Ch12worksheetAPpsyMentalDisorders
... Identify the following symptoms of schizophrenia a. Hey tan man too much fun in the sunb. John grew the house, the bird flew upside down, and the car did flips in the drivewayc. I am working for the C.I.A. as a spy to fight communismd. I think there are people out to get mee. “Sowshot” It may not me ...
... Identify the following symptoms of schizophrenia a. Hey tan man too much fun in the sunb. John grew the house, the bird flew upside down, and the car did flips in the drivewayc. I am working for the C.I.A. as a spy to fight communismd. I think there are people out to get mee. “Sowshot” It may not me ...
Jason Bernard Christopher Rodriguez Christian Lopez
... People with antisocial or alcoholic parents are at increased risk. ...
... People with antisocial or alcoholic parents are at increased risk. ...
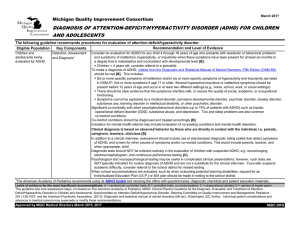
diagnosis of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (adhd)
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
... Consider an evaluation for ADHD for any child 4 through 18 years of age who presents with academic or behavioral problems and symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, or impulsivity when these symptoms have been present for at least six months to a degree that is maladaptive and inconsistent with dev ...
Mental Health and Mental Illness II
... Everyone has ups and downs in their mood. Bipolar disorder is a medical condition Mood swings people have are out of proportion, or unrelated to things going on in their life. ...
... Everyone has ups and downs in their mood. Bipolar disorder is a medical condition Mood swings people have are out of proportion, or unrelated to things going on in their life. ...
Mental Illness pwrpt
... Anxiety Disorders • A disorder that usually causes strong nervousness, worry, or panic and interferes with daily living and functioning. • Can be treated with medicine and/or counseling. Some can be cured completely • Anxiety can be constant over a long time or it may occur in short bursts ...
... Anxiety Disorders • A disorder that usually causes strong nervousness, worry, or panic and interferes with daily living and functioning. • Can be treated with medicine and/or counseling. Some can be cured completely • Anxiety can be constant over a long time or it may occur in short bursts ...
informativespeechoutline
... identify mental illnesses. According to http://www.webmd.com/mentalhealth/dissociative-identity-disorder-multiple-personality-disorder, it is estimated that people with the disorder spend seven years in a mental health system before receiving ...
... identify mental illnesses. According to http://www.webmd.com/mentalhealth/dissociative-identity-disorder-multiple-personality-disorder, it is estimated that people with the disorder spend seven years in a mental health system before receiving ...
Psychobehavioral
... of 1.5-2.0 mEq/L. Dehydration, salt restriction, diuretic use, childbirth and infection predispose patients to these side effects. Which of the following is NOT one of these side effects? A. Diarrhea B. Vomiting C. Drowsiness D. muscular weakness E. lack of coordination ...
... of 1.5-2.0 mEq/L. Dehydration, salt restriction, diuretic use, childbirth and infection predispose patients to these side effects. Which of the following is NOT one of these side effects? A. Diarrhea B. Vomiting C. Drowsiness D. muscular weakness E. lack of coordination ...
Depression and Mental Disorders PP
... Bipolar disorder is characterized by major depressive episodes and a manic episode (Manic Depressive Disorder) ...
... Bipolar disorder is characterized by major depressive episodes and a manic episode (Manic Depressive Disorder) ...
Chapter 5: Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... – Both conditions show rapid onset and dissipation – Both conditions occur most often in females • Causes – Little is known, but trauma and stress seem heavily involved • Treatment – Persons with dissociative amnesia and fugue usually get better without treatment – Most remember what they have forgo ...
... – Both conditions show rapid onset and dissipation – Both conditions occur most often in females • Causes – Little is known, but trauma and stress seem heavily involved • Treatment – Persons with dissociative amnesia and fugue usually get better without treatment – Most remember what they have forgo ...
Somatoform and Dissociative Disorders
... Combined: Hypochondriasis, maybe Somatization Disorder Pain Disorder ...
... Combined: Hypochondriasis, maybe Somatization Disorder Pain Disorder ...
So that explains the voices
... These disorders are marked by the loss of functioning of a specific body part but have no physiological cause. ...
... These disorders are marked by the loss of functioning of a specific body part but have no physiological cause. ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Understand the characteristics of all of the major psychological disorders (know their symptoms & other diagnostic features): Anxiety Disorders: phobias specific phobia biological reasons for phobia learning theory concerning phobias social phobia agoraphobia obsessive-compulsive disor ...
... Understand the characteristics of all of the major psychological disorders (know their symptoms & other diagnostic features): Anxiety Disorders: phobias specific phobia biological reasons for phobia learning theory concerning phobias social phobia agoraphobia obsessive-compulsive disor ...
Mental Health 101
... Thoughts, images, or impulses that occur over and over again and feel out of the person’s control. Repetitive behaviours or thought that a person engages in to neutralize, counteract, or make their obsessions go away. Can also include avoiding situations that trigger their obsessions Time consuming ...
... Thoughts, images, or impulses that occur over and over again and feel out of the person’s control. Repetitive behaviours or thought that a person engages in to neutralize, counteract, or make their obsessions go away. Can also include avoiding situations that trigger their obsessions Time consuming ...
Personality disorder
... psychic numbing, reliving the trauma, and increased physiological arousal Diagnosed only if symptoms persist for six months or longer May immediately follow event or occur later ...
... psychic numbing, reliving the trauma, and increased physiological arousal Diagnosed only if symptoms persist for six months or longer May immediately follow event or occur later ...
View Presentation
... States have been diagnosed • Increasing numbers of children diagnosed with ADHD may be a reflection of changing social expectations, rather than an increase in the frequency of this neurological condition ...
... States have been diagnosed • Increasing numbers of children diagnosed with ADHD may be a reflection of changing social expectations, rather than an increase in the frequency of this neurological condition ...
appsychchapt16
... Hyperalertness to danger. The individual often has difficulty shutting down the fightor-flight response that was activated during the event. This causes sleeplessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, restlessness, and sometimes the development of an exaggerated startle. Hypervigilance an ...
... Hyperalertness to danger. The individual often has difficulty shutting down the fightor-flight response that was activated during the event. This causes sleeplessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, restlessness, and sometimes the development of an exaggerated startle. Hypervigilance an ...
Dissociative and Personality Disorder
... • An individual in a fugue state is unaware of or confused about his identity, and in some cases will assume a new identity (although this is the exception). • Can involve unplanned traveling or wandering ...
... • An individual in a fugue state is unaware of or confused about his identity, and in some cases will assume a new identity (although this is the exception). • Can involve unplanned traveling or wandering ...
Appendix 2
... the use of laxatives or diuretics. Bulimia affects the same group of Symptoms people as anorexia, i.e. young women. The causes are much the same, but the symptoms are different. Also, because the sufferer often looks quite healthy, it is easier to deny, and can be kept secret. Bulimia is ten times ...
... the use of laxatives or diuretics. Bulimia affects the same group of Symptoms people as anorexia, i.e. young women. The causes are much the same, but the symptoms are different. Also, because the sufferer often looks quite healthy, it is easier to deny, and can be kept secret. Bulimia is ten times ...
Kleptomania
... personal use or monetary value. Kleptomania should be distinguished from shoplifting, in which the action is usually well-planned and motivated by need or monetary gain. Some clinicians view kleptomania as part of the obsessive-compulsive spectrum of disorders, reasoning that many individuals experi ...
... personal use or monetary value. Kleptomania should be distinguished from shoplifting, in which the action is usually well-planned and motivated by need or monetary gain. Some clinicians view kleptomania as part of the obsessive-compulsive spectrum of disorders, reasoning that many individuals experi ...
Abnormal Psychology A look at
... Extreme sensitivity to what others think or say about them Social inhibitions( unwilling to get involved with others unless certain of being likes) Belief that they are unappealing or inferior to ...
... Extreme sensitivity to what others think or say about them Social inhibitions( unwilling to get involved with others unless certain of being likes) Belief that they are unappealing or inferior to ...
McMaster Regional Mood Disorders Program
... implementation of recommendations in the community. Consultants will provide diagnostic assessment and specific treatment recommendations. Thereafter consultants may be contacted by phone or patients referred for re-consultation. Legal charges pending is an exclusionary criterion. Active substance a ...
... implementation of recommendations in the community. Consultants will provide diagnostic assessment and specific treatment recommendations. Thereafter consultants may be contacted by phone or patients referred for re-consultation. Legal charges pending is an exclusionary criterion. Active substance a ...
Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders
... Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders The dissociative and somatoform disorders were historically linked with anxiety disorders as forms of neuroses. Anxiety is expressed directly in different forms in the anxiety disorders, but its role in the dissociative and somatoform disorders is inferred. Diss ...
... Dissociative and Somatoform Disorders The dissociative and somatoform disorders were historically linked with anxiety disorders as forms of neuroses. Anxiety is expressed directly in different forms in the anxiety disorders, but its role in the dissociative and somatoform disorders is inferred. Diss ...