File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
... Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical combination of two or more substances on which the identities are retained Nonmetal – is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes ...
INTRODUCTION TO GENERAL CHEMISTRY Basic Principles
... region of a sublevel where electron is located (probability of finding the electron is high); • 4) An orbital can have maximum 2 electrons Number of orbitals ...
... region of a sublevel where electron is located (probability of finding the electron is high); • 4) An orbital can have maximum 2 electrons Number of orbitals ...
UNIT 1 - Grafton Public Schools
... What are the three kinds of subatomic particles? What makes one element different from another? How do isotopes of an element differ? How do you calculate the atomic mass of an element? How do nuclear reactions differ from chemical reactions? What are the three types of nuclear radiation? How much o ...
... What are the three kinds of subatomic particles? What makes one element different from another? How do isotopes of an element differ? How do you calculate the atomic mass of an element? How do nuclear reactions differ from chemical reactions? What are the three types of nuclear radiation? How much o ...
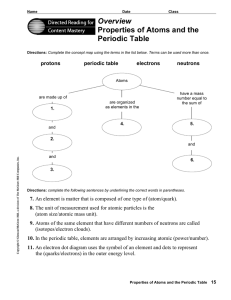
Reading Assignment Worksheet on Atoms - District 196 e
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. Terms can be used more than once. ...
Unit 7: The Nature of Matter Essential Questions:
... o Describe the structure of an atom o Discus the early history of the study of the atom; including the contributions of Aristotle, Democritus, Joseph Priestly, Antoine Lavoisier, John Dalton, J.J. Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, Niels Bohr, and Gilbert Lewis o Explain the organization of the Periodic Ta ...
... o Describe the structure of an atom o Discus the early history of the study of the atom; including the contributions of Aristotle, Democritus, Joseph Priestly, Antoine Lavoisier, John Dalton, J.J. Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, Niels Bohr, and Gilbert Lewis o Explain the organization of the Periodic Ta ...
Atomic Theories Powerpoint
... Took his own experiments and those of others to write a paper, which later became known as the Modern Atomic Theory It gave a compilation of the information at the time and allowed other scientist to test his ideas. ...
... Took his own experiments and those of others to write a paper, which later became known as the Modern Atomic Theory It gave a compilation of the information at the time and allowed other scientist to test his ideas. ...
Atomic History - Seneca High School
... John Dalton Dalton’s Atomic Theory All elements are composed of submicroscopic indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine. Chemical reactions oc ...
... John Dalton Dalton’s Atomic Theory All elements are composed of submicroscopic indivisible particles called atoms. Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of different elements are different. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine. Chemical reactions oc ...
Ess Chem - 2013
... - There are 4 orbitals: o S: 1 shape, can hold a max of 2 electrons. o P: 3 shapes, can hold a max of 6 electrons. (shaped like dumbbells) o D: 5 shapes, can hold a max of 10 electrons. o F: 7 shapes, can hold a max of 14 electrons. - Know how to write electron configurations! Periodic Table and Tre ...
... - There are 4 orbitals: o S: 1 shape, can hold a max of 2 electrons. o P: 3 shapes, can hold a max of 6 electrons. (shaped like dumbbells) o D: 5 shapes, can hold a max of 10 electrons. o F: 7 shapes, can hold a max of 14 electrons. - Know how to write electron configurations! Periodic Table and Tre ...
Name - wsscience
... Ernest Rutherford, a student of Dalton, conducted an alpha particle experiment on gold foil having accepted Dalton’s explanation of atomic structure. Rutherford was surprised as alpha particles _________________________________ disproportionately more than expected as they passed through a thin shee ...
... Ernest Rutherford, a student of Dalton, conducted an alpha particle experiment on gold foil having accepted Dalton’s explanation of atomic structure. Rutherford was surprised as alpha particles _________________________________ disproportionately more than expected as they passed through a thin shee ...
Ppt
... • The shielding of the nucleus by the electrons is greater • The introduction of the next energy ...
... • The shielding of the nucleus by the electrons is greater • The introduction of the next energy ...
Chapter 1 Review Sheet
... 1. element – the most simple form of matter that can’t be broken down by either chemical or physical means 2. compound – two or more elements that are chemically combined 3. atom – the smallest representative part of an element 4. atomic mass unit – the unit used to measure the relative mass of atom ...
... 1. element – the most simple form of matter that can’t be broken down by either chemical or physical means 2. compound – two or more elements that are chemically combined 3. atom – the smallest representative part of an element 4. atomic mass unit – the unit used to measure the relative mass of atom ...
Chemistry--Chapter 5: Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... In contrast, the negatively charged ________________(12) occupy most of the volume of the atom. The number of ________________(13) in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic ________________(14) of that element. Because atoms are electrically neutral, the number of protons and ________________(15) in a ...
... In contrast, the negatively charged ________________(12) occupy most of the volume of the atom. The number of ________________(13) in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic ________________(14) of that element. Because atoms are electrically neutral, the number of protons and ________________(15) in a ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Unit Notes Elements
... Elements- An element is either classified as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. The classification depends on the element’s location on the periodic table. Properties of Metals: o Metals are elements that have luster, conduct heat and electricity, and usually bend without breaking. Metals are also duc ...
... Elements- An element is either classified as a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid. The classification depends on the element’s location on the periodic table. Properties of Metals: o Metals are elements that have luster, conduct heat and electricity, and usually bend without breaking. Metals are also duc ...
Elements Compounds Mixtures
... specific amt of solvent at a given temp. – can’t absorb any more. Alloy: Metal solutions that are Solids dissolved in solids— Brass: copper and Zinc Gold: gold and copper ...
... specific amt of solvent at a given temp. – can’t absorb any more. Alloy: Metal solutions that are Solids dissolved in solids— Brass: copper and Zinc Gold: gold and copper ...
Proton Positively charged subatomic (smaller than an atom) particle
... atom) particle found orbiting the nucleus. Atomic Number- Represents the number of protons, which determines the element type. ...
... atom) particle found orbiting the nucleus. Atomic Number- Represents the number of protons, which determines the element type. ...
Atomic History
... • Bohr Model (Niels Bohr 1913) – electrons are found in specific energy levels in which they can travel w/out radiating energy. – The lowest energy electrons are found closest to the nucleus. The further from the nucleus an electron is, the more energy it has. – When all electrons of an atom ...
... • Bohr Model (Niels Bohr 1913) – electrons are found in specific energy levels in which they can travel w/out radiating energy. – The lowest energy electrons are found closest to the nucleus. The further from the nucleus an electron is, the more energy it has. – When all electrons of an atom ...
Text Questions from Corwin - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... 42. This “atomic fingerprint” indicated that… ...
... 42. This “atomic fingerprint” indicated that… ...
Chemical Equations - Warren County Schools
... results: a small portion of the particles were deflected, indicating a small, concentrated positive charge. Note that the image is not to scale; in reality the nucleus is vastly smaller than the electron shell. ...
... results: a small portion of the particles were deflected, indicating a small, concentrated positive charge. Note that the image is not to scale; in reality the nucleus is vastly smaller than the electron shell. ...
Chapter Test on 4, 5 2016-2017 _____1. You ar
... 25. In a solution, the part that does the dissolving is called the ___________________ 26. In a solution, the part that gets dissolved is called the ________________________ 27. A mixture where the parts will settle after a while is a ______________________ 28. The atomic mass unit (amu) is the mass ...
... 25. In a solution, the part that does the dissolving is called the ___________________ 26. In a solution, the part that gets dissolved is called the ________________________ 27. A mixture where the parts will settle after a while is a ______________________ 28. The atomic mass unit (amu) is the mass ...
Gateway Chemistry Review (Answer Key) Structure and Properties
... How many protons and neutrons does one atom of the following elements contain? Element ...
... How many protons and neutrons does one atom of the following elements contain? Element ...
J.J. Thomson and the Cathode Ray Tube 1897
... atomic masses in periodic table? Isotopes! • Reported numbers actually the average atomic mass units for all masses, This reflects the relative abundance of isotopes for any given element. • In nature almost all elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes ...
... atomic masses in periodic table? Isotopes! • Reported numbers actually the average atomic mass units for all masses, This reflects the relative abundance of isotopes for any given element. • In nature almost all elements occur as a mixture of two or more isotopes ...
Unit 2
... 1) Greeks (Democritus) – 400 B.C. 2) Dalton – 1803 A small particle with several smaller pieces within. ...
... 1) Greeks (Democritus) – 400 B.C. 2) Dalton – 1803 A small particle with several smaller pieces within. ...
Chemical Reactions
... Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Begin by taking an element “inventory” for reactants and products. 2. Pick an element that only occurs once on each side. 3. Determine which side (product or reactant) has fewer of that element and put the coefficient that will make each side equal in front of the mo ...
... Balancing Chemical Equations 1. Begin by taking an element “inventory” for reactants and products. 2. Pick an element that only occurs once on each side. 3. Determine which side (product or reactant) has fewer of that element and put the coefficient that will make each side equal in front of the mo ...