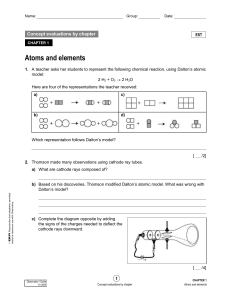
Name___________________________________ Physical
... D) Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic particle. E) Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. ...
... D) Electrons are negatively charged and are the heaviest subatomic particle. E) Neutrons have no charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. ...
electron configuration
... The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pulled into the positively charged nucleus. ...
... The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pulled into the positively charged nucleus. ...
Chemistry-Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Page
... positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
... positive H and two other atoms (slightly negative O or N) - Easily broken by Temp or pH - Found in: H2O, Proteins, Nucleic Acids ...
Atomic Structure
... • Nitrogen is in the second row so it has two orbits surrounding its nucleus. • The nucleus should contain 7 protons. • There should be 7 total electrons. 2 in the first orbit and 5 in the second orbit. • Figure the number of neutrons by subtracting the number of protons from the atomic mass. (14 – ...
... • Nitrogen is in the second row so it has two orbits surrounding its nucleus. • The nucleus should contain 7 protons. • There should be 7 total electrons. 2 in the first orbit and 5 in the second orbit. • Figure the number of neutrons by subtracting the number of protons from the atomic mass. (14 – ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Solon City Schools
... Radioactive C-14 is formed in the upper atmosphere by nuclear reactions initiated by neutrons in cosmic radiation 14N + 1 n ---> 14C + 1H o The C-14 is oxidized to CO2, which circulates through the biosphere. When a plant dies, the C-14 is not replenished. But the C-14 continues to decay with t1/2 = ...
... Radioactive C-14 is formed in the upper atmosphere by nuclear reactions initiated by neutrons in cosmic radiation 14N + 1 n ---> 14C + 1H o The C-14 is oxidized to CO2, which circulates through the biosphere. When a plant dies, the C-14 is not replenished. But the C-14 continues to decay with t1/2 = ...
Atoms and Atomic Structure Learning Targets
... Describe the nucleus of an atom and what makes it up. Identify how to determine the mass of an atom. Explain what the electron cloud of an atom is and what makes it up. Explain what the energy levels (orbitals/shells) are within the electron cloud and how many electrons can fit on each level. Identi ...
... Describe the nucleus of an atom and what makes it up. Identify how to determine the mass of an atom. Explain what the electron cloud of an atom is and what makes it up. Explain what the energy levels (orbitals/shells) are within the electron cloud and how many electrons can fit on each level. Identi ...
Chapter 1 File
... Chemists make their observations in the macroscopic world and seek to understand the fundamental properties of matter at the level of the microscopic world (i.e. molecules and atoms). The reason why certain chemicals react the way they do is a direct consequence of their atomic structure. The word " ...
... Chemists make their observations in the macroscopic world and seek to understand the fundamental properties of matter at the level of the microscopic world (i.e. molecules and atoms). The reason why certain chemicals react the way they do is a direct consequence of their atomic structure. The word " ...
Atomic Structure Notes_BohrRing Activity
... different #’s of neutrons › # of neutrons = Atomic mass # - Atomic # › Atomic mass = neutrons + protons ...
... different #’s of neutrons › # of neutrons = Atomic mass # - Atomic # › Atomic mass = neutrons + protons ...
document
... electron as a cloud (region of space) An electron’s location at any time can not be pinpointed exactly, yet you have a good idea of where it should be. Also, each energy level contains subshells called orbitals (these are the s, p, d and f orbitals). ...
... electron as a cloud (region of space) An electron’s location at any time can not be pinpointed exactly, yet you have a good idea of where it should be. Also, each energy level contains subshells called orbitals (these are the s, p, d and f orbitals). ...
Science-M2-Basic-Che..
... elements. You can use the carbon atom to show its atomic number and mass and then elicit the atomic number and mass of the other atom. Finally, draw an isotope of carbon (perhaps carbon 14) and one of the other atom, point out the difference between the two carbons and elicit the difference between ...
... elements. You can use the carbon atom to show its atomic number and mass and then elicit the atomic number and mass of the other atom. Finally, draw an isotope of carbon (perhaps carbon 14) and one of the other atom, point out the difference between the two carbons and elicit the difference between ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... 24. A sample of nickel (average atomic mass 58.69 u) has a mass of 11.74 g. How many atoms does it contain? ...
... 24. A sample of nickel (average atomic mass 58.69 u) has a mass of 11.74 g. How many atoms does it contain? ...
11129_evl_ch1_ste_eleve (3)
... is used extensively today in cellphone batteries and will also be used, in the near future, in batteries for hybrid or electric cars. In 2008, one battery out of every four sold in the world was manufactured in China. China therefore has a certain economic interest in Tibet. Mining the resource is r ...
... is used extensively today in cellphone batteries and will also be used, in the near future, in batteries for hybrid or electric cars. In 2008, one battery out of every four sold in the world was manufactured in China. China therefore has a certain economic interest in Tibet. Mining the resource is r ...
Atoms, Elements, and Ions
... • The atom is extremely small. One teaspoon of water has 3 times as many atoms as the Atlantic Ocean has teaspoons of water. • If a large sports stadium were an atom, a marble would represent the nucleus. ...
... • The atom is extremely small. One teaspoon of water has 3 times as many atoms as the Atlantic Ocean has teaspoons of water. • If a large sports stadium were an atom, a marble would represent the nucleus. ...
Practice problems for chapter 1, 3 and 5 1) A small amount of salt
... 1) A small amount of salt dissolved in water is an example of a __________. 2) Which one of the following is a pure substance? A) concrete B) wood C) salt water D) elemental copper E) milk 3) For which of the following can the composition vary? A) pure substance B) element C) both homogeneous and he ...
... 1) A small amount of salt dissolved in water is an example of a __________. 2) Which one of the following is a pure substance? A) concrete B) wood C) salt water D) elemental copper E) milk 3) For which of the following can the composition vary? A) pure substance B) element C) both homogeneous and he ...
Lesson 1 & 2 Periodic table trends and formation
... An element is a substance made of only one kind of atom. 2. What is the atomic mass of an element? The atomic mass is the mass of an atom of a particular element. It is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of a particular element, averaged over all the isotopes of the e ...
... An element is a substance made of only one kind of atom. 2. What is the atomic mass of an element? The atomic mass is the mass of an atom of a particular element. It is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of a particular element, averaged over all the isotopes of the e ...
Name: Date: ______ Period: Unit 3 – Atomic Structure Review
... 1. Who was the ancient Greek philosopher who first proposed the notion of the atom? Democritus 2. What was Dalton’s atomic model called? Billard ball model 3. Who’s model first introduced the concept of energy levels? Bohr 4. What were the major problems of Dalton’s atomic theory? Did not have an in ...
... 1. Who was the ancient Greek philosopher who first proposed the notion of the atom? Democritus 2. What was Dalton’s atomic model called? Billard ball model 3. Who’s model first introduced the concept of energy levels? Bohr 4. What were the major problems of Dalton’s atomic theory? Did not have an in ...
Atomic Theory Note Packet
... 5. Atomic mass is the weighted average of the isotopes of a particular element. For example ~99% of carbon is Carbon-12 and ~1% is Carbon-14. In any sample of carbon on earth you will generally find this ratio. When you use a sample of carbon it contains both isotopes, so you need a way of determini ...
... 5. Atomic mass is the weighted average of the isotopes of a particular element. For example ~99% of carbon is Carbon-12 and ~1% is Carbon-14. In any sample of carbon on earth you will generally find this ratio. When you use a sample of carbon it contains both isotopes, so you need a way of determini ...
The Chemical Earth
... Valence energy level The outermost shell of an atom is referred to as the valence energy level. Similarly, the electrons that occupy the outermost shell are called valence electrons. In the periodic table elements with the same number of valence electrons occur in the same column or group. ...
... Valence energy level The outermost shell of an atom is referred to as the valence energy level. Similarly, the electrons that occupy the outermost shell are called valence electrons. In the periodic table elements with the same number of valence electrons occur in the same column or group. ...
Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... Structure of the Atom • Atoms consist of two regions: 1.Nucleus: Which is a very small region located in the center of an atom which contain positively (+) charged particles called protons and one or more (=) neutral particles called neutrons. 2.Electron cloud: A region very large compared to the n ...
... Structure of the Atom • Atoms consist of two regions: 1.Nucleus: Which is a very small region located in the center of an atom which contain positively (+) charged particles called protons and one or more (=) neutral particles called neutrons. 2.Electron cloud: A region very large compared to the n ...
Introduction to the Modern Concept of Atomic Structure
... the nucleus is not obvious. They may help hold the protons (which electron ...
... the nucleus is not obvious. They may help hold the protons (which electron ...
PPT - gserianne.com
... • atoms with the same atomic numbers but with different atomic weights • atoms with the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons • oxygen (atomic number 8) has the following isotopes (16O, 17O, 18O) • unstable isotopes (radioisotopes or radionuclides) are radioactive; ...
... • atoms with the same atomic numbers but with different atomic weights • atoms with the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons • oxygen (atomic number 8) has the following isotopes (16O, 17O, 18O) • unstable isotopes (radioisotopes or radionuclides) are radioactive; ...
Chapter 3
... When connected to electric current the remaining the gas forms a BEAM OF LIGHT. The beam always started at the NEGATIVE electrode and flowed to the POSITIVE electrode. The electrode is named by what type of particle it ...
... When connected to electric current the remaining the gas forms a BEAM OF LIGHT. The beam always started at the NEGATIVE electrode and flowed to the POSITIVE electrode. The electrode is named by what type of particle it ...