Chapter 2 Test Review - Mercer Island School District
... vertically on the periodic table? Horizontally? A valence electron in an electron found on the highest or outermost energy level. An atom can have a maximum of 8 valence electrons. Threre are the same amount of valence electrons within a vertical column\ Valence electrons increase moving left ...
... vertically on the periodic table? Horizontally? A valence electron in an electron found on the highest or outermost energy level. An atom can have a maximum of 8 valence electrons. Threre are the same amount of valence electrons within a vertical column\ Valence electrons increase moving left ...
Name: Period: _____ Date
... 8. _____ average mass of all the isotopes of an element 9. _____ any charged particle, an atom that has gained or lost electrons 10. _____ s, p, d, f…sublevels of the electron cloud 11. _____ any element that tends to take electrons and get a negative charge 12. _____ part of an atom with a negative ...
... 8. _____ average mass of all the isotopes of an element 9. _____ any charged particle, an atom that has gained or lost electrons 10. _____ s, p, d, f…sublevels of the electron cloud 11. _____ any element that tends to take electrons and get a negative charge 12. _____ part of an atom with a negative ...
Unit 2
... 60. A chemical bond resulting from the sharing of electrons between two atoms is called a(n) _____ A. Lewis structure. B. ionic bond. C. orbital bond. D. covalent bond. 61. The electrons available to be lost, gained, or shared in the formation of chemical compounds are referred to as _ A. ions. B. e ...
... 60. A chemical bond resulting from the sharing of electrons between two atoms is called a(n) _____ A. Lewis structure. B. ionic bond. C. orbital bond. D. covalent bond. 61. The electrons available to be lost, gained, or shared in the formation of chemical compounds are referred to as _ A. ions. B. e ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table
... c. as elements descend atoms grow larger 4. Elements in rows are called series or periods a. elements are arranged by inc. # of protons (atomic #) b. Total of 7 periods c. Descending periods increase electrons in shells. This is due to increasing mass. d. As one goes across period atoms grow smaller ...
... c. as elements descend atoms grow larger 4. Elements in rows are called series or periods a. elements are arranged by inc. # of protons (atomic #) b. Total of 7 periods c. Descending periods increase electrons in shells. This is due to increasing mass. d. As one goes across period atoms grow smaller ...
Chemistry for Changing Times
... 1.00 g of hydrogen. How much hydrogen can be made from 90.0 g CH4? ...
... 1.00 g of hydrogen. How much hydrogen can be made from 90.0 g CH4? ...
Labs - newtunings.com
... 5.2h Metals tend to react with nonmetals to form ionic compounds. Nonmetals tend to react with other nonmetals to form molecular (covalent) compounds. Ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions have both ionic and covalent bonding. 5.2i When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is forme ...
... 5.2h Metals tend to react with nonmetals to form ionic compounds. Nonmetals tend to react with other nonmetals to form molecular (covalent) compounds. Ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions have both ionic and covalent bonding. 5.2i When a bond is broken, energy is absorbed. When a bond is forme ...
Document
... 55. An element with atomic number-26 is _____. A) Ca B) Fe C) Co D) Ni 56. The element [Ne]3s1 is in the _____ group. A) 1st B) 2nd C) 13th D) 17th 57. The element [Ne]3s23p3 is in the _____ group. A) 13th B) 2nd C) 15th D) 17th 58. The element [Ar]4s23d8 is a/an _____. A) alkali metal B) transition ...
... 55. An element with atomic number-26 is _____. A) Ca B) Fe C) Co D) Ni 56. The element [Ne]3s1 is in the _____ group. A) 1st B) 2nd C) 13th D) 17th 57. The element [Ne]3s23p3 is in the _____ group. A) 13th B) 2nd C) 15th D) 17th 58. The element [Ar]4s23d8 is a/an _____. A) alkali metal B) transition ...
Chemistry Test #1 Study Guide © Chris Khan
... Diatomic Molecule—contains two atoms; Polyatomic Molecule—more than 2 atoms Ion—atom with + or – charge; Cation—net positive charge; Anion—net negative charge Allotrope—one of two or more distinct forms of an element Organic Compounds have carbon while Inorganic don’t Ionic Compounds—have a metal an ...
... Diatomic Molecule—contains two atoms; Polyatomic Molecule—more than 2 atoms Ion—atom with + or – charge; Cation—net positive charge; Anion—net negative charge Allotrope—one of two or more distinct forms of an element Organic Compounds have carbon while Inorganic don’t Ionic Compounds—have a metal an ...
Ch 3: Atomic Structure - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... Excited Atoms and the Fourth of July 1. What is light, and how do various colors of light differ? 2. What is going on at the level of atoms and molecules when fireworks produce colored light? 3. How does the instability of copper chloride at high temperatures ineterfere with its ability to emit blue ...
... Excited Atoms and the Fourth of July 1. What is light, and how do various colors of light differ? 2. What is going on at the level of atoms and molecules when fireworks produce colored light? 3. How does the instability of copper chloride at high temperatures ineterfere with its ability to emit blue ...
Ch 3: Atomic Structure - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... Excited Atoms and the Fourth of July 1. What is light, and how do various colors of light differ? 2. What is going on at the level of atoms and molecules when fireworks produce colored light? 3. How does the instability of copper chloride at high temperatures ineterfere with its ability to emit blue ...
... Excited Atoms and the Fourth of July 1. What is light, and how do various colors of light differ? 2. What is going on at the level of atoms and molecules when fireworks produce colored light? 3. How does the instability of copper chloride at high temperatures ineterfere with its ability to emit blue ...
Chapter 5 Review
... Who discovered the neutron, and in what year? How does the mass of a neutron compare to the mass of a proton? Dalton theorized that atoms are indivisible, and atoms of the same element are identical. Today ... ...
... Who discovered the neutron, and in what year? How does the mass of a neutron compare to the mass of a proton? Dalton theorized that atoms are indivisible, and atoms of the same element are identical. Today ... ...
CHAPTER 5 READING GUIDE – LIGHT AND QUANTIZED ENERGY
... 22. The light of the ______________ sign is produced by passing ______________through a tube filled with neon gas. 23. Neon’s atomic _______________ spectrum consists of several individual lines of _____________ corresponding to the frequencies of the radiation emitted by the atoms of neon. 24. Eac ...
... 22. The light of the ______________ sign is produced by passing ______________through a tube filled with neon gas. 23. Neon’s atomic _______________ spectrum consists of several individual lines of _____________ corresponding to the frequencies of the radiation emitted by the atoms of neon. 24. Eac ...
Introduction to atoms
... • Atomic number increases from left to right on periodic table. • The atomic weight of the atom is indicated below the symbol (in amu). • Why are these weights not whole numbers? ...
... • Atomic number increases from left to right on periodic table. • The atomic weight of the atom is indicated below the symbol (in amu). • Why are these weights not whole numbers? ...
Atoms and Elements Class Notes and Class Work
... Physical Change: a change in a substance with new properties being produces (without a new substance). A physical change does not produce a new substance. Chemical Change: an alteration in a substance in a substance in which a new substance(s) is produced. , having new physical and chemical properti ...
... Physical Change: a change in a substance with new properties being produces (without a new substance). A physical change does not produce a new substance. Chemical Change: an alteration in a substance in a substance in which a new substance(s) is produced. , having new physical and chemical properti ...
Elements and the Periodic Table
... C. Semi-Metals (metalloids) 1.Found along the zig-zag (stair step) line on the periodic table; also called metalloids 2. They are semi-conductors that have properties of both metals and non-metals. ...
... C. Semi-Metals (metalloids) 1.Found along the zig-zag (stair step) line on the periodic table; also called metalloids 2. They are semi-conductors that have properties of both metals and non-metals. ...
Atomic Numbers Notes
... WARM UP “Learn to enjoy the little things – there are so many of them.” 1. What does this quote mean to you? 2. How can you practice this in your everyday life? 3. How does this apply to Chemistry? ...
... WARM UP “Learn to enjoy the little things – there are so many of them.” 1. What does this quote mean to you? 2. How can you practice this in your everyday life? 3. How does this apply to Chemistry? ...
Unit 1 Atoms and Periodic Table Intro Periodic Table Notes
... • electrons located in the valence shell • # of valence e- will determine the reactivity of the atom. • The more Valence e’s the more stable and HAPPY (Noble Gases) • The less valence e’s the more reactive and EXPLOSIVE or ...
... • electrons located in the valence shell • # of valence e- will determine the reactivity of the atom. • The more Valence e’s the more stable and HAPPY (Noble Gases) • The less valence e’s the more reactive and EXPLOSIVE or ...
Atoms and Atomic Theory
... mean? A good starting point is to analyze what it does not mean. For example, the atomic mass of Cl is often quoted on a periodic table as 35.5 and can be represented by the following symbol; ...
... mean? A good starting point is to analyze what it does not mean. For example, the atomic mass of Cl is often quoted on a periodic table as 35.5 and can be represented by the following symbol; ...
atoms - SP Moodle
... Electron Shell 1 can hold: Electron Shell 2 can hold: 8eElectron Shell 3 can hold: 18e- ...
... Electron Shell 1 can hold: Electron Shell 2 can hold: 8eElectron Shell 3 can hold: 18e- ...
Document
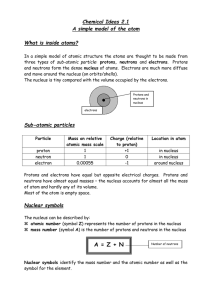
... three types of sub-atomic particle: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the dense nucleus of atoms. Electrons are much more diffuse and move around the nucleus (on orbits/shells). The nucleus is tiny compared with the volume occupied by the electrons. Protons and neutrons in n ...
... three types of sub-atomic particle: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the dense nucleus of atoms. Electrons are much more diffuse and move around the nucleus (on orbits/shells). The nucleus is tiny compared with the volume occupied by the electrons. Protons and neutrons in n ...
chapter2 - AlvarezHChem
... 2. Emit other particles and are transformed into other elements • Particles emitted 1. Beta (β) particles: High speed electrons 2. Alpha (α) particles: helium nuclei 3. Gamma (γ) rays: high energy light ...
... 2. Emit other particles and are transformed into other elements • Particles emitted 1. Beta (β) particles: High speed electrons 2. Alpha (α) particles: helium nuclei 3. Gamma (γ) rays: high energy light ...
Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide (2012-2013)
... The pH of a substance can be determined using ____________________ paper Neutral substances have a pH of __________. An example of a common neutral substance is ____________. Acids- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range fo ...
... The pH of a substance can be determined using ____________________ paper Neutral substances have a pH of __________. An example of a common neutral substance is ____________. Acids- Name 3 properties (ex: feel, taste, uses, etc.): 1. _______________ 2. _______________ 3. _____________ a. pH range fo ...
Periodic Table and Electrons
... The names of groups and periods on the periodic chart are alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases. Metalloids have properties of metals and nonmetals. They are located between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Some are used in semiconductors. Peri ...
... The names of groups and periods on the periodic chart are alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, transition metals, halogens, and noble gases. Metalloids have properties of metals and nonmetals. They are located between metals and nonmetals on the periodic table. Some are used in semiconductors. Peri ...
Name Test Review Chapters 4 and 25 Honors Chemistry 1. Fill in
... Discovered the neutron. _______________________________ Created the first atomic theory based on experimental evidence. ___________________________ Discovered the electron. __________________________ Discovered the nucleus. ___________________________ Discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass. ____ ...
... Discovered the neutron. _______________________________ Created the first atomic theory based on experimental evidence. ___________________________ Discovered the electron. __________________________ Discovered the nucleus. ___________________________ Discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass. ____ ...