Module 69 - Dissociative Disorders
... – At different times, different alters take over. – Person’s primary personality often not aware of the alters. ...
... – At different times, different alters take over. – Person’s primary personality often not aware of the alters. ...
Bianca_Paranoid Personality Disorder
... fears that, when she leaves the office at night, someone will sneak into her desk and steal her notes. Her distrust of others pervades all her interpersonal dealings. Her suspicions that she is being cheated even taint routine transactions in banks and stores. Anita like to think of herself as ratio ...
... fears that, when she leaves the office at night, someone will sneak into her desk and steal her notes. Her distrust of others pervades all her interpersonal dealings. Her suspicions that she is being cheated even taint routine transactions in banks and stores. Anita like to think of herself as ratio ...
ICD-9-CM coding for patients with Tourette syndrome* Comorbid
... NOTE: Insurance compensation for services for patients with TS is complicated by the diagnosis being in ICD-9’s 290-319 series (mental disorders), which may trigger use of mental health benefit rules rather than those for medical benefits. This despite clear evidence confirming it as a neurological ...
... NOTE: Insurance compensation for services for patients with TS is complicated by the diagnosis being in ICD-9’s 290-319 series (mental disorders), which may trigger use of mental health benefit rules rather than those for medical benefits. This despite clear evidence confirming it as a neurological ...
Name: Mental Disorders Diagnosis There are 11 different scenarios
... Mark is in an unhappiness that he can’t escape. Tim even notices that Mark has had thoughts of death or suicide from things that have come up in conversation. Based on the characteristics that Tim has noticed about Mark, what mental health disorder could Mark be experiencing? ...
... Mark is in an unhappiness that he can’t escape. Tim even notices that Mark has had thoughts of death or suicide from things that have come up in conversation. Based on the characteristics that Tim has noticed about Mark, what mental health disorder could Mark be experiencing? ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... Reduce supportive consequences of talk about physical symptoms ...
... Reduce supportive consequences of talk about physical symptoms ...
Unit 6
... himself or herself into separate personalities that can act independently Cause: Haunted, confused personality History of traumatic experiences or child abuse Long-term habit of escaping from almost every problem Have very strong, conflicting desires and needs in their lifestyles. ...
... himself or herself into separate personalities that can act independently Cause: Haunted, confused personality History of traumatic experiences or child abuse Long-term habit of escaping from almost every problem Have very strong, conflicting desires and needs in their lifestyles. ...
chapter 16 lecture notes: psychological disorders
... previous memories, thoughts, and feelings Dissociative Amnesia: selective memory loss often brought on by extreme stress. Dissociative Fugue: flight from one's home and identity accompanies amnesia Dissociative Identity Disorder: rare dissociative disorder in which a person exhibits two or mor ...
... previous memories, thoughts, and feelings Dissociative Amnesia: selective memory loss often brought on by extreme stress. Dissociative Fugue: flight from one's home and identity accompanies amnesia Dissociative Identity Disorder: rare dissociative disorder in which a person exhibits two or mor ...
Disorder therapy ppt - Fort Bend ISD / Homepage
... for the disruption in memory. • Retrograde/ Anterograde Amnesia • Organic amnesia can be retrograde or anterograde. ...
... for the disruption in memory. • Retrograde/ Anterograde Amnesia • Organic amnesia can be retrograde or anterograde. ...
Abnormal Psych
... Loss of memory due to psychological rather than physiological causes. The memory loss is usually confined to personal information only ...
... Loss of memory due to psychological rather than physiological causes. The memory loss is usually confined to personal information only ...
What Are Mental and Emotional Disorder?
... Also called manic-depression, this disorder involves extreme mood swings for no apparent reason. A person with this disorder usually experiences alternating periods of excessive activity called mania and depression. ...
... Also called manic-depression, this disorder involves extreme mood swings for no apparent reason. A person with this disorder usually experiences alternating periods of excessive activity called mania and depression. ...
Major Psychological Disorders
... the name for a group of conditions in which the physical pain and symptoms a person feels are related to psychological factors. • Hypochondriasis • Conversion disorder ...
... the name for a group of conditions in which the physical pain and symptoms a person feels are related to psychological factors. • Hypochondriasis • Conversion disorder ...
Mental Illness and Therapy - Agajanian-Psychology
... • Phobias (Agoraphobia) - Strong irrational fear of an object or situation ...
... • Phobias (Agoraphobia) - Strong irrational fear of an object or situation ...
Panic Disorder - Cloudfront.net
... health consolation, the percentage is even more dramatic in general medical settings. Its more common for woman to have this disorder than men. ...
... health consolation, the percentage is even more dramatic in general medical settings. Its more common for woman to have this disorder than men. ...
314.9 Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Not
... 1. Individuals whose symptoms and impainnent meet the criteria for AttentionDeficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Predominantly Inattentive Type but whose age at onset is 7 years or after 2. Individuals with clinically significant impairment who present with inattention and whose symptom pattern does not ...
... 1. Individuals whose symptoms and impainnent meet the criteria for AttentionDeficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Predominantly Inattentive Type but whose age at onset is 7 years or after 2. Individuals with clinically significant impairment who present with inattention and whose symptom pattern does not ...
Social Psychology: Personal Perspectives (Chapter 14)
... Case example: Social phobia "I couldn't go on dates or to parties. For a while, I couldn't even go to class. My sophomore year of college I had to come home for a semester." "My fear would happen in any social situation. I would be anxious before I even left the house, and it would escalate as I go ...
... Case example: Social phobia "I couldn't go on dates or to parties. For a while, I couldn't even go to class. My sophomore year of college I had to come home for a semester." "My fear would happen in any social situation. I would be anxious before I even left the house, and it would escalate as I go ...
Intro Psych March7
... Case example: Social phobia "I couldn't go on dates or to parties. For a while, I couldn't even go to class. My sophomore year of college I had to come home for a semester." "My fear would happen in any social situation. I would be anxious before I even left the house, and it would escalate as I go ...
... Case example: Social phobia "I couldn't go on dates or to parties. For a while, I couldn't even go to class. My sophomore year of college I had to come home for a semester." "My fear would happen in any social situation. I would be anxious before I even left the house, and it would escalate as I go ...
AP_Chapter_16_psychological_disorders[1][1]
... 1. Definition: physical symptoms that resemble those of a neurological disorder develop. The symptoms are triggered by mental factors such as conflicts or other stresses. 2. US Naval Academy: entered with 20/20 vision, many leave with blurred vision. ...
... 1. Definition: physical symptoms that resemble those of a neurological disorder develop. The symptoms are triggered by mental factors such as conflicts or other stresses. 2. US Naval Academy: entered with 20/20 vision, many leave with blurred vision. ...
Jeopardy
... in which a person is being controlled by another’s behavior. A condition in which a person neglects his or herself to care for another. ...
... in which a person is being controlled by another’s behavior. A condition in which a person neglects his or herself to care for another. ...
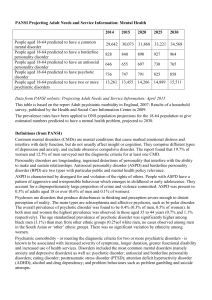
Mental Health Projections: PANSI 2015
... of depression and anxiety, and include obsessive compulsive disorder. The report found that 19.7% of women and 12.5% of men surveyed met the diagnostic criteria for at least one CMD. Personality disorders are longstanding, ingrained distortions of personality that interfere with the ability to make ...
... of depression and anxiety, and include obsessive compulsive disorder. The report found that 19.7% of women and 12.5% of men surveyed met the diagnostic criteria for at least one CMD. Personality disorders are longstanding, ingrained distortions of personality that interfere with the ability to make ...
PSYCHOLOGY (9th Edition) David Myers
... Twin studies suggest that our genes may be partly responsible for developing fears and anxiety. Twins are more likely to share phobias. ...
... Twin studies suggest that our genes may be partly responsible for developing fears and anxiety. Twins are more likely to share phobias. ...
Lars and the Real Girl
... lacks close friends or confidants other than first-degree relatives appears indifferent to praise/criticism “Dependency and love are dangerous” ...
... lacks close friends or confidants other than first-degree relatives appears indifferent to praise/criticism “Dependency and love are dangerous” ...
Multiple Personality Disorder
... can be challenging to treat, often requiring longer treatments that typically aim to help control symptoms more than to achieve integration. ...
... can be challenging to treat, often requiring longer treatments that typically aim to help control symptoms more than to achieve integration. ...
H382: The Problems Kids Have
... Other Specified Depressive Disorder Unspecified Depressive Disorder ...
... Other Specified Depressive Disorder Unspecified Depressive Disorder ...















![AP_Chapter_16_psychological_disorders[1][1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008609904_1-bcd0b4691952c52f8b5635246f54a50a-300x300.png)