic): with rock fragments/grains and ce ...
Provenance (geology)

Provenance in geology, is the reconstruction of the history of sediments movements over time. The Earth is not a static but a dynamic planet, all rocks are subject to transition between the three main rock types, which are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous rocks (the rock cycle). Rocks exposed to the surface, sooner or later, are broken down into sediments. Sediments are expected to be able to provide evidence of the erosion history of their parent source rocks. The purpose of provenance study is to restore the tectonic, paleo-geographic and paleo-climatic history.