2.1 Subatomic Particles Prequiz (E)
... D) they are neutral particles E) they are emitted by all matter 4. Of the following, the smallest and lightest subatomic particle is the __________. A) nucleus B) proton C) neutron D) electron E) alpha particle 5. The atomic number indicates __________. A) the number of different isotopes of an elem ...
... D) they are neutral particles E) they are emitted by all matter 4. Of the following, the smallest and lightest subatomic particle is the __________. A) nucleus B) proton C) neutron D) electron E) alpha particle 5. The atomic number indicates __________. A) the number of different isotopes of an elem ...
Semester 1 Final Review Powerpoint
... atoms. The properties of this rearrangement are different than the original reagents. (EX: Carbon (a solid) is burned in O2 and results in a gas! These two carbon compounds have very different ...
... atoms. The properties of this rearrangement are different than the original reagents. (EX: Carbon (a solid) is burned in O2 and results in a gas! These two carbon compounds have very different ...
1s 2s 2p - Solon City Schools
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different ...
... All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms Atoms of a given element are identical in size, mass, and other properties; atoms of different John Dalton elements differ in size, mass, and other properties Atoms cannot be subdivided, created, or destroyed Atoms of different ...
1 - Bal Bharati Public School
... Q.18. Briefly describe the features of the Rutherford Model of an atom. what are the drawbacks ? Q.19. How do isotopes and isobars differ? Write three applications of isotopes. Q. 20. What observations in scattering experiment led Rutherford to make the following conclusions: (i) Most of the space i ...
... Q.18. Briefly describe the features of the Rutherford Model of an atom. what are the drawbacks ? Q.19. How do isotopes and isobars differ? Write three applications of isotopes. Q. 20. What observations in scattering experiment led Rutherford to make the following conclusions: (i) Most of the space i ...
Structure of the Atom JJ Thomson- discovered the electron in late
... as protons are found to be at the center of this nucleus. James Chadwick- discovers the NEUTRON in 1932. The neutron is located in the nucleus and has NO CHARGE. The following table summarizes the subatomic particles listed in order of discovery: ...
... as protons are found to be at the center of this nucleus. James Chadwick- discovers the NEUTRON in 1932. The neutron is located in the nucleus and has NO CHARGE. The following table summarizes the subatomic particles listed in order of discovery: ...
Chapter 16: The Properties of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... Section 1 – The Structure of Atoms The Development of the Atomic Model There was a problem with Rutherford’s model of the atom. The proton alone could not account for the mass of the nucleus, there was a missing particle • In the early 1900’s, scientists knew that hydrogen consisted of one proton a ...
... Section 1 – The Structure of Atoms The Development of the Atomic Model There was a problem with Rutherford’s model of the atom. The proton alone could not account for the mass of the nucleus, there was a missing particle • In the early 1900’s, scientists knew that hydrogen consisted of one proton a ...
Unit 2, Day 25
... is used because the mass of each subatomic particle is too small to measure in grams The mass of each atom is equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. (Electrons are ignored, because their mass is so small that they don’t affect the mass enough) ...
... is used because the mass of each subatomic particle is too small to measure in grams The mass of each atom is equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons. (Electrons are ignored, because their mass is so small that they don’t affect the mass enough) ...
Atomic Information
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses, due to the different number of neutrons. • The mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus. The mass number is useful when designating ...
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses, due to the different number of neutrons. • The mass number is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in the nucleus. The mass number is useful when designating ...
Slide 1
... Bohr-Rutherford Diagram of an Atom • A Bohr-Rutherford diagram shows the numbers and locations of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom. We can determine these numbers from the atomic number and the atomic mass (mass number) on the P.T. • The number of protons = atomic number • The number of n ...
... Bohr-Rutherford Diagram of an Atom • A Bohr-Rutherford diagram shows the numbers and locations of protons, neutrons and electrons in an atom. We can determine these numbers from the atomic number and the atomic mass (mass number) on the P.T. • The number of protons = atomic number • The number of n ...
Dear 3EFG, Refer to your notes for the formula and other data. But
... which is essentially four protons and electrons combining to make He. Radioactivity comes out of the nucleus of atoms. The nucleus is radioactive because it is unstable. Like electrons in an excited state dropping back down to ground state and releasing a photon, nuclei need an outlet for their exci ...
... which is essentially four protons and electrons combining to make He. Radioactivity comes out of the nucleus of atoms. The nucleus is radioactive because it is unstable. Like electrons in an excited state dropping back down to ground state and releasing a photon, nuclei need an outlet for their exci ...
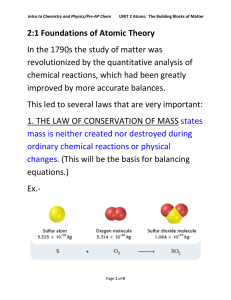
2:1 Foundations of Atomic Theory In the 1790s the study of matter
... knowing both the name and atomic number of the element and the mass of the isotope. The MASS NUMBER is the total number of protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus of an isotope. The three isotopes of hydrogen mentioned above have mass numbers of 1, 2 and 3. Isotopes are usually identified by s ...
... knowing both the name and atomic number of the element and the mass of the isotope. The MASS NUMBER is the total number of protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus of an isotope. The three isotopes of hydrogen mentioned above have mass numbers of 1, 2 and 3. Isotopes are usually identified by s ...
Answer on Question #47967 - Chemistry – Other
... e. A model in which the protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom 8. The nucleus of an atom is ____________. a. Positively charged and has a high density b. Negatively charged and has a high density c. Positively charged and has a low density d. Negat ...
... e. A model in which the protons, electrons, and neutrons are evenly distributed throughout the volume of the atom 8. The nucleus of an atom is ____________. a. Positively charged and has a high density b. Negatively charged and has a high density c. Positively charged and has a low density d. Negat ...
Models of the Atom: A Historical perspective
... All matter is made of atoms Atoms of the same element are identical Each element has different atoms Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. ...
... All matter is made of atoms Atoms of the same element are identical Each element has different atoms Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds. • Atoms are rearranged in reactions. ...
The Scientists - WordPress.com
... If Thomson’s plum pudding model were correct, the alpha particles would have deflected a little as they passed through the foil. ...
... If Thomson’s plum pudding model were correct, the alpha particles would have deflected a little as they passed through the foil. ...
atoms - Images
... the universe was made of indivisible units. › He called these units atoms. Comes from atomos that means, “unable to be cut or divided.” ...
... the universe was made of indivisible units. › He called these units atoms. Comes from atomos that means, “unable to be cut or divided.” ...
Chapter 5: Atomic Structure
... particles since they determine chemical behavior: Electron, Neutron and Proton • Electron has a charge of -1.602 X 10-19 C and a proton has a charge of 1.602 X 10-19 C so this quantity of Coulombs is known as one electronic charge and atomic and subatomic particles usually have a charge that is mult ...
... particles since they determine chemical behavior: Electron, Neutron and Proton • Electron has a charge of -1.602 X 10-19 C and a proton has a charge of 1.602 X 10-19 C so this quantity of Coulombs is known as one electronic charge and atomic and subatomic particles usually have a charge that is mult ...
Chem12-Unit 1-1-Development of Atomic Theory
... regarded as a wave that has quantized its energy. Electrons have no precise orbits. Instead, their motion can only be described by the probability of finding them in certain regions surrounding the nucleus. These regions are called orbitals. These orbitals form an electron cloud around the nucleus. ...
... regarded as a wave that has quantized its energy. Electrons have no precise orbits. Instead, their motion can only be described by the probability of finding them in certain regions surrounding the nucleus. These regions are called orbitals. These orbitals form an electron cloud around the nucleus. ...
Exam Review Answers - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Alkali: These elements are all shiny, silvery metals that are extremely reactive. Alkaline Earth Metals: Shiny, silvery-white colour, highly reactive but not as reactive as the Alkali metals Halogens: The halogens are the most reactive non-metals Nobel Gases: These gases are un-reactive and ...
... Alkali: These elements are all shiny, silvery metals that are extremely reactive. Alkaline Earth Metals: Shiny, silvery-white colour, highly reactive but not as reactive as the Alkali metals Halogens: The halogens are the most reactive non-metals Nobel Gases: These gases are un-reactive and ...
Periodic Table Trends - Magoffin County Schools
... corner of the periodic table. The smallest elements are in the upper right corner. ...
... corner of the periodic table. The smallest elements are in the upper right corner. ...
atom
... What happens when you lose or gain neutrons in an atom? Many elements have atoms that exist with varying numbers of neutrons within their nuclei. Isotopes: Forms of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
... What happens when you lose or gain neutrons in an atom? Many elements have atoms that exist with varying numbers of neutrons within their nuclei. Isotopes: Forms of an element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. ...
24 Sept 08 - Seattle Central College
... Of the following, which is most likely to become a cation as a result of a chemical reaction? What would be the charge on that cation? 1. N; –3 2. Ne; +1 3. Na: +1 ...
... Of the following, which is most likely to become a cation as a result of a chemical reaction? What would be the charge on that cation? 1. N; –3 2. Ne; +1 3. Na: +1 ...
Honors Biology Chapter 2 Power Point
... If lose 1 e- = +1 charge If gain 1 e- = -1 charge If lose 2 e- = +2 charge If gain 2 e- = -2 charge ...
... If lose 1 e- = +1 charge If gain 1 e- = -1 charge If lose 2 e- = +2 charge If gain 2 e- = -2 charge ...