2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
... Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. ...
... Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. ...
Atomic Theory - Hutchk12.org
... This new discovery of parts of atoms that Thomson called electrons means that to get a better picture (model, theory, explanation) of atoms, scientists had to admit that atoms had parts and one of these parts were negative particles called ...
... This new discovery of parts of atoms that Thomson called electrons means that to get a better picture (model, theory, explanation) of atoms, scientists had to admit that atoms had parts and one of these parts were negative particles called ...
CHM1011 Lecture 1 – Atomic Structure Discovery of the Atom
... properties as well as particle-like properties • De Broglie proposed that matter should exhibit WPD properties given by λ=h/p; where p=mv • Electrons have wavelength motions that are restricted to an orbit of fixed energy called resonant waves • Schrödinger’s “wave equation”, using ψ to determine th ...
... properties as well as particle-like properties • De Broglie proposed that matter should exhibit WPD properties given by λ=h/p; where p=mv • Electrons have wavelength motions that are restricted to an orbit of fixed energy called resonant waves • Schrödinger’s “wave equation”, using ψ to determine th ...
What is an ion?
... When atoms get close to each other their electron “clouds” can overlap and interact. ...
... When atoms get close to each other their electron “clouds” can overlap and interact. ...
atomic - WordPress.com
... received two Nobel Prizes (one for physics and one for chemistry) • She discovered and isolated the radioactive element radium. ...
... received two Nobel Prizes (one for physics and one for chemistry) • She discovered and isolated the radioactive element radium. ...
History of the Atomic Theory
... nuclei of most atoms known at the time; said that all atoms of a given element had the same number of positive charges (protons); rearranged Mendeleev’s periodic table ...
... nuclei of most atoms known at the time; said that all atoms of a given element had the same number of positive charges (protons); rearranged Mendeleev’s periodic table ...
SECTION REVIEW
... ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in an atom of that element. ________ 13. An atom of nitrogen has 7 protons and 7 neutrons. ________ 14. Relative a ...
... ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in an atom of that element. ________ 13. An atom of nitrogen has 7 protons and 7 neutrons. ________ 14. Relative a ...
Intro to Chemistry
... regardless of how many neutrons it has and living systems use 12C the same way as 14C. Researchers and clinicians who want to track a particular substance can use a tracer. ...
... regardless of how many neutrons it has and living systems use 12C the same way as 14C. Researchers and clinicians who want to track a particular substance can use a tracer. ...
World of Chemistry Chapter 11—Modern Atomic Theory
... A. Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus but could not describe the electrons in his model B. Rutherford imagined that the electrons moved around the nucleus in circular orbits like planets around the sun C. Rutherford could NOT explain why the negative electrons did not collapse into the positiv ...
... A. Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus but could not describe the electrons in his model B. Rutherford imagined that the electrons moved around the nucleus in circular orbits like planets around the sun C. Rutherford could NOT explain why the negative electrons did not collapse into the positiv ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions I. Atomic Theory A. Dalton`s Postulates
... 1. For main group elements, the charges of the ions formed by the atoms can be predicted by applying this principle: Atoms that are close to a noble gas( the nonmetals) form ions that contain the same number of electrons as the neighboring noble gas atom. 2. Metals of group 1A –3A form positive ions ...
... 1. For main group elements, the charges of the ions formed by the atoms can be predicted by applying this principle: Atoms that are close to a noble gas( the nonmetals) form ions that contain the same number of electrons as the neighboring noble gas atom. 2. Metals of group 1A –3A form positive ions ...
Chapter 3
... • 16O is the most abundant stable O isotope. • How many protons and neutrons are in 16O? 8 protons and 8 neutrons 17O is the least abundant stable O isotope. How many protons and neutrons are in 17O? 8 protons and 9 neutrons 18O is the second most abundant stable O isotope. How many protons a ...
... • 16O is the most abundant stable O isotope. • How many protons and neutrons are in 16O? 8 protons and 8 neutrons 17O is the least abundant stable O isotope. How many protons and neutrons are in 17O? 8 protons and 9 neutrons 18O is the second most abundant stable O isotope. How many protons a ...
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding
... • We will state the octet rule. • We will see how to write Lewis structures. • We will explain why people use resonance structures. ...
... • We will state the octet rule. • We will see how to write Lewis structures. • We will explain why people use resonance structures. ...
Oct 242:59 PM Oct 242:59 PM Oct 242:59 PM Oct 242:59 PM Oct
... energy level of an atom. (NEVER MORE THAN 8!) Ø VALENCE ELECTRONS determine the chemical properties and ability to form bonds with other atoms. Ø An atom is happiest or MOST STABLE when its outer shell is full or empty (and if it is empty it is gone so the shell inside of it is now the outermost she ...
... energy level of an atom. (NEVER MORE THAN 8!) Ø VALENCE ELECTRONS determine the chemical properties and ability to form bonds with other atoms. Ø An atom is happiest or MOST STABLE when its outer shell is full or empty (and if it is empty it is gone so the shell inside of it is now the outermost she ...
Atomic Models - South Houston High School
... 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ...
... 1. All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. 3. Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ...
Entry Task
... • Elements like to have 8 electrons orbiting in the outside electron shell • Group numbers can tell you how many electrons are in the outer shell – Group 1- has 1 – Group 2- has 2 – Group 13- has 3 – Group 14- has 4 – Group 15-has 5 – Group 16- has 6 – group 17- has 7 – group 18- has 8 • If a group ...
... • Elements like to have 8 electrons orbiting in the outside electron shell • Group numbers can tell you how many electrons are in the outer shell – Group 1- has 1 – Group 2- has 2 – Group 13- has 3 – Group 14- has 4 – Group 15-has 5 – Group 16- has 6 – group 17- has 7 – group 18- has 8 • If a group ...
File
... quantum theory to Rutherford’s atomic structure by assuming that electrons travel in stationary orbits defined by their angular momentum. This led to the calculation of possible energy levels for these orbits and the postulation that the emission of light occurs when an electron moves into a lower e ...
... quantum theory to Rutherford’s atomic structure by assuming that electrons travel in stationary orbits defined by their angular momentum. This led to the calculation of possible energy levels for these orbits and the postulation that the emission of light occurs when an electron moves into a lower e ...
What do atoms look like?
... mass number and atomic mass? • Atomic Mass= weighted average of the masses of all known isotopes of an element. • Mass Number = protons + neutrons for a particular isotope of an element ***Round atomic mass to the nearest whole number to get the mass number for the most common isotope of that elemen ...
... mass number and atomic mass? • Atomic Mass= weighted average of the masses of all known isotopes of an element. • Mass Number = protons + neutrons for a particular isotope of an element ***Round atomic mass to the nearest whole number to get the mass number for the most common isotope of that elemen ...
Answer = 1.81 x 10 24 molecules
... • Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole – number ratios to form chemical compounds • In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...
... • Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties • Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed • Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole – number ratios to form chemical compounds • In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged ...
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
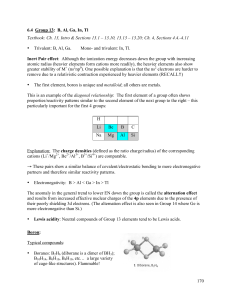
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
... Inert Pair effect: Although the ionization energy decreases down the group with increasing atomic radius (heavier elements form cations more readily), the heavier elements also show greater stability of M+ (ns2np0). One possible explanation is that the ns2 electrons are harder to remove due to a rel ...
Bucher Regents Review
... 1. The placement or location of elements on the periodic table gives an indication of physical and chemical properties of that element. The elements on the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. A few elements have smaller atomic masses than the elements that precede them ...
... 1. The placement or location of elements on the periodic table gives an indication of physical and chemical properties of that element. The elements on the periodic table are arranged in order of increasing atomic number. A few elements have smaller atomic masses than the elements that precede them ...
S2 Chemistry - Aberdeen Grammar School
... Compounds can only be separated into their elements using chemical methods such as electrolysis or heating with carbon. ...
... Compounds can only be separated into their elements using chemical methods such as electrolysis or heating with carbon. ...