Study List
... for the first ionization energy of any atom as well as multiple ionizations of the same atom. use simple attraction and repulsion ideas to explain how atomic size and ionization energy are inversely related. explain why each successive ionization energy is larger than the previous on in terms of ...
... for the first ionization energy of any atom as well as multiple ionizations of the same atom. use simple attraction and repulsion ideas to explain how atomic size and ionization energy are inversely related. explain why each successive ionization energy is larger than the previous on in terms of ...
Atomic Theory - Boone County Schools
... Rutherford was the first scientist to suggest that protons and neutrons were found in the nucleus and that electrons “orbited” around the nucleus. ...
... Rutherford was the first scientist to suggest that protons and neutrons were found in the nucleus and that electrons “orbited” around the nucleus. ...
Mendeleev`s periodic table
... Task periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds. Describe how Mendeleev used his table to predict the existence and properties ...
... Task periodic table by using properties of these elements and their compounds. Describe how Mendeleev used his table to predict the existence and properties ...
Exam Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... b) All atoms of one element differ from the atoms of every other element. c) Chemical change is the union or separation of atoms. d) Atoms combine in small whole number ratios. 24. J. J. Thomson's experiments with discharge tubes demonstrated that a) alpha particles are the nuclei of helium atoms. b ...
... b) All atoms of one element differ from the atoms of every other element. c) Chemical change is the union or separation of atoms. d) Atoms combine in small whole number ratios. 24. J. J. Thomson's experiments with discharge tubes demonstrated that a) alpha particles are the nuclei of helium atoms. b ...
C-3 Study Guide Name PART A: Use the terms/statements from the
... 23. An atom is electrically neutral because the numbers of protons and electrons are equal. 24. Most of the volume of an atom is occupied by the electrons. 25. The radius of an atom extends to the outer edge of the region occupied by the electrons. 26. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that hav ...
... 23. An atom is electrically neutral because the numbers of protons and electrons are equal. 24. Most of the volume of an atom is occupied by the electrons. 25. The radius of an atom extends to the outer edge of the region occupied by the electrons. 26. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that hav ...
Lecture 2 - U of L Class Index
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
... An element is defined by its atomic number. Changing the number of protons in an atom (as in a nuclear reaction) changes the element. While atoms of the same element must have the same atomic number, they may have different mass numbers. If so, they are referred to as isotopes. Most elements have mo ...
ATOMS
... symbol that tells how many atoms of an element there are in the compound. It means “written below”. • For example: H20 (2 is the subscript) There are 2 atoms of hydrogen (H) and 1 atom of oxygen (O). This makes up 1 molecule of water. ...
... symbol that tells how many atoms of an element there are in the compound. It means “written below”. • For example: H20 (2 is the subscript) There are 2 atoms of hydrogen (H) and 1 atom of oxygen (O). This makes up 1 molecule of water. ...
Inside the Atom connections to the lower secondary (KS3
... • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics related content in the KS3 curriculum is taught in the chemi ...
... • a simple (Dalton) atomic model • differences between atoms, elements and compounds • chemical symbols and formulae for elements and compounds • conservation of mass changes of state and chemical reactions. Most of the nuclear physics related content in the KS3 curriculum is taught in the chemi ...
SNC 1D chem chpt2
... to represent different chemicals are the same in each language, although we do call elements different names. We use a standard atomic notation to represent elements. Mass # is written above, atomic # below and the symbol in large letters to the left. ...
... to represent different chemicals are the same in each language, although we do call elements different names. We use a standard atomic notation to represent elements. Mass # is written above, atomic # below and the symbol in large letters to the left. ...
Elements02
... little. Today we know that the fourth rule is incorrect, because we now know that atoms can be created and destroyed (can you say atomic bomb?). Atoms can be divided into smaller parts called protons and neutrons. These subatomic particles are found in the nucleus (centre) of the atom, and are surro ...
... little. Today we know that the fourth rule is incorrect, because we now know that atoms can be created and destroyed (can you say atomic bomb?). Atoms can be divided into smaller parts called protons and neutrons. These subatomic particles are found in the nucleus (centre) of the atom, and are surro ...
Chapter 2
... Avogadro proposed that "at the same temperature and pressure, equal volumes of different gases contain the same number of particles". If Avogadro's hypothesis is correct, Gay-Lussaci result (figure 2.5): ...
... Avogadro proposed that "at the same temperature and pressure, equal volumes of different gases contain the same number of particles". If Avogadro's hypothesis is correct, Gay-Lussaci result (figure 2.5): ...
Chemistry Comes Alive: Part A
... • Atomic weight = average of mass numbers of all isotopes Radioisotopes • Spontaneous decay (radioactivity) • Similar chemistry to stable isotopes • Can be detected with scanners Radioisotopes • Valuable tools for biological research and medicine • Cause damage to living tissue: • Useful against loc ...
... • Atomic weight = average of mass numbers of all isotopes Radioisotopes • Spontaneous decay (radioactivity) • Similar chemistry to stable isotopes • Can be detected with scanners Radioisotopes • Valuable tools for biological research and medicine • Cause damage to living tissue: • Useful against loc ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Atoms can lose or gain electrons when bonding to make ionic compounds We keep track of the number of electrons that can be lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus ...
... Atoms can lose or gain electrons when bonding to make ionic compounds We keep track of the number of electrons that can be lost or gained with oxidation numbers (also known as charges) Ions are charged particles –when an atom has too many or too few electrons to be neutral No change to the nucleus ...
Glencoe Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom for the Wiki
... Based on atomic theory but no experiment evidence at the time • The ratio of the masses of one element that combine with a constant mass of another element can be expressed in small whole numbers. ...
... Based on atomic theory but no experiment evidence at the time • The ratio of the masses of one element that combine with a constant mass of another element can be expressed in small whole numbers. ...
State Changes Scavenger Hunt
... Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers to these questions. 1. All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of _______________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ___________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of atoms. The many different materials we encounter a ...
... Go to the “ChemTime Clock” area to find the answers to these questions. 1. All materials, whether solid, liquid or gas, are made of _______________. Atoms are the smallest _______ of ___________. Scientists have found over _______ different kinds of atoms. The many different materials we encounter a ...
Chapter 1 Notes: The Science of Chemistry
... energy level (will eventually drop back to the ground state and release energy as a result) See diagram discussing sublevels, orbitals, orbital shape, and energy levels. Aufbau principle- electrons fill orbitals of lowest energy first Pauli exclusion principle- only 2 electrons fit in each orb ...
... energy level (will eventually drop back to the ground state and release energy as a result) See diagram discussing sublevels, orbitals, orbital shape, and energy levels. Aufbau principle- electrons fill orbitals of lowest energy first Pauli exclusion principle- only 2 electrons fit in each orb ...
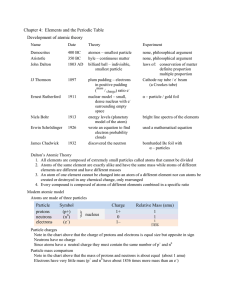
Chapter 4: Elements and the Periodic Table Development of atomic
... Like group 1 metals, group 2 metals are never found as uncombined elements in nature Magnesium (when mixed with a small amount of aluminum) makes lightweight wheels and ladders Calcium ions are needed by the body for bone and muscle growth Ca and Mg are found in dairy products and in leafy green veg ...
... Like group 1 metals, group 2 metals are never found as uncombined elements in nature Magnesium (when mixed with a small amount of aluminum) makes lightweight wheels and ladders Calcium ions are needed by the body for bone and muscle growth Ca and Mg are found in dairy products and in leafy green veg ...
Notes #2 - MRs. Muenks` Site
... ○ ___________ = completely different compound! JOHN DALTON (1803) ● Dalton’s ________________________ 1. All matter is composed of atoms, which are indivisible and indestructible 2. All atoms of the same element are identical 3. All atoms of different elements are different 4. Compounds are composed ...
... ○ ___________ = completely different compound! JOHN DALTON (1803) ● Dalton’s ________________________ 1. All matter is composed of atoms, which are indivisible and indestructible 2. All atoms of the same element are identical 3. All atoms of different elements are different 4. Compounds are composed ...
No Slide Title
... – Proton - a positively charged particle – Neutron - a neutral particle – Electron - a negatively charged particle (much lighter than a Proton or Neutron) ...
... – Proton - a positively charged particle – Neutron - a neutral particle – Electron - a negatively charged particle (much lighter than a Proton or Neutron) ...
Lesson 7
... Atomic Number: the number of protons in the nucleus Protons are tightly held in the nucleus of an atom. It would take a nuclear reaction (such as that inside an atomic bomb or a nuclear reactor) to combine two nuclei into one. Mass Number: The mass of an atom consists of the contents of its nucleus ...
... Atomic Number: the number of protons in the nucleus Protons are tightly held in the nucleus of an atom. It would take a nuclear reaction (such as that inside an atomic bomb or a nuclear reactor) to combine two nuclei into one. Mass Number: The mass of an atom consists of the contents of its nucleus ...
Day 23 How Atoms Differ - WaylandHighSchoolChemistry
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...
... Schrödinger and Heisenberg, and many, many more. Used their brains to venture in the realm of inner space and found the world of the atom was a weird and wondrous place. ...