New Features of Connectivity in Piriform Cortex Visualized by
... input from olfactory receptor neurons. However, physiological and anatomical studies suggest that this cortical area is organized in a fundamentally different way than the primary cortical areas for nonchemical senses (Haberly, 1998). Physiological studies have shown that neurons in piriform cortex ...
... input from olfactory receptor neurons. However, physiological and anatomical studies suggest that this cortical area is organized in a fundamentally different way than the primary cortical areas for nonchemical senses (Haberly, 1998). Physiological studies have shown that neurons in piriform cortex ...
Multisensory anatomical pathways - Centre de Recherche Cerveau
... In all cases, these heteromodal connections were described as not very dense, representing only few hundred projecting neurons. While this low strength of projection could be interpreted as of low functional impact, it is important to consider that these projections are observed following small size ...
... In all cases, these heteromodal connections were described as not very dense, representing only few hundred projecting neurons. While this low strength of projection could be interpreted as of low functional impact, it is important to consider that these projections are observed following small size ...
neuron number decreases in the rat ventral, but not dorsal, medial
... The StereoInvestigator program allows individual cells to be tracked with the use of markers and will perform a tally of multiple counts if separate markers are used for different cell types as was done here for neurons and glia. In the cortex, neurons and glia can be unambiguously distinguished bas ...
... The StereoInvestigator program allows individual cells to be tracked with the use of markers and will perform a tally of multiple counts if separate markers are used for different cell types as was done here for neurons and glia. In the cortex, neurons and glia can be unambiguously distinguished bas ...
ORIGIN OF THE PERICELLULAR BASKETS OF THE PYRAMIDAL
... impregnated by silver and could not be followed. Probably because of this no pericellular baskets were found in this infant. 8-month-old infant. The motor cortex of this infant was characterized by its extraordinary complexity of axonic fibers and dendrites. Pericellular baskets were seen on rare oc ...
... impregnated by silver and could not be followed. Probably because of this no pericellular baskets were found in this infant. 8-month-old infant. The motor cortex of this infant was characterized by its extraordinary complexity of axonic fibers and dendrites. Pericellular baskets were seen on rare oc ...
Reflections on agranular architecture: predictive coding in the motor
... Figure 2. Graphical representation of the computational interactions between expectation and error units: the interactions depicted here are based on the differential equations describing the neuronal dynamics implied by generalised predictive coding (e.g., Equation 3 in [30]). Note the hierarchical ...
... Figure 2. Graphical representation of the computational interactions between expectation and error units: the interactions depicted here are based on the differential equations describing the neuronal dynamics implied by generalised predictive coding (e.g., Equation 3 in [30]). Note the hierarchical ...
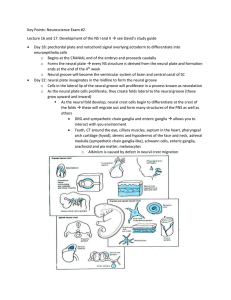
Key Points: Neuroscience Exam #2 Lecture 16 and 17: Development of
... o Static= measure of the amount of stretch Type II are sensitive to the amount of stretch but not the rate; when tension is released, these are quite of AP o Dynamic= how fast is the stretch occurring Type Ia are sensitive to change in rate of stretch o Muscle spindle function: motor If a musc ...
... o Static= measure of the amount of stretch Type II are sensitive to the amount of stretch but not the rate; when tension is released, these are quite of AP o Dynamic= how fast is the stretch occurring Type Ia are sensitive to change in rate of stretch o Muscle spindle function: motor If a musc ...
May 21, 04.doc
... Sensory deprivation has been a productive approach to investigate the effects of environmental stimuli on adult and developing brain. Whereas lack of normal excitatory inputs leaves some cortical neurotransmitter systems unaffected (Goodman et al., 1993; Schlaggar et al, 1993), it can lead to down r ...
... Sensory deprivation has been a productive approach to investigate the effects of environmental stimuli on adult and developing brain. Whereas lack of normal excitatory inputs leaves some cortical neurotransmitter systems unaffected (Goodman et al., 1993; Schlaggar et al, 1993), it can lead to down r ...
May 11, 04copy.doc
... Sensory deprivation has been a productive approach to investigate the effects of environmental stimuli on adult and developing brain. Whereas lack of normal excitatory inputs leaves some cortical neurotransmitter systems unaffected (Goodman et al., 1993; Schlaggar et al, 1993), it can lead to down r ...
... Sensory deprivation has been a productive approach to investigate the effects of environmental stimuli on adult and developing brain. Whereas lack of normal excitatory inputs leaves some cortical neurotransmitter systems unaffected (Goodman et al., 1993; Schlaggar et al, 1993), it can lead to down r ...
Multisensory contributions to low-level, `unisensory` processing
... the thalamocortical relay of sensory inputs. It carries spatially specific information through a circumscribed subcortical route, which projects to the middle layers (lower 3 and 4) of a primary sensory region of cortex. In the case of the auditory system, it is the pathway that courses through the ...
... the thalamocortical relay of sensory inputs. It carries spatially specific information through a circumscribed subcortical route, which projects to the middle layers (lower 3 and 4) of a primary sensory region of cortex. In the case of the auditory system, it is the pathway that courses through the ...
Document
... • Contributes to motor functions by transmitting information from the cerebellum and basal ganglia to the cerebral primary ...
... • Contributes to motor functions by transmitting information from the cerebellum and basal ganglia to the cerebral primary ...
Region Specific Micromodularity in the Uppermost Layers in Primate
... The remaining blocks were cut serially in either the coronal or tangential plane by frozen microtomy (at 40–50 µm thickness). Single and Double Labeling In our preceeding rodent study (Ichinohe et al., 2003b), in order to visualize micromodularity at the border of layers 1 and 2, we used zinc, PV, M ...
... The remaining blocks were cut serially in either the coronal or tangential plane by frozen microtomy (at 40–50 µm thickness). Single and Double Labeling In our preceeding rodent study (Ichinohe et al., 2003b), in order to visualize micromodularity at the border of layers 1 and 2, we used zinc, PV, M ...
Lissencephaly - Cambridge University Press
... cortex showed a thin molecular layer, beneath which there was a continuous mass of neurons, without lamination. Neurons were pyramidal, of moderate size and mixed randomly with a population of smaller neurons. This sheet of neurons extended towards the ventricles. Tapering bands of myelin radiated i ...
... cortex showed a thin molecular layer, beneath which there was a continuous mass of neurons, without lamination. Neurons were pyramidal, of moderate size and mixed randomly with a population of smaller neurons. This sheet of neurons extended towards the ventricles. Tapering bands of myelin radiated i ...
Cytoarchitecture of the canine perirhinal and postrhinal cortex
... According to current terminology, the perirhinal cortex in the monkey brain (Murray and Bussey 1999) includes cytoarchitectonic areas 35 and 36 in the rhinal sulcus. It is, however, extended laterally and caudally in comparison to earlier cytoarchitectonic maps of Brodmann (1909). Laterally, the per ...
... According to current terminology, the perirhinal cortex in the monkey brain (Murray and Bussey 1999) includes cytoarchitectonic areas 35 and 36 in the rhinal sulcus. It is, however, extended laterally and caudally in comparison to earlier cytoarchitectonic maps of Brodmann (1909). Laterally, the per ...
Thalamus Notes
... position sense, and respond to either superficial mechanics stimulation of the skin, mechanical distortion of deep tissues, or joint rotation, but not to more than one of these. These informations are then integrated in the cortex into perceptions of form, size and texture. The cortical cytoarchitec ...
... position sense, and respond to either superficial mechanics stimulation of the skin, mechanical distortion of deep tissues, or joint rotation, but not to more than one of these. These informations are then integrated in the cortex into perceptions of form, size and texture. The cortical cytoarchitec ...
Projections from the superior temporal sulcus to the agranular frontal
... Several electrophysiological studies have shown that neurons in area STP have complex sensory properties. Firstly, although STP neurons are predominantly purely visual, a signi®cant proportion of them have also somatosensory and/or auditory responses (Bruce et al., 1981; Bayliss et al., 1987). Secon ...
... Several electrophysiological studies have shown that neurons in area STP have complex sensory properties. Firstly, although STP neurons are predominantly purely visual, a signi®cant proportion of them have also somatosensory and/or auditory responses (Bruce et al., 1981; Bayliss et al., 1987). Secon ...
The basic nonuniformity of the cerebral cortex
... allometry 兩 brain size 兩 primates 兩 number of neurons 兩 cortical surface ...
... allometry 兩 brain size 兩 primates 兩 number of neurons 兩 cortical surface ...
May 30, 04copy.doc
... Sensory deprivation has been a productive approach to investigate the effects of environmental stimuli on adult and developing brain. Whereas lack of normal excitatory inputs leaves some cortical neurotransmitter systems unaffected (Goodman et al., 1993; Schlaggar et al, 1993), it can lead to down r ...
... Sensory deprivation has been a productive approach to investigate the effects of environmental stimuli on adult and developing brain. Whereas lack of normal excitatory inputs leaves some cortical neurotransmitter systems unaffected (Goodman et al., 1993; Schlaggar et al, 1993), it can lead to down r ...
connections of the cerebral cortex
... Perhaps the shift to area 4 is a later specialization, and the extensive origin of the pyramidal tracts is consonant with the motor activities of the premotor areas observed in higher mammals after destruction of area 4. Area 8 : area frontalis intermedia ( F C ) (fig. 3, 6 ) . Included in the front ...
... Perhaps the shift to area 4 is a later specialization, and the extensive origin of the pyramidal tracts is consonant with the motor activities of the premotor areas observed in higher mammals after destruction of area 4. Area 8 : area frontalis intermedia ( F C ) (fig. 3, 6 ) . Included in the front ...
Input to the Cerebellar Cortex
... opposite direction for the succeeding compensatory movement.This effect is called dysmetria, and it results in uncoordinated movements that are called ataxia. ...
... opposite direction for the succeeding compensatory movement.This effect is called dysmetria, and it results in uncoordinated movements that are called ataxia. ...
Heterotopic Transcallosal Projections Are Present throughout the
... Transcallosal projection neurons are a population of pyramidal excitatory neurons located in layers II/III and to a lesser extent layer V of the cortex. Their axons form the corpus callosum thereby providing an inter-hemispheric connection in the brain. While transcallosal projection neurons have be ...
... Transcallosal projection neurons are a population of pyramidal excitatory neurons located in layers II/III and to a lesser extent layer V of the cortex. Their axons form the corpus callosum thereby providing an inter-hemispheric connection in the brain. While transcallosal projection neurons have be ...
The Somatosensory System
... • Deep gray matter structure part of the diencephalon • Convey different types of input to the cortex ...
... • Deep gray matter structure part of the diencephalon • Convey different types of input to the cortex ...
Cerebral cortex

The cerebral cortex is the cerebrum's (brain) outer layer of neural tissue in humans and other mammals. It is divided into two cortices, along the sagittal plane: the left and right cerebral hemispheres divided by the medial longitudinal fissure. The cerebral cortex plays a key role in memory, attention, perception, awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. The human cerebral cortex is 2 to 4 millimetres (0.079 to 0.157 in) thick.In large mammals, the cerebral cortex is folded, giving a much greater surface area in the confined volume of the skull. A fold or ridge in the cortex is termed a gyrus (plural gyri) and a groove or fissure is termed a sulcus (plural sulci). In the human brain more than two-thirds of the cerebral cortex is buried in the sulci.The cerebral cortex is gray matter, consisting mainly of cell bodies (with astrocytes being the most abundant cell type in the cortex as well as the human brain as a whole) and capillaries. It contrasts with the underlying white matter, consisting mainly of the white myelinated sheaths of neuronal axons. The phylogenetically most recent part of the cerebral cortex, the neocortex (also called isocortex), is differentiated into six horizontal layers; the more ancient part of the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, has at most three cellular layers. Neurons in various layers connect vertically to form small microcircuits, called cortical columns. Different neocortical regions known as Brodmann areas are distinguished by variations in their cytoarchitectonics (histological structure) and functional roles in sensation, cognition and behavior.