Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
1 - Hatboro
... 20. Meaning of kilo? 21. If a substance has a mass of 3.2g and a volume of 8.7 ml. What is its density. 22. How do you convert from celsius to kelvin? 23. Where on the periodic table are the metals? Metalloids? Nonmetals? Nobel gases? 24. What is Dalton's atomic theory? 25. What is an atomic mass un ...
... 20. Meaning of kilo? 21. If a substance has a mass of 3.2g and a volume of 8.7 ml. What is its density. 22. How do you convert from celsius to kelvin? 23. Where on the periodic table are the metals? Metalloids? Nonmetals? Nobel gases? 24. What is Dalton's atomic theory? 25. What is an atomic mass un ...
1 st Nine Weeks Study Guide for Chemistry
... E. How do you tell an element from a compound? Element is one type of atom, a compound is two or more elements chemically combined. F. What are physical properties? Give at least five examples. Have to do with appearance, density, malleable, ductile. Boiling point G. What are chemical properties? Gi ...
... E. How do you tell an element from a compound? Element is one type of atom, a compound is two or more elements chemically combined. F. What are physical properties? Give at least five examples. Have to do with appearance, density, malleable, ductile. Boiling point G. What are chemical properties? Gi ...
CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS: ELEMENTS AND ATOMS
... the nucleus the volume is about 1/10 trillionth the volume of the atom The nucleus is essentially the entire mass of the atom The nucleus is positively charged the amount of positive charge of the nucleus balances the negative charge of the electrons The electrons move around in the empty space of ...
... the nucleus the volume is about 1/10 trillionth the volume of the atom The nucleus is essentially the entire mass of the atom The nucleus is positively charged the amount of positive charge of the nucleus balances the negative charge of the electrons The electrons move around in the empty space of ...
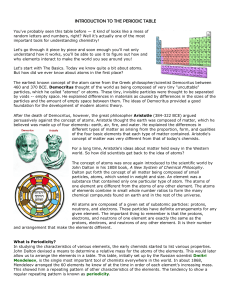
INTRODUCTION TO THE PERIODIC TABLE
... For a long time, Aristotle's ideas about matter held sway in the Western world. So how did scientists get back to the idea of atoms? The concept of atoms was once again introduced to the scientific world by John Dalton in his 1808 book, A New System of Chemical Philosophy. Dalton put forth the conce ...
... For a long time, Aristotle's ideas about matter held sway in the Western world. So how did scientists get back to the idea of atoms? The concept of atoms was once again introduced to the scientific world by John Dalton in his 1808 book, A New System of Chemical Philosophy. Dalton put forth the conce ...
review-basics-atomic-structure-and-electron-configurations-v1
... 16.) Why is Louis de Broglie’s proposal that all particles have wavelike properties significant for small particles such as electrons but not significant for large objects such as ourselves? ...
... 16.) Why is Louis de Broglie’s proposal that all particles have wavelike properties significant for small particles such as electrons but not significant for large objects such as ourselves? ...
AP Chapter 2 Objectives
... Give the approximate size, relative mass, and charge of an atom, proton, neutron, and electron Distinguish between physical and chemical properties and also physical and chemical changes. ...
... Give the approximate size, relative mass, and charge of an atom, proton, neutron, and electron Distinguish between physical and chemical properties and also physical and chemical changes. ...
CHEMISTRY
... become IONS- they have a charge. Ex. a Hydrogen atom that loses it’s electron is called a hydrogen ion, H+, or a proton. ...
... become IONS- they have a charge. Ex. a Hydrogen atom that loses it’s electron is called a hydrogen ion, H+, or a proton. ...
Blue File
... Over the years Many Scientists have put forward ‘models’ that they have arrived at from their research of what they understand an atom to look like……. Firstly came : ‘J.J Thompson’s ‘Plum Pudding ‘ model which showed that ‘atoms were tiny balls of positive charge with tiny negative particles stuck i ...
... Over the years Many Scientists have put forward ‘models’ that they have arrived at from their research of what they understand an atom to look like……. Firstly came : ‘J.J Thompson’s ‘Plum Pudding ‘ model which showed that ‘atoms were tiny balls of positive charge with tiny negative particles stuck i ...
Unit 4 – Electrons in Atoms and Periodic Trends Accelerated
... Write T for true or F for false. If a statement is false, replace the underlined word with one that will make the statement true. 3. If two electrons occupy the same orbital, they must have opposite spins. 4. The principal quantum number describes the energy level of an electron in an atom. 5. The ...
... Write T for true or F for false. If a statement is false, replace the underlined word with one that will make the statement true. 3. If two electrons occupy the same orbital, they must have opposite spins. 4. The principal quantum number describes the energy level of an electron in an atom. 5. The ...
Unit 1 Problem Set
... observable quantity of the element has never been achieved, and may well never be. This is because meitnerium decays very rapidly. (a) Suggest the electron configuration of the ground-state atom of the element. ...
... observable quantity of the element has never been achieved, and may well never be. This is because meitnerium decays very rapidly. (a) Suggest the electron configuration of the ground-state atom of the element. ...
Periodic Trends.notebook January 15, 2015 Periodic Trends Atomic Radius
... Atomic Radius Distance from the nucleus to the highest energy level Increases as you go down a group. This trend occurs because as you move from perriod to period an extra energy level is added. ex. Na has 3 energy levels and K has 4 energy level. K has a larger ionic radius. ...
... Atomic Radius Distance from the nucleus to the highest energy level Increases as you go down a group. This trend occurs because as you move from perriod to period an extra energy level is added. ex. Na has 3 energy levels and K has 4 energy level. K has a larger ionic radius. ...
Atoms and elements Metals and non-metals
... 2. Work out which group the element is in and draw that number of electrons in the outer circle – with eight for Group 0 elements – except helium. 3. Fill the other circles with as many electrons as needed. Remember – two in the first circle, and eight in the second and third circles. 4. Finally, ch ...
... 2. Work out which group the element is in and draw that number of electrons in the outer circle – with eight for Group 0 elements – except helium. 3. Fill the other circles with as many electrons as needed. Remember – two in the first circle, and eight in the second and third circles. 4. Finally, ch ...
Document
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
... Valence Electrons • Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of the atom. • Valence electrons are the only electrons generally involved in bond formation. • The valence electrons in the s and p orbitals are written around the element symbol. • These electrons are the ...
Chemistry Of Life
... “Atomic Number” = number of protons The atomic number determines what type of element an atom is. All atoms of carbon have six for their atomic number. All atoms of oxygen have eight protons. The atomic number never changes in ...
... “Atomic Number” = number of protons The atomic number determines what type of element an atom is. All atoms of carbon have six for their atomic number. All atoms of oxygen have eight protons. The atomic number never changes in ...
Joyce Wang
... mass of an electron from the other value. • He performed the “Mikllikan oil-drop experiment” and measured the charge of an electron. • By using this value, he could find the mass of the electron which he found to be 9.10 x 10^ -28 g • The modern value is 9.10939 x 10^ -28 g ...
... mass of an electron from the other value. • He performed the “Mikllikan oil-drop experiment” and measured the charge of an electron. • By using this value, he could find the mass of the electron which he found to be 9.10 x 10^ -28 g • The modern value is 9.10939 x 10^ -28 g ...
Guided Overview Ch
... Rutherford and the gold foil experiment description: results: implications: ...
... Rutherford and the gold foil experiment description: results: implications: ...
Nature of Matter
... Element – a pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom. -Over 100 elements are known, but only about 24 are found in living organisms. -Elements are represented by symbols, Ex : C = Carbon, H = Hydrogen, etc. -An element’s atomic number = # protons in an atom of the element. ...
... Element – a pure substance that consists entirely of one type of atom. -Over 100 elements are known, but only about 24 are found in living organisms. -Elements are represented by symbols, Ex : C = Carbon, H = Hydrogen, etc. -An element’s atomic number = # protons in an atom of the element. ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... Periodic Table • A chart in which all known elements are listed in order of atomic number • http://theodoregray.com/periodictable/ ...
... Periodic Table • A chart in which all known elements are listed in order of atomic number • http://theodoregray.com/periodictable/ ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the ...
... Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the ...
+ mass isotope 2
... All matter is made of atoms. Atoms of an element are identical. Each element has different atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. • His ideas account for the law of conservation of mass (atoms are neither created nor dest ...
... All matter is made of atoms. Atoms of an element are identical. Each element has different atoms. Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. • His ideas account for the law of conservation of mass (atoms are neither created nor dest ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... Atomic Theory of Matter The theory that atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter reemerged in the early 19th century, championed by John Dalton. ...
... Atomic Theory of Matter The theory that atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter reemerged in the early 19th century, championed by John Dalton. ...