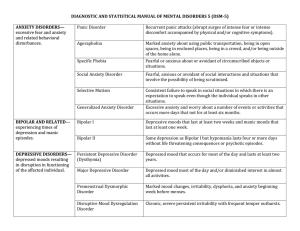
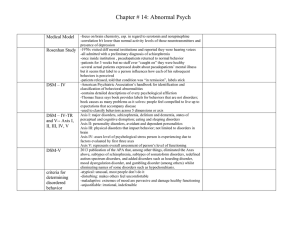
psych mod 22 terms
... situations or objects that he or she is attempting to avoid and continuing exposure treatments until the anxiety decreases. Somatoform disorders: marked by a pattern of recurring, multiple, and significant bodily (somatic) symptoms that extend over several years. The bodily symptoms (pain, vomiting, ...
... situations or objects that he or she is attempting to avoid and continuing exposure treatments until the anxiety decreases. Somatoform disorders: marked by a pattern of recurring, multiple, and significant bodily (somatic) symptoms that extend over several years. The bodily symptoms (pain, vomiting, ...
Chapter 16 - Psychological Disorders Lesson 3 Quiz
... Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 6. The sort of disorders that Freud referred to as hysteria are now called a. panic disorders. b. somatoform disorders. c. obsessive-compulsive disorders. d. schizophrenia. 7. Why do most psychologists believe that ...
... Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 6. The sort of disorders that Freud referred to as hysteria are now called a. panic disorders. b. somatoform disorders. c. obsessive-compulsive disorders. d. schizophrenia. 7. Why do most psychologists believe that ...
Mood Disorder: Management in the Modern Age
... • Demand for more flexible, person-centred care and selfmanagement • Advances in computer science and bio-engineering • Rapid growth in smart technologies • Britain is ready for digital mental health ...
... • Demand for more flexible, person-centred care and selfmanagement • Advances in computer science and bio-engineering • Rapid growth in smart technologies • Britain is ready for digital mental health ...
Unit 6: Psychopathology Name: I. Defining Psychological Disorders
... XIV. The steps to depression… • A. • B. • C. • D. • Back to #1 again…. • It’s a cycle! XV. Dissociative Disorders • A. Characterized by… ...
... XIV. The steps to depression… • A. • B. • C. • D. • Back to #1 again…. • It’s a cycle! XV. Dissociative Disorders • A. Characterized by… ...
Bipolar Disorder
... Mood disturbance sufficiently severe to cause marked impairment in occupational functioning or in usual social activities or relations with others, or to necessitate hospitalization to prevent harm to self or others At no time during the disturbance have there been delusions or hallucinations for as ...
... Mood disturbance sufficiently severe to cause marked impairment in occupational functioning or in usual social activities or relations with others, or to necessitate hospitalization to prevent harm to self or others At no time during the disturbance have there been delusions or hallucinations for as ...
Attention Deficit/ Hyperactivity Disorder - DSM-5
... illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. The descriptions will help clinicians better identify typical ADHD symptoms at each stage of patients’ lives. Using DSM-5, several of the individual’s ADHD symptoms must be present prior to age 12 years ...
... illustrate the types of behavior children, older adolescents, and adults with ADHD might exhibit. The descriptions will help clinicians better identify typical ADHD symptoms at each stage of patients’ lives. Using DSM-5, several of the individual’s ADHD symptoms must be present prior to age 12 years ...
File
... Similar to conversion disorders, but the primary symptom is pain with no physical cause Difficult to diagnose; must rule out true physical pain that has biological cause Somatoform pain usually occurs at times of high stress; generally beneficial in some way (disability payments, getting out of scho ...
... Similar to conversion disorders, but the primary symptom is pain with no physical cause Difficult to diagnose; must rule out true physical pain that has biological cause Somatoform pain usually occurs at times of high stress; generally beneficial in some way (disability payments, getting out of scho ...
31) Dr. Sardonicus is a clinician who treats clients with
... 16) When we make situational attributions, we are identifying the cause of an action as something ...
... 16) When we make situational attributions, we are identifying the cause of an action as something ...
No Slide Title
... Freudian psychodynamic view Trauma, conflict experience Repression “Conversion” to physical symptoms Primary gain Attention and support Secondary gain ...
... Freudian psychodynamic view Trauma, conflict experience Repression “Conversion” to physical symptoms Primary gain Attention and support Secondary gain ...
Chapter 13: Psychological Disorders Abnormal Behavior: The
... A sudden loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting Dissociative Fugue When a person lose their memory for their entire lives along with their sense of personal identity ...
... A sudden loss of memory for important personal information that is too extensive to be due to normal forgetting Dissociative Fugue When a person lose their memory for their entire lives along with their sense of personal identity ...
Major Disorders as Defined by DSM-5
... abnormal thoughts, feeling and behaviors in response to these symptoms. ...
... abnormal thoughts, feeling and behaviors in response to these symptoms. ...
DSM-5 Condensed Training
... each individual. Manual makes NO recommendations for Tx or ForensicsCompentency/Criminal Resp./Disability Dx Criteria Sets: Summarize characteristic syndromes of signs/symptoms that point to underlying disorder, follows developmental path Published by American Psychiatric Association ...
... each individual. Manual makes NO recommendations for Tx or ForensicsCompentency/Criminal Resp./Disability Dx Criteria Sets: Summarize characteristic syndromes of signs/symptoms that point to underlying disorder, follows developmental path Published by American Psychiatric Association ...
Somatoform Disorders
... Somatoform disorders: persons who are overly preoccupied with their health or body. All of these disorders share one thing in common = no identifiable medical condition causing the physical complaints. Hypochondriasis: physical complaints without a clear cause; anxiety focused on the possibility of ...
... Somatoform disorders: persons who are overly preoccupied with their health or body. All of these disorders share one thing in common = no identifiable medical condition causing the physical complaints. Hypochondriasis: physical complaints without a clear cause; anxiety focused on the possibility of ...
Chapter 5
... over time) • 15% of all Teens will display some signs of depression • Most common mental health concerns ...
... over time) • 15% of all Teens will display some signs of depression • Most common mental health concerns ...
Notes_14 abnormal - Biloxi Public Schools
... -complete loss of identity followed by assumption of a new identity - aka: multiple personality disorder -rare condition involving existence of 2+ separate personalities housed in one body -identities may or may not be aware of each other -sufferer is essentially converting psychological stress to p ...
... -complete loss of identity followed by assumption of a new identity - aka: multiple personality disorder -rare condition involving existence of 2+ separate personalities housed in one body -identities may or may not be aware of each other -sufferer is essentially converting psychological stress to p ...
CHAPTER 11
... hallucinations combined with symptoms of depression or manic mood Delusional disorder – Less bizarre than schizophrenia delusions; usually related to a particular topic and have some foundation in real life. Shared psychotic disorder – Two or more people who share shame delusional belief; one origin ...
... hallucinations combined with symptoms of depression or manic mood Delusional disorder – Less bizarre than schizophrenia delusions; usually related to a particular topic and have some foundation in real life. Shared psychotic disorder – Two or more people who share shame delusional belief; one origin ...
Unit13
... stressor that results in the development of clinically significant emotional or behavioral symptoms that impair social/occupational functioning or are in excess of expected reaction to the stressor Occurs within 3 months after onset of stressor and persists for no longer than 6 months after stress ...
... stressor that results in the development of clinically significant emotional or behavioral symptoms that impair social/occupational functioning or are in excess of expected reaction to the stressor Occurs within 3 months after onset of stressor and persists for no longer than 6 months after stress ...
Unit 12 At Home RQ 12
... hospitals after they falsely claimed to be “hearing voices.” This study best illustrated the negative effects of a. the medical model. b. psychoanalytic theory. c. hallucinations. d. linkage analysis. e. diagnostic labels. ____ 12. The ability of mental health professionals to quickly communicate th ...
... hospitals after they falsely claimed to be “hearing voices.” This study best illustrated the negative effects of a. the medical model. b. psychoanalytic theory. c. hallucinations. d. linkage analysis. e. diagnostic labels. ____ 12. The ability of mental health professionals to quickly communicate th ...
Depression
... 1. Emergent: admit to hospital for high suicide risk or danger to self or others. May require certification. 2. Treatment Options: a) Medication (SSRI, SNRI, Bupropion, Mirtazipine, TCA, and MAOI) If patient is started on medication they must be monitored weekly for suicidal ideation for 4 to 6 week ...
... 1. Emergent: admit to hospital for high suicide risk or danger to self or others. May require certification. 2. Treatment Options: a) Medication (SSRI, SNRI, Bupropion, Mirtazipine, TCA, and MAOI) If patient is started on medication they must be monitored weekly for suicidal ideation for 4 to 6 week ...
Chapter 16: DEVELOPMENTAL PSYCHOPATHOLOGY
... Good verbal skills Clear desire to establish social relationships Deficient social cognitive and social-communication skills ...
... Good verbal skills Clear desire to establish social relationships Deficient social cognitive and social-communication skills ...
Dissociative Disorders
... symptoms before entering treatment or learning about the disorder. They suggest the increase in cases is due to greater clinical awareness of the disorder, improved diagnostic description of DID symptoms, and increased screening for dissociative symptoms. ...
... symptoms before entering treatment or learning about the disorder. They suggest the increase in cases is due to greater clinical awareness of the disorder, improved diagnostic description of DID symptoms, and increased screening for dissociative symptoms. ...