atoms - My CCSD
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
... identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. ...
T212 Atomic Structure Past Paper Questions
... Explain why the difference between the 4th and 5th ionization energies is much greater than the difference between any two other successive values. (2) ...
... Explain why the difference between the 4th and 5th ionization energies is much greater than the difference between any two other successive values. (2) ...
1b Atomic Structure
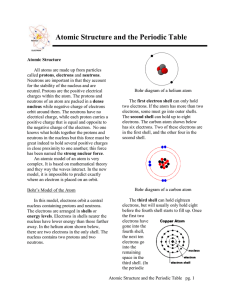
... has been named the strong nuclear force. An atomic model of an atom is very complex. It is based on mathematical theory and they way the waves interact. In the new model, it is impossible to predict exactly where an electron is placed on an orbit. Bohr’s Model of the Atom In this model, electrons or ...
... has been named the strong nuclear force. An atomic model of an atom is very complex. It is based on mathematical theory and they way the waves interact. In the new model, it is impossible to predict exactly where an electron is placed on an orbit. Bohr’s Model of the Atom In this model, electrons or ...
PRACTICE PROBLEMS EXAM 1,2 and 3 1311
... 14) The average atomic weight of copper, which has two naturally occurring isotopes, is 63.5. One of the isotopes has an atomic weight of 62.9 amu and constitutes 69.1% of the copper isotopes. The other isotope has an abundance of 30.9%. The atomic weight (amu) of the second isotope is __________ am ...
... 14) The average atomic weight of copper, which has two naturally occurring isotopes, is 63.5. One of the isotopes has an atomic weight of 62.9 amu and constitutes 69.1% of the copper isotopes. The other isotope has an abundance of 30.9%. The atomic weight (amu) of the second isotope is __________ am ...
Atoms and Elements
... The periodic law states that the properties of elements recur in a repeating pattern when arranged according to increasing atomic number. ...
... The periodic law states that the properties of elements recur in a repeating pattern when arranged according to increasing atomic number. ...
Lecture4
... Alpha particles (named after and denoted by the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α) consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is produced in the process of alpha decay. The alpha particle can be written as He2+, 42He2+ or 42He .So ...
... Alpha particles (named after and denoted by the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α) consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is produced in the process of alpha decay. The alpha particle can be written as He2+, 42He2+ or 42He .So ...
Fall 2015 Review-2
... ____ 37. The metals in Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A ____. a. gain electrons when they form ions c. all have ions with a 1 charge b. all form ions with a negative charge d. lose electrons when they form ions ____ 38. Which of the following statements correctly compares the relative size of an ion to its neu ...
... ____ 37. The metals in Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A ____. a. gain electrons when they form ions c. all have ions with a 1 charge b. all form ions with a negative charge d. lose electrons when they form ions ____ 38. Which of the following statements correctly compares the relative size of an ion to its neu ...
Inside the proton
... particles can probe shorter distances. At SLAC the electrons had enough energy to probe deep inside the protons. Also, there was enough energy to disrupt the proton and make new particles: the collisions were inelastic. This process is called deep inelastic scattering. ...
... particles can probe shorter distances. At SLAC the electrons had enough energy to probe deep inside the protons. Also, there was enough energy to disrupt the proton and make new particles: the collisions were inelastic. This process is called deep inelastic scattering. ...
PAP Chemistry - Fall Final Review
... 6. What did Rutherford discover from the Gold Foil Experiment – p.72 The nucleus and that the atom was mostly empty space 7. When is a bright-line spectrum produced by an atom? IE – How does an atom give off color (especially when burned)? The resting state or the ground state is when the electron i ...
... 6. What did Rutherford discover from the Gold Foil Experiment – p.72 The nucleus and that the atom was mostly empty space 7. When is a bright-line spectrum produced by an atom? IE – How does an atom give off color (especially when burned)? The resting state or the ground state is when the electron i ...
Chapter 11 Modern Atomic Theory
... Recall and understand that the noble gases have full outer shells that represent stable electronic configurations Recall the definition of ionization energy Recall the definition of electron affinity Recall and understand the variation in ionization energy when moving about the periodic tabl ...
... Recall and understand that the noble gases have full outer shells that represent stable electronic configurations Recall the definition of ionization energy Recall the definition of electron affinity Recall and understand the variation in ionization energy when moving about the periodic tabl ...
Section 4.2
... How does an atom's structure determine how it reacts with other atoms? The key is the atom's electrons. Electrons differ in the amount of energy they have and how tightly they are held by the protons in the nucleus. Based on these properties, chemists describe an atom's electrons as belonging to cer ...
... How does an atom's structure determine how it reacts with other atoms? The key is the atom's electrons. Electrons differ in the amount of energy they have and how tightly they are held by the protons in the nucleus. Based on these properties, chemists describe an atom's electrons as belonging to cer ...
Elements and atomic structure
... The smallest part of an element that is representative of that element. The nucleus is the central region of the atom that contains most of the mass and all the positive charge. The nucleus contains protons (p+) and neutrons (n) Electrons (e-) occupy the space outside of the nucleus. ...
... The smallest part of an element that is representative of that element. The nucleus is the central region of the atom that contains most of the mass and all the positive charge. The nucleus contains protons (p+) and neutrons (n) Electrons (e-) occupy the space outside of the nucleus. ...
Review Material
... can be expressed by EK T. Gas molecules collide with each other and with the walls of their container, but they do so without loss of energy (The collisions are said, by scientists, to be "perfectly elastic"). ...
... can be expressed by EK T. Gas molecules collide with each other and with the walls of their container, but they do so without loss of energy (The collisions are said, by scientists, to be "perfectly elastic"). ...
Unit 3
... Use the following terms in 2-4 sentences that describe how we can find the following on the periodic table. You may work with 1 partner. ...
... Use the following terms in 2-4 sentences that describe how we can find the following on the periodic table. You may work with 1 partner. ...
Atomic Structure Review Packet
... 26. State the total number of valence electrons in a lithium atom in the ground state. ...
... 26. State the total number of valence electrons in a lithium atom in the ground state. ...
We will have a brief glimpse of atomic structure. The notion of atomic
... But it is very well known that diffraction is a property that can only be exhibited by waves and not by particles.Thus since waves and particles both show diffraction, it was Louis de Broglie who gave the famous hypothesis of wave-particle duality of matter. Naturally, the next question came up as t ...
... But it is very well known that diffraction is a property that can only be exhibited by waves and not by particles.Thus since waves and particles both show diffraction, it was Louis de Broglie who gave the famous hypothesis of wave-particle duality of matter. Naturally, the next question came up as t ...
2.4 The Periodic Table
... 2.2 Elements and Atomic Number • Atomic Number (Z) is the number of protons in atoms of a given element. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. • Atoms are neutral because the number of positively charged protons and the number of negatively charged electr ...
... 2.2 Elements and Atomic Number • Atomic Number (Z) is the number of protons in atoms of a given element. All atoms of a particular element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. • Atoms are neutral because the number of positively charged protons and the number of negatively charged electr ...
Chapter 3 Powerpoint
... When connected to electric current the remaining the gas forms a BEAM OF LIGHT. The beam always started at the NEGATIVE electrode and flowed to the POSITIVE electrode. The electrode is named by what type of particle it ...
... When connected to electric current the remaining the gas forms a BEAM OF LIGHT. The beam always started at the NEGATIVE electrode and flowed to the POSITIVE electrode. The electrode is named by what type of particle it ...
NGSS Ps1. 1 Targets 1 and 2- Atoms, Elements, Molecules, and
... Scientist used to believe that matter was made up of four elements (air, earth, fire and water). We now know that all matter in the universe is made of slightly more than 100 different substances called elements. ...
... Scientist used to believe that matter was made up of four elements (air, earth, fire and water). We now know that all matter in the universe is made of slightly more than 100 different substances called elements. ...
NGSS Ps1. 1 Targets 1 and 2- Atoms, Elements, Molecules, and
... Scientist used to believe that matter was made up of four elements (air, earth, fire and water). We now know that all matter in the universe is made of slightly more than 100 different substances called elements. ...
... Scientist used to believe that matter was made up of four elements (air, earth, fire and water). We now know that all matter in the universe is made of slightly more than 100 different substances called elements. ...
Polyatomic Ions (Memorize for Wednesday, January 31
... Oxidation Numbers (similar to valence electrons) Group 1 = +1 Group 2 = +2 Groups 13-18 = group # - 10 for most elements d-block elements must be looked up (groups 3-12 use roman numerals) oxidation numbers for ALL compounds MUST equal zero Metal-Non-metal (binary ionic compounds, only 2 elements) M ...
... Oxidation Numbers (similar to valence electrons) Group 1 = +1 Group 2 = +2 Groups 13-18 = group # - 10 for most elements d-block elements must be looked up (groups 3-12 use roman numerals) oxidation numbers for ALL compounds MUST equal zero Metal-Non-metal (binary ionic compounds, only 2 elements) M ...
- Palisades School District
... 1. The oxidation number of any uncombined element is O. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equal the charge on the ion. 3. The more electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in ...
... 1. The oxidation number of any uncombined element is O. 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equal the charge on the ion. 3. The more electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in ...
Sample Exam 1
... Part One: Multiple Choice – circle one answer only. 1. When methane is burned with oxygen, the products are carbon dioxide and water. If you produce 36 g of water and 44 grams of carbon dioxide from 16 grams of methane, how many grams of oxygen were needed for the reaction? a) 64 g b) 80 g c) 32 g d ...
... Part One: Multiple Choice – circle one answer only. 1. When methane is burned with oxygen, the products are carbon dioxide and water. If you produce 36 g of water and 44 grams of carbon dioxide from 16 grams of methane, how many grams of oxygen were needed for the reaction? a) 64 g b) 80 g c) 32 g d ...