Review Packet
... 111. What is a positively charged electron? 112. The measure of which a radioactive substance loses half of its radioactivity. 113. Where are the heaviest elements (greater than lead) created? 114. What is the type of decay that releases an electron and turns a neutron into a proton? 115. This equat ...
... 111. What is a positively charged electron? 112. The measure of which a radioactive substance loses half of its radioactivity. 113. Where are the heaviest elements (greater than lead) created? 114. What is the type of decay that releases an electron and turns a neutron into a proton? 115. This equat ...
Concepts of Physical Science
... 11. A vertical column on the periodic table; numbered from 1 to 18 12. Exhibit both metallic and nonmetallic properties; eight elements (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At) 13. A horizontal row on the periodic table numbered 1 through 7 14. any electron in the outermost occupied shell of an atom. 15. th ...
... 11. A vertical column on the periodic table; numbered from 1 to 18 12. Exhibit both metallic and nonmetallic properties; eight elements (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, Po, At) 13. A horizontal row on the periodic table numbered 1 through 7 14. any electron in the outermost occupied shell of an atom. 15. th ...
Atomic theory notes
... John Dalton: Early 1800s ~ discovered 4 parts of atomic theory 1. All elements are composed of atoms that cannot be divided 2. All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass 3. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. Atoms cannot be creat ...
... John Dalton: Early 1800s ~ discovered 4 parts of atomic theory 1. All elements are composed of atoms that cannot be divided 2. All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same mass 3. An atom of one element cannot be changed into an atom of a different element. Atoms cannot be creat ...
Final Exam Class Review - Mrs. Kittrell`s Science Classes
... A beta particle is a fast moving electron which is emitted from the nucleus of an atom undergoing radioactive decay. ...
... A beta particle is a fast moving electron which is emitted from the nucleus of an atom undergoing radioactive decay. ...
Identify which of the three subatomic particles (p+, n, e–): is the
... ‘neutrons’ and ‘electrons’. An atom is a thing made up from protons neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom contains the nucleus witch inside contains protons ( P+) neutrons (N). the outside of the attom is a cloud that is created by electrons forming a cloud around the nucleus by moving quick ...
... ‘neutrons’ and ‘electrons’. An atom is a thing made up from protons neutrons and electrons. The center of an atom contains the nucleus witch inside contains protons ( P+) neutrons (N). the outside of the attom is a cloud that is created by electrons forming a cloud around the nucleus by moving quick ...
Gizmos: Types of Reactions
... Introduction: Chemical equations show how compounds and elements react with one another. An element is a substance consisting of one kind of atom, such as aluminum (Al) or oxygen gas (O2). A compound is a substance made of more than one kind of atom, such as water (H2O) or table salt (NaCl). Questio ...
... Introduction: Chemical equations show how compounds and elements react with one another. An element is a substance consisting of one kind of atom, such as aluminum (Al) or oxygen gas (O2). A compound is a substance made of more than one kind of atom, such as water (H2O) or table salt (NaCl). Questio ...
ChemicalBondingPowerpoint
... Water is a small, highly polar molecule. As a result, it is an extremely efficient solvent and has a high capacity for absorbing energy. ...
... Water is a small, highly polar molecule. As a result, it is an extremely efficient solvent and has a high capacity for absorbing energy. ...
File - Mr. Gittermann
... • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
... • Electrons: Subatomic particle with a negative charge found in a certain region of space around the nucleus called the electron cloud; kept close to the atom due to the attraction between the opposite charges of the electron and proton ...
What is an atom?
... pin point exact location, speed, and direction • Located outside nucleus in electron cloud • Electron cloud contains energy levels • Energy levels contain orbitals ...
... pin point exact location, speed, and direction • Located outside nucleus in electron cloud • Electron cloud contains energy levels • Energy levels contain orbitals ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE abbr
... Organize the known elements such that it became easy to learn chemical and physical properties. Create a tool that could predict the existence of elements yet to be discovered. ...
... Organize the known elements such that it became easy to learn chemical and physical properties. Create a tool that could predict the existence of elements yet to be discovered. ...
Chemistry Vocab for Quiz 12/21 or 12/22 Atom – The smallest
... Element – A substance that cannot be broken down into another substance by physical or chemical means. Compound – A substance made of 2 or elements chemically combined in a specific ratio. Chemical bond – the force that holds 2 atoms together. Mixture – Two or more substances that are mixed together ...
... Element – A substance that cannot be broken down into another substance by physical or chemical means. Compound – A substance made of 2 or elements chemically combined in a specific ratio. Chemical bond – the force that holds 2 atoms together. Mixture – Two or more substances that are mixed together ...
Ch 3 studentElements Ions Isotopes
... 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements ...
... 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure Notes
... A. Dimitri Mendeleev (1869) (Russian) – publishing the 1st periodic table based on increasing atomic mass no. 1. The elements fell into 7 columns based on chemical & physical properties 2. He left spaces for undiscovered elements B. Henry Mosely (1913) (British) publishes the “modern” periodic table ...
... A. Dimitri Mendeleev (1869) (Russian) – publishing the 1st periodic table based on increasing atomic mass no. 1. The elements fell into 7 columns based on chemical & physical properties 2. He left spaces for undiscovered elements B. Henry Mosely (1913) (British) publishes the “modern” periodic table ...
Ch. 5 Outline Notes
... a. Hypothesized _________________ using experiments B. __________________ Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of ________________ 2. Atoms are _______________________ and cannot be __________________ into smaller particles (later proved _______________) 3. All atoms of one element are exactly ______ ...
... a. Hypothesized _________________ using experiments B. __________________ Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made of ________________ 2. Atoms are _______________________ and cannot be __________________ into smaller particles (later proved _______________) 3. All atoms of one element are exactly ______ ...
Document
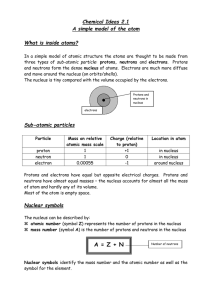
... three types of sub-atomic particle: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the dense nucleus of atoms. Electrons are much more diffuse and move around the nucleus (on orbits/shells). The nucleus is tiny compared with the volume occupied by the electrons. Protons and neutrons in n ...
... three types of sub-atomic particle: protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the dense nucleus of atoms. Electrons are much more diffuse and move around the nucleus (on orbits/shells). The nucleus is tiny compared with the volume occupied by the electrons. Protons and neutrons in n ...
Biochemistry Introduction day 1
... Chemical Reactions: when elements and compounds interact with each other to form new substances. Reactant: A substance that undergoes a chemical reaction. Product: A substance formed from chemical reaction. Chemical Equations: Communicate what is happening in a chemical reaction. It can be done in a ...
... Chemical Reactions: when elements and compounds interact with each other to form new substances. Reactant: A substance that undergoes a chemical reaction. Product: A substance formed from chemical reaction. Chemical Equations: Communicate what is happening in a chemical reaction. It can be done in a ...
SLE133 – “Chemistry in Our World” Summary Notes Week 1
... Isotopes are atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers. Eg: Isotopes of Hydrogen; Isotope Symbol Atomic Number Mass Number ...
... Isotopes are atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers. Eg: Isotopes of Hydrogen; Isotope Symbol Atomic Number Mass Number ...
Packet
... 39. For the following elements, provide information as to group, block and metal status as indicated on the top of the chart. Element ...
... 39. For the following elements, provide information as to group, block and metal status as indicated on the top of the chart. Element ...
Snc2d Chapter 5 Practice Test
... 10. a) What is a “diatomic element”? b) Write the formulas for ALL the diatomic elements. 11. NEATLY Fill in the chart below with the correct name or formula. Correct spelling is essential. ...
... 10. a) What is a “diatomic element”? b) Write the formulas for ALL the diatomic elements. 11. NEATLY Fill in the chart below with the correct name or formula. Correct spelling is essential. ...
Study Guide 1st Semester
... 31. What is a valence electron? 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkal ...
... 31. What is a valence electron? 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkal ...
Unit 4 – Atomic Structure Study Guide
... Dalton considered atoms to be whole and indivisible, that is, only whole atoms can be combined to form compounds. In the above formula, there are 1.5 Mg atoms, which is not possible based upon the indivisibility of an atom. 4. Complete the following table on the subatomic particles. PARTICLE Proto ...
... Dalton considered atoms to be whole and indivisible, that is, only whole atoms can be combined to form compounds. In the above formula, there are 1.5 Mg atoms, which is not possible based upon the indivisibility of an atom. 4. Complete the following table on the subatomic particles. PARTICLE Proto ...
Name
... 1. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in an atom of bromine-80? Write the symbol notation for this isotope. ...
... 1. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in an atom of bromine-80? Write the symbol notation for this isotope. ...
Periodic Table ppt
... Elements are formed with a nucleus, and inside the nucleus is protons and neutrons. Around the nucleus are energy fields, and inside the energy fields are are electrons. ...
... Elements are formed with a nucleus, and inside the nucleus is protons and neutrons. Around the nucleus are energy fields, and inside the energy fields are are electrons. ...