June Exam Review Material World
... A) The element is located in period 1 and is an alkaline earth metal. B) The element is located in period 1 and is an alkali metal. C) The element is located in period 2 and is an alkali metal. D) The element is located in period 2 and is an alkaline earth metal. 15. Four elements from the periodic ...
... A) The element is located in period 1 and is an alkaline earth metal. B) The element is located in period 1 and is an alkali metal. C) The element is located in period 2 and is an alkali metal. D) The element is located in period 2 and is an alkaline earth metal. 15. Four elements from the periodic ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY or Thermodynamics
... • How do we measure and calculate the energy changes that are associated with physical changes and chemical reactions? • What is the relationship between energy changes, heat, and work? • How can we determine whether a chemical reaction is product-favored or reactant-favored at equilibrium? • How ca ...
... • How do we measure and calculate the energy changes that are associated with physical changes and chemical reactions? • What is the relationship between energy changes, heat, and work? • How can we determine whether a chemical reaction is product-favored or reactant-favored at equilibrium? • How ca ...
Chemical Reactions
... the correct orientation and at sufficient speed to react. However, chemists do not yet fully understand the mechanism of even this relatively simple reaction. The process may go through as many as 100 intermediate steps! ...
... the correct orientation and at sufficient speed to react. However, chemists do not yet fully understand the mechanism of even this relatively simple reaction. The process may go through as many as 100 intermediate steps! ...
Transition Metal Oxides - University of Washington
... standard tables of thermodynamic data at any temperature [13,20]. Given the initial CO, O2 and CO2 partial pressures (Pi;in ), it is a trivial exercise in undergraduate chemical thermodynamics to solve Eq. (9) and the appropriate mass balances (dictated by the reaction’s stoichiometry) for the final ...
... standard tables of thermodynamic data at any temperature [13,20]. Given the initial CO, O2 and CO2 partial pressures (Pi;in ), it is a trivial exercise in undergraduate chemical thermodynamics to solve Eq. (9) and the appropriate mass balances (dictated by the reaction’s stoichiometry) for the final ...
Chapter 5
... • How do we measure and calculate the energy changes that are associated with physical changes and chemical reactions? • What is the relationship between energy changes, heat, and work? • How can we determine whether a chemical reaction is product-favored or reactant-favored at equilibrium? • How ca ...
... • How do we measure and calculate the energy changes that are associated with physical changes and chemical reactions? • What is the relationship between energy changes, heat, and work? • How can we determine whether a chemical reaction is product-favored or reactant-favored at equilibrium? • How ca ...
Section 2 Chemical Formulas and Equations
... put together to make chemical formulas that describe substances. Chemical formulas are added together to describe a chemical reaction just as words make a sentence. ...
... put together to make chemical formulas that describe substances. Chemical formulas are added together to describe a chemical reaction just as words make a sentence. ...
Lab 3. Chemical Reactions
... Each element or compound has unique properties that make it distinguishable from other elements or compounds. Physical properties, such as color, luster, softness, electrical conductivity, the temperature at which it melts or boils, crystal structure etc. are characteristics that are visible or meas ...
... Each element or compound has unique properties that make it distinguishable from other elements or compounds. Physical properties, such as color, luster, softness, electrical conductivity, the temperature at which it melts or boils, crystal structure etc. are characteristics that are visible or meas ...
CHEMISTRY
... Chemical equations have to be consistent with the Law of Conservation of Mass, which says that atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. To avoid breaking the Law of Conservation of Mass, you have to learn how to balance equations. Atoms are made up of protons, which have a positive ...
... Chemical equations have to be consistent with the Law of Conservation of Mass, which says that atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical reactions. To avoid breaking the Law of Conservation of Mass, you have to learn how to balance equations. Atoms are made up of protons, which have a positive ...
Atomic Theory PPT
... charge equal in magnitude to the electron’s negative charge. However, it is about 1800 times heavier than the electron. Every element has a specific number of protons. Change the number of protons and you have a new element. Imagine the possibilities! Rutherford had theorized that there must be anot ...
... charge equal in magnitude to the electron’s negative charge. However, it is about 1800 times heavier than the electron. Every element has a specific number of protons. Change the number of protons and you have a new element. Imagine the possibilities! Rutherford had theorized that there must be anot ...
(pdf)
... a one-dimensional composition model was built, describing interdependent ion and neutral densities for altitudes between 600 and 2000 km. 36 neutral species are modeled, undergoing vertical transport below the exobase. The temperature and eddy coefficient profiles are taken from De La Haye et al. (2 ...
... a one-dimensional composition model was built, describing interdependent ion and neutral densities for altitudes between 600 and 2000 km. 36 neutral species are modeled, undergoing vertical transport below the exobase. The temperature and eddy coefficient profiles are taken from De La Haye et al. (2 ...
Chapter 5
... and chemical reactions? • What is the relationship between energy changes, heat, and work? • How can we determine whether a chemical reaction is product-favored or reactant-favored at equilibrium? • How can we determine whether a chemical reaction or physical change will occur spontaneously, that is ...
... and chemical reactions? • What is the relationship between energy changes, heat, and work? • How can we determine whether a chemical reaction is product-favored or reactant-favored at equilibrium? • How can we determine whether a chemical reaction or physical change will occur spontaneously, that is ...
Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Three
... Law of Definite Proportions: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by weight. Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, then the masses of one element that combines with a fixed mass of the other element are in the rat ...
... Law of Definite Proportions: A given compound always contains exactly the same proportion of elements by weight. Law of Multiple Proportions: If two elements can combine to form more than one compound, then the masses of one element that combines with a fixed mass of the other element are in the rat ...
HC CH 4 sec 1
... If you grind a piece of copper into dust, each speck of red dust would still have the properties of copper. • If you could continue to make the dust particles smaller, you would eventually come upon a particle that could no longer be divided and still have the chemical properties of copper. • This ...
... If you grind a piece of copper into dust, each speck of red dust would still have the properties of copper. • If you could continue to make the dust particles smaller, you would eventually come upon a particle that could no longer be divided and still have the chemical properties of copper. • This ...
Lecture Notes
... Note 1: We use the symbols “-e” and “+e” for the electron and proton charge, respectively. This is known as the elementary charge. Note 2: Atoms are electrically neutral. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. This number is known as the “ atomic number ” (symbol: Z). The chemica ...
... Note 1: We use the symbols “-e” and “+e” for the electron and proton charge, respectively. This is known as the elementary charge. Note 2: Atoms are electrically neutral. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. This number is known as the “ atomic number ” (symbol: Z). The chemica ...
F Practice Test #2 Solutions
... C) No reaction will occur. D) Both KNO3 and NiS precipitate from solution. E) KNO3 will precipitate from solution. 10. Which of the following statements concerning equilibrium is not true? A) The equilibrium constant is independent of temperature. B) The value of the equilibrium constant for a given ...
... C) No reaction will occur. D) Both KNO3 and NiS precipitate from solution. E) KNO3 will precipitate from solution. 10. Which of the following statements concerning equilibrium is not true? A) The equilibrium constant is independent of temperature. B) The value of the equilibrium constant for a given ...
Chemical-Principles-7th-Edition-Zumdahl-Test-Bank
... KEY: general chemistry | early atomic theory | chemical substance | chemical formula | ionic substance 17. The ion 127I– has A) 53 protons, 74 neutrons, 52 electrons B) 53 protons, 74 neutrons, 54 electrons C) 53 protons, 53 neutrons, 53 electrons D) 53 protons, 74 neutrons, 53 electrons E) 53 proto ...
... KEY: general chemistry | early atomic theory | chemical substance | chemical formula | ionic substance 17. The ion 127I– has A) 53 protons, 74 neutrons, 52 electrons B) 53 protons, 74 neutrons, 54 electrons C) 53 protons, 53 neutrons, 53 electrons D) 53 protons, 74 neutrons, 53 electrons E) 53 proto ...
atoms - HCC Learning Web
... Law of Multiple Proportions If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. When two or more compounds exist from the ...
... Law of Multiple Proportions If two elements, A and B, form more than one compound, the masses of B that combine with a given mass of A are in the ratio of small whole numbers. Dalton predicted this law and observed it while developing his atomic theory. When two or more compounds exist from the ...
Astrochemistry and Star Formation
... assorted sources and predict abundances of molecules as functions of time and physical conditions. It is the modelers who are at the core of the field, since it is they who compare calculated and observational results to deduce details of the present and perhaps the past of the source. Chemical mode ...
... assorted sources and predict abundances of molecules as functions of time and physical conditions. It is the modelers who are at the core of the field, since it is they who compare calculated and observational results to deduce details of the present and perhaps the past of the source. Chemical mode ...
The Preparation of an Explosive: Nitrogen
... One mole of N2 is created at 944 kJ mol-1 and 3 I-I at 151 kJ mol-1 producing 1397 KJ mol-1. The change in energy is equal to the enthalphy of the reactants deducting the enthalphy of the products, giving the highly exothermic reaction (Fig. 3) and overall energy change of -437 kJ mol-1. 5 Results a ...
... One mole of N2 is created at 944 kJ mol-1 and 3 I-I at 151 kJ mol-1 producing 1397 KJ mol-1. The change in energy is equal to the enthalphy of the reactants deducting the enthalphy of the products, giving the highly exothermic reaction (Fig. 3) and overall energy change of -437 kJ mol-1. 5 Results a ...
Challenge Problems
... was made by the German chemist Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner (1780–1849). In 1816, Döbereiner noticed that the then accepted atomic mass of strontium (50) was midway between the atomic masses of calcium (27.5) and barium (72.5). Note that the accepted atomic masses for these elements today are very dif ...
... was made by the German chemist Johann Wolfgang Döbereiner (1780–1849). In 1816, Döbereiner noticed that the then accepted atomic mass of strontium (50) was midway between the atomic masses of calcium (27.5) and barium (72.5). Note that the accepted atomic masses for these elements today are very dif ...
Search for the Electron Electric Dipole Moment Using PbO
... •Collisional cross-sections as expected anticipated density OK •Signal sizes large, consistent with expectation; improvements under way should reach target count rate: 1011/s. •Shot-noise limited frequency measurement using quantum beats in fluorescence •g-factors of -doublet states match precisel ...
... •Collisional cross-sections as expected anticipated density OK •Signal sizes large, consistent with expectation; improvements under way should reach target count rate: 1011/s. •Shot-noise limited frequency measurement using quantum beats in fluorescence •g-factors of -doublet states match precisel ...
Contents and Concepts
... 1. When is a large negative number (more negative than about – 10 kJ), the reaction is spontaneous as written, and reactants transform almost entirely into products when equilibrium is reached. 2. When ∆Go is a large positive number (more positive than about + 10 kJ), the reaction is not spontaneous ...
... 1. When is a large negative number (more negative than about – 10 kJ), the reaction is spontaneous as written, and reactants transform almost entirely into products when equilibrium is reached. 2. When ∆Go is a large positive number (more positive than about + 10 kJ), the reaction is not spontaneous ...
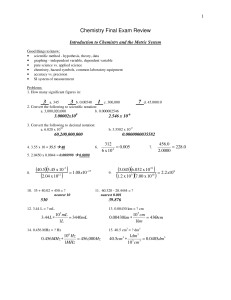
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... Good things to know: • Pre-periodic table patterns: Newland’s Law of Octaves, Dobereiner’s Triads • Mendeleev’s Periodic table (based on atomic mass), holes in his table • Moseley, atomic number, protons, Modern Periodic Law • basic characteristics and names of the major groups • metals, nonmetals, ...
... Good things to know: • Pre-periodic table patterns: Newland’s Law of Octaves, Dobereiner’s Triads • Mendeleev’s Periodic table (based on atomic mass), holes in his table • Moseley, atomic number, protons, Modern Periodic Law • basic characteristics and names of the major groups • metals, nonmetals, ...
FREE Sample Here
... 4. Oxygen has an atomic mass of 16 and an atomic number of 8. A. Oxygen has 16 neutrons. B. Oxygen has 8 electrons. C. Oxygen can form two bonds with other atoms. D. Oxygen has 16 neutrons and 8 electrons. E. Oxygen has 8 electrons and can form two bonds with other atoms. ...
... 4. Oxygen has an atomic mass of 16 and an atomic number of 8. A. Oxygen has 16 neutrons. B. Oxygen has 8 electrons. C. Oxygen can form two bonds with other atoms. D. Oxygen has 16 neutrons and 8 electrons. E. Oxygen has 8 electrons and can form two bonds with other atoms. ...