Chapter 4 Outline Onlevel 2013
... 1. By knowing the half life of an element we can determine the age of a substance containing that element. 2. The half - life, (T1/2 ) of a substance is the time it takes for ½ the nuclei in a radioactive sample to decay. 3. Carbon - 14 has a half life of 5730 years. 146C ==> 147N + 0-1e (Carbon 14 ...
... 1. By knowing the half life of an element we can determine the age of a substance containing that element. 2. The half - life, (T1/2 ) of a substance is the time it takes for ½ the nuclei in a radioactive sample to decay. 3. Carbon - 14 has a half life of 5730 years. 146C ==> 147N + 0-1e (Carbon 14 ...
Atomictheory
... Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of atoms that cannot be divided. • All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. • An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of different elements. At ...
... Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of atoms that cannot be divided. • All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass. Atoms of different elements are different and have different masses. • An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of different elements. At ...
Chemistry Midterm Review Study Guide 2012
... 4. a. Which has the larger radius, Al or In? In b. Which has the larger radius, Se or Ca? Ca c. Which has a larger radius, Ca or Ca+2 Ca (would get smaller if lost 2 e-) d. Which has greater ionization energies as a class, metals or nonmetals? nonmetals e. Which has the greater ionization energy, As ...
... 4. a. Which has the larger radius, Al or In? In b. Which has the larger radius, Se or Ca? Ca c. Which has a larger radius, Ca or Ca+2 Ca (would get smaller if lost 2 e-) d. Which has greater ionization energies as a class, metals or nonmetals? nonmetals e. Which has the greater ionization energy, As ...
Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... 1. Students will be familiar with the laws of chemical composition: law of conservation of mass, law of multiple proportions, and law of constant composition. 2. Students will become familiar with the work of classical atomic theorists such as Lavoisier and Dalton. 3. Students will be able to state ...
... 1. Students will be familiar with the laws of chemical composition: law of conservation of mass, law of multiple proportions, and law of constant composition. 2. Students will become familiar with the work of classical atomic theorists such as Lavoisier and Dalton. 3. Students will be able to state ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... contains is called atomic number. Neutron (中子) is another subatomic particle in nucleus, having the similar mass as the proton but electrically neutral. It has very important role in holding the atomic nucleus together. The atom for a given element should have a set number of proton, but the number ...
... contains is called atomic number. Neutron (中子) is another subatomic particle in nucleus, having the similar mass as the proton but electrically neutral. It has very important role in holding the atomic nucleus together. The atom for a given element should have a set number of proton, but the number ...
Chapter 3 Discovering the atom and subatomic particles (History of
... contains is called atomic number. Neutron (中子) is another subatomic particle in nucleus, having the similar mass as the proton but electrically neutral. It has very important role in holding the atomic nucleus together. The atom for a given element should have a set number of proton, but the number ...
... contains is called atomic number. Neutron (中子) is another subatomic particle in nucleus, having the similar mass as the proton but electrically neutral. It has very important role in holding the atomic nucleus together. The atom for a given element should have a set number of proton, but the number ...
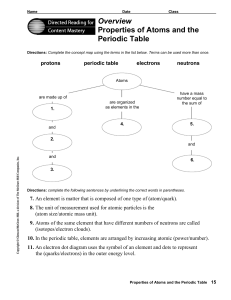
Overview Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
... Directions: Use the terms below to complete the following paragraphs about atoms, atomic mass, and isotopes. Terms may be used more than once. ...
Unit #3 Atoms / Atomic Structure / Subatomic Particles
... The most common isotope of carbon is C12 , therefore it is on the periodic chart. However, C14 also exists in minute quantities (less than 1% of all carbon atoms are this isotope). It is incorporated into the molecules of living substances and remains there even after death (until it "decays"). ...
... The most common isotope of carbon is C12 , therefore it is on the periodic chart. However, C14 also exists in minute quantities (less than 1% of all carbon atoms are this isotope). It is incorporated into the molecules of living substances and remains there even after death (until it "decays"). ...
Unit 3 Power Point
... The most common isotope of carbon is C12 , therefore it is on the periodic chart. However, C14 also exists in minute quantities (less than 1% of all carbon atoms are this isotope). It is incorporated into the molecules of living substances and remains there even after death (until it "decays"). ...
... The most common isotope of carbon is C12 , therefore it is on the periodic chart. However, C14 also exists in minute quantities (less than 1% of all carbon atoms are this isotope). It is incorporated into the molecules of living substances and remains there even after death (until it "decays"). ...
File
... Noble gas atoms have full valence shells. They are stable, low-energy, and unreactive. Other atoms “want” to be like noble gas atoms. They give away or acquire e–. ...
... Noble gas atoms have full valence shells. They are stable, low-energy, and unreactive. Other atoms “want” to be like noble gas atoms. They give away or acquire e–. ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 5. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply ...
... 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form compounds. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. 5. Atoms are indivisible in chemical processes. That is, atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. A chemical reaction simply ...
Study guide for percent abundance chapter 4 spaced out
... b. The release of energy by the electron c. The release of energy by the excited nucleus d. The excitation of the electron e. The absorption of energy by the electron ...
... b. The release of energy by the electron c. The release of energy by the excited nucleus d. The excitation of the electron e. The absorption of energy by the electron ...
Chemistry II Chapter 2 Notes
... for water by measuring the volumes of gases that combined to form a given volume of water. • Avogadro’s hypothesis-based on this work stated that equal volumes of gases at standard temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles. ...
... for water by measuring the volumes of gases that combined to form a given volume of water. • Avogadro’s hypothesis-based on this work stated that equal volumes of gases at standard temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles. ...
CHAPTER 2 - HCC Learning Web
... • A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms • In a covalent bond, the shared electrons count as part of each atom’s valence shell • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of on ...
... • A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms • In a covalent bond, the shared electrons count as part of each atom’s valence shell • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of on ...
Development of Atomic Theory
... All substances made of atoms, which are small, cannot be created or divided or destroyed. Atoms of same element are alike; different elements made of different atoms. Atoms join with different atoms to form new substances. ...
... All substances made of atoms, which are small, cannot be created or divided or destroyed. Atoms of same element are alike; different elements made of different atoms. Atoms join with different atoms to form new substances. ...
CHEMISTRY AND ORGANIC MOLECULES Matter: Has mass and
... Protons and neutrons have same mass (about 2000X that of electron) So electrons really don’t figure into atomic mass Proton, electron equal, but opposite, charges Protons, neutrons equal masses Atomic Number: at lower left of atomic symbol = number of protons Atomic Weight: protons plus neutrons Iso ...
... Protons and neutrons have same mass (about 2000X that of electron) So electrons really don’t figure into atomic mass Proton, electron equal, but opposite, charges Protons, neutrons equal masses Atomic Number: at lower left of atomic symbol = number of protons Atomic Weight: protons plus neutrons Iso ...
Chemistry Curriculum Guide
... Standard CH.2 a, b, c The student will investigate and understand that the placement of elements on the periodic table is a function of their atomic structure. The periodic table is a tool used for the investigations of a) average atomic mass, mass number, and atomic number; b) isotopes, half lives, ...
... Standard CH.2 a, b, c The student will investigate and understand that the placement of elements on the periodic table is a function of their atomic structure. The periodic table is a tool used for the investigations of a) average atomic mass, mass number, and atomic number; b) isotopes, half lives, ...
Document
... • Using the clues from the 7 blue scientist cards, match up the models (yellow cards) with the appropriate scientist card • When you feel that you have made the appropriate matches, make sure that your cards are in chronological order (Hint: There are dates on the blue cards!) ...
... • Using the clues from the 7 blue scientist cards, match up the models (yellow cards) with the appropriate scientist card • When you feel that you have made the appropriate matches, make sure that your cards are in chronological order (Hint: There are dates on the blue cards!) ...
Slide 1
... Atoms of the same element are identical Can combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged, but atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another by a chemical reaction ...
... Atoms of the same element are identical Can combine to form compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged, but atoms of one element are not changed into atoms of another by a chemical reaction ...
DEVELOPMENT OF THE ATOMIC MODEL
... Elements could combine in different ratios, but when they did, they would make different compounds This is now known as the “Law of Multiple Proportions” ...
... Elements could combine in different ratios, but when they did, they would make different compounds This is now known as the “Law of Multiple Proportions” ...
Sir Joseph John Thompson - Physics
... Waves resonate if the frequency is just right for the container (musical instrument). The orbital is the container for the electron and only certain orbitals will work for electrons of a certain energy. the wavelength of a particle l=h/p plank’s ...
... Waves resonate if the frequency is just right for the container (musical instrument). The orbital is the container for the electron and only certain orbitals will work for electrons of a certain energy. the wavelength of a particle l=h/p plank’s ...
History of the atom
... location and velocity of an electron at any point in time • You can estimate where an electron will be 90% of the time • An electron cloud shows where an electron spends most of its time ...
... location and velocity of an electron at any point in time • You can estimate where an electron will be 90% of the time • An electron cloud shows where an electron spends most of its time ...
Standard Atomic Notation 17 35 mass # atomic
... Niels Bohr, suggested the following: electrons can move around the nucleus in nearly circular orbits each electron has a specific amount of energy the farther away from the nucleus the greater the amount of energy electrons cannot exist 'between' these orbits, butcan move up and down from one or ...
... Niels Bohr, suggested the following: electrons can move around the nucleus in nearly circular orbits each electron has a specific amount of energy the farther away from the nucleus the greater the amount of energy electrons cannot exist 'between' these orbits, butcan move up and down from one or ...
KEY DEMOCRITUS • All matter is made of tiny particles • Solid
... Atomic Theory o All elements are made of atoms o All atoms of an element are identical o Atoms are not created or destroyed Solid sphere model of atom Discovered the electron Cathode ray tube experiment o Beam of electrons was… o attracted to positive end of magnet o repelled by negative end of magn ...
... Atomic Theory o All elements are made of atoms o All atoms of an element are identical o Atoms are not created or destroyed Solid sphere model of atom Discovered the electron Cathode ray tube experiment o Beam of electrons was… o attracted to positive end of magnet o repelled by negative end of magn ...