Periodic Trends
... atoms. Let’s take Na and Cl for example. They are both on n=3. But Cl has 17 protons pulling on n=3 and Na only has 11 protons pulling on n=3. Cl is smaller because it’s nuclear charge is greater. That fact is very important for the trends. Once we can see that the nonmetals tend to be smaller with ...
... atoms. Let’s take Na and Cl for example. They are both on n=3. But Cl has 17 protons pulling on n=3 and Na only has 11 protons pulling on n=3. Cl is smaller because it’s nuclear charge is greater. That fact is very important for the trends. Once we can see that the nonmetals tend to be smaller with ...
General CHemistry Unit 2 Homework Notes
... Subscripts in a chemical formula represent the relative number of each type of atom. The subscript always follows the symbol for the element. Example: In a water molecule, H2O, there are 2 hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Parentheses are used when a subscript affects a group of atoms. Example: th ...
... Subscripts in a chemical formula represent the relative number of each type of atom. The subscript always follows the symbol for the element. Example: In a water molecule, H2O, there are 2 hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. Parentheses are used when a subscript affects a group of atoms. Example: th ...
Regents questions
... Arranging the elements by atomic weight leads to an order slightly different from that in a modern periodic table, where the arrangement is by atomic number. Why does this happen? ...
... Arranging the elements by atomic weight leads to an order slightly different from that in a modern periodic table, where the arrangement is by atomic number. Why does this happen? ...
Mid-Term OR Study Guide
... (C) Write the complete electron configuration for barium. Do not use kernel notation. (D) Draw the Lewis electron dot notation for barium. It is entirely possible that you will be given the orbital notation of an element, and you will need to be able answer questions A, C, and D above, as well as de ...
... (C) Write the complete electron configuration for barium. Do not use kernel notation. (D) Draw the Lewis electron dot notation for barium. It is entirely possible that you will be given the orbital notation of an element, and you will need to be able answer questions A, C, and D above, as well as de ...
Honors Chemistry
... explain why the ____________ electrons did not “fall” into the positive nucleus. ...
... explain why the ____________ electrons did not “fall” into the positive nucleus. ...
Classifying Atoms
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
... appears on pages 698–699 of the Appendix. Of the more than 100 known elements listed there, 92 occur naturally on Earth in significant amounts. The rest are synthetic elements produced by scientists. In each row of the periodic table, elements are listed from left to right in order of increasing num ...
Atoms Introduction Notes and Vocabulary
... Introduction to Atoms- Vocabulary and Notes ATOM - smallest piece of an element that is still that element ELEMENT - matter that is made of only ONE type of atoms. Ex.: Iron, Silver, Carbon, Gold, Oxygen, and others located on the Periodic Table of Elements. PROTON – positively charged particle foun ...
... Introduction to Atoms- Vocabulary and Notes ATOM - smallest piece of an element that is still that element ELEMENT - matter that is made of only ONE type of atoms. Ex.: Iron, Silver, Carbon, Gold, Oxygen, and others located on the Periodic Table of Elements. PROTON – positively charged particle foun ...
5.1 section summary
... properties of elements. For example, it could not explain why metals have colors when heated in flame. To be able to explain the chemical properties of elements or compounds, scientists need to have a model that can describe the behavior of electrons within atoms. The chemical properties of atoms ar ...
... properties of elements. For example, it could not explain why metals have colors when heated in flame. To be able to explain the chemical properties of elements or compounds, scientists need to have a model that can describe the behavior of electrons within atoms. The chemical properties of atoms ar ...
are made up of
... Severalscientists,including Newlands, Meyer, and Mendeleevworked on classificationsystems that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron a ...
... Severalscientists,including Newlands, Meyer, and Mendeleevworked on classificationsystems that grouped elements accordingto their properties. They found that these properties repeated in a regular or periodic manner. This fact was used to predict properties of undiscovered elements. Reviewelectron a ...
Define:
... 71. What is the frequency of ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 4.92 x 10-8m? 72. What is the wavelength of a gamma ray with a frequency of 3.72 x 1020Hz? 73. If three electrons are available to fill three empty 2p orbitals, how will the electrons be distributed? 74. Stable electron configuratio ...
... 71. What is the frequency of ultraviolet light with a wavelength of 4.92 x 10-8m? 72. What is the wavelength of a gamma ray with a frequency of 3.72 x 1020Hz? 73. If three electrons are available to fill three empty 2p orbitals, how will the electrons be distributed? 74. Stable electron configuratio ...
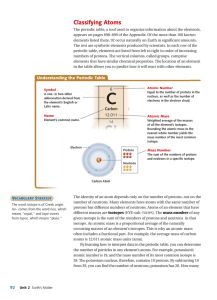
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
Chemistry Review - pams-hoey
... nucleus 2. Radioactive decay: The spontaneous breakdown of an unstable atomic nucleus 3. Decay Series: The series of steps by which a radioactive nucleus decays into a non-radioactive nucleus. 4. Alpha Decay: Occurs when a nucleus releases an alpha particle 5. Beta Decay: Loses a beta particle causi ...
... nucleus 2. Radioactive decay: The spontaneous breakdown of an unstable atomic nucleus 3. Decay Series: The series of steps by which a radioactive nucleus decays into a non-radioactive nucleus. 4. Alpha Decay: Occurs when a nucleus releases an alpha particle 5. Beta Decay: Loses a beta particle causi ...
Review for Bonding Test
... C 14 (C) has how many neutrons? 14 because the 14 is telling you that it is an isotope and has more neutrons than protons. Li 7 (Li) has what mass number? ...
... C 14 (C) has how many neutrons? 14 because the 14 is telling you that it is an isotope and has more neutrons than protons. Li 7 (Li) has what mass number? ...
國立屏東教育大學95學年度研究所碩士班入學考試
... (B) one bonding molecular orbital and one antibonding molecular orbital (C) two bonding molecular orbitals and two antibonding molecular orbitals (D) two bonding molecular orbitals and one antibonding molecular orbital (E) three bonding molecular orbitals and three antibonding molecular orbitals 11. ...
... (B) one bonding molecular orbital and one antibonding molecular orbital (C) two bonding molecular orbitals and two antibonding molecular orbitals (D) two bonding molecular orbitals and one antibonding molecular orbital (E) three bonding molecular orbitals and three antibonding molecular orbitals 11. ...
Chapter 5: The Periodic Law
... • This comprises the elements in Group 2 (2A). Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Ra. • *Properties* These metals have higher densities and higher melting points as well as higher ionization energies. Ergo they are not as reactive as the alkali metals. They all have 2 valence electrons which are fairly easy to ...
... • This comprises the elements in Group 2 (2A). Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, and Ra. • *Properties* These metals have higher densities and higher melting points as well as higher ionization energies. Ergo they are not as reactive as the alkali metals. They all have 2 valence electrons which are fairly easy to ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... Yttrium (Y element 39) Iridium (Ir element 77) Silver (Ag element 47) 2. Review your venn diagram on page 3. Add additional information based on ...
... Yttrium (Y element 39) Iridium (Ir element 77) Silver (Ag element 47) 2. Review your venn diagram on page 3. Add additional information based on ...
Review of Major Concepts Taught in Grade 9 Chemistry
... Valence electrons are the electrons found in the outermost electron orbit or shell. ...
... Valence electrons are the electrons found in the outermost electron orbit or shell. ...
Models of the atom
... •384-322 B.C. – Aristotle- believed in the four elements of air, earth, water and fire. Aristotle felt that regardless of the number of times you cut a form of matter in half, you would always have a smaller piece of that matter. This view held for 2000 years primarily because Aristotle was the tuto ...
... •384-322 B.C. – Aristotle- believed in the four elements of air, earth, water and fire. Aristotle felt that regardless of the number of times you cut a form of matter in half, you would always have a smaller piece of that matter. This view held for 2000 years primarily because Aristotle was the tuto ...