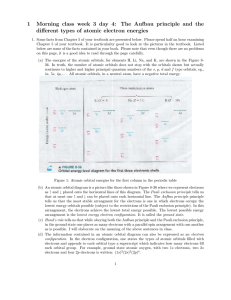
1 Morning class week 3 day 4: The Aufbau principle and the different
... (a) In the H atom, the total energy of an electron in a 1s orbital is -13.6 eV. (An eV is a unit of energy. 1eV/atom or 1 eV/molecule = 96.5 kJ/mole.) What is the average kinetic and potential energy of an electron in a H 1s orbital. (b) Examine Figure 8-36, where the total energy of the 1s orbital ...
... (a) In the H atom, the total energy of an electron in a 1s orbital is -13.6 eV. (An eV is a unit of energy. 1eV/atom or 1 eV/molecule = 96.5 kJ/mole.) What is the average kinetic and potential energy of an electron in a H 1s orbital. (b) Examine Figure 8-36, where the total energy of the 1s orbital ...
Chemical Bonds - coellochemistry
... Share electrons: all elements want 8 valence electrons (***except H and He want 2 valence electrons***) The sharing of covalent compounds gives ...
... Share electrons: all elements want 8 valence electrons (***except H and He want 2 valence electrons***) The sharing of covalent compounds gives ...
Answer Key of worksheet (History of an Atom)
... c. Lightweight, negative electrons move in the nucleus. d. Electrons are compact together. Bohr States That Electrons Can Jump Between Levels 18. In Bohr’s atomic model, electrons travel in definite paths around the nucleus at specific levels. Each level is a certain distance from the nucleus. Elect ...
... c. Lightweight, negative electrons move in the nucleus. d. Electrons are compact together. Bohr States That Electrons Can Jump Between Levels 18. In Bohr’s atomic model, electrons travel in definite paths around the nucleus at specific levels. Each level is a certain distance from the nucleus. Elect ...
File
... A proton is made up of 2 up quarks and 1 down quark = charge of +1 a neutron contains 1 up quark and 2 down quarks, yielding a net charge of 0 All you’ve learned about atomic structure is just a model Model- help you visualize or understand something too large or small to see all at once ...
... A proton is made up of 2 up quarks and 1 down quark = charge of +1 a neutron contains 1 up quark and 2 down quarks, yielding a net charge of 0 All you’ve learned about atomic structure is just a model Model- help you visualize or understand something too large or small to see all at once ...
Chapter 2.1, 2.2 Review Packet – Answer Key
... Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes are identified by their mass number, the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Because they have the same number of electrons in each atom, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical p ...
... Atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes are identified by their mass number, the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Because they have the same number of electrons in each atom, all isotopes of an element have the same chemical p ...
Week 9 CCA Test Review
... Why do elements with similar valence level of electrons have similar chemical properties? They will react the same way, because they ...
... Why do elements with similar valence level of electrons have similar chemical properties? They will react the same way, because they ...
HighFour Chemistry Round 1 Category C: Grades 9 – 10 Thursday
... 8 mols HNO3 Based on the partially-balanced chemical equation, to balance out the 3 moles of Cu atoms on the left side of the reaction, there should be 3 moles of Cu ( in Cu(NO3)2 ) on the right side of the reaction. Hence, ...
... 8 mols HNO3 Based on the partially-balanced chemical equation, to balance out the 3 moles of Cu atoms on the left side of the reaction, there should be 3 moles of Cu ( in Cu(NO3)2 ) on the right side of the reaction. Hence, ...
Bohr Models 1
... Write the number of P and N in the nucleus and draw the correct number of electrons on each energy level. The energy levels are: (2, 8, 18, 32, 50, 72). Many times an energy level will be satisfied with eight electrons. Place a happy or sad face next to each atoms to show its status as an atom. ...
... Write the number of P and N in the nucleus and draw the correct number of electrons on each energy level. The energy levels are: (2, 8, 18, 32, 50, 72). Many times an energy level will be satisfied with eight electrons. Place a happy or sad face next to each atoms to show its status as an atom. ...
Name___________________________________ Physical
... 10) Which of the following correctly shows the formula for a hydrate? A) MgSO4 (H2 O)7 B) H2 O C) H2 O2 ...
... 10) Which of the following correctly shows the formula for a hydrate? A) MgSO4 (H2 O)7 B) H2 O C) H2 O2 ...
Ch. 2: Biochemistry
... Valence electrons: in the outermost shell, or valence shell Elements with full valence shell are chemically inert Chemical behavior of atom determined by distribution of electrons in electron shells, MOSTLY by valence electrons ...
... Valence electrons: in the outermost shell, or valence shell Elements with full valence shell are chemically inert Chemical behavior of atom determined by distribution of electrons in electron shells, MOSTLY by valence electrons ...
Particulate View of Matter
... An atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons is an ion. Ions carry an electric charge. An ionic bond is an electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms. ...
... An atom that has lost or gained one or more electrons is an ion. Ions carry an electric charge. An ionic bond is an electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms. ...
Atomic-model
... oxygen and carbon combined to make two compounds. He discovered that for the same amount of carbon, one had exactly twice as much oxygen as the other (De Leon, N). This led him to propose the Law of Multiple Proportions, which states that when two or more elements form more than one compound, the r ...
... oxygen and carbon combined to make two compounds. He discovered that for the same amount of carbon, one had exactly twice as much oxygen as the other (De Leon, N). This led him to propose the Law of Multiple Proportions, which states that when two or more elements form more than one compound, the r ...
Atomic Structure + Isotopes
... If each atom in a single marble were the same size as a grain of sand, you would end up with enough sand to cover the whole of Oregon with a layer close to a thousand feet (2/3 or a mile) thick. If you walked around the equator of the earth continually without stopping to sleep or eat, it would ta ...
... If each atom in a single marble were the same size as a grain of sand, you would end up with enough sand to cover the whole of Oregon with a layer close to a thousand feet (2/3 or a mile) thick. If you walked around the equator of the earth continually without stopping to sleep or eat, it would ta ...
ATOMIC THEORY WORKSHEET 1.
... reactions the old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
... reactions the old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
ATOMIC THEORY WORKSHEET 1. Which of the following
... reactions the old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
... reactions the old bonds between atoms are broken down and new bonds are formed. Atoms, however, can be created or destroyed in nuclear reactions: radioactive decays, nuclear fission and fusion. ...
Aim # 8: How do we write and balance a chemical equation?
... Note: Oxygen is a diatomic molecule. 3. Balance the equation by supplying coefficients that will make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the arrow. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO (balanced) Begin by examining the first element on the left side and comparing it to itself on the right side ...
... Note: Oxygen is a diatomic molecule. 3. Balance the equation by supplying coefficients that will make the number of atoms of each element the same on both sides of the arrow. 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO (balanced) Begin by examining the first element on the left side and comparing it to itself on the right side ...
Physical Science Chapter 16 Notes Section 1: Structure of the Atom
... ♦ The current periodic table is arranged in order of increasing mass atomic number number ♦ In any square of the periodic table you can find the following information: the symbol for the element, the atomic number, and the average atomic mass. Also, some periodic tables will indicate the state of th ...
... ♦ The current periodic table is arranged in order of increasing mass atomic number number ♦ In any square of the periodic table you can find the following information: the symbol for the element, the atomic number, and the average atomic mass. Also, some periodic tables will indicate the state of th ...
Section 4.2 The Structure of an Atom
... 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Two different elements can false have the same atomic number. 10. What is the mass number of an atom? The mass number of an atom is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of that atom. ...
... 9. Is the following sentence true or false? Two different elements can false have the same atomic number. 10. What is the mass number of an atom? The mass number of an atom is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of that atom. ...
Chapter 2: Matter is Made up of Atoms
... • Theory: well tested explanation that explains many observations. May change over time • Law: fact of nature observed so often it is accepted as truth. Doesn’t change. ...
... • Theory: well tested explanation that explains many observations. May change over time • Law: fact of nature observed so often it is accepted as truth. Doesn’t change. ...
Parts of the Atom - Dalton Local Schools
... a. Two protons push each other away or repel. b. Two protons push each other away or repel. c. Protons and electrons are attracted to each other because the have opposite charges. d. All three of the above statements are true. e. All of the answers are false. ...
... a. Two protons push each other away or repel. b. Two protons push each other away or repel. c. Protons and electrons are attracted to each other because the have opposite charges. d. All three of the above statements are true. e. All of the answers are false. ...
Thompson`s “Plum Pudding” Model
... number n. Electrons can jump from one orbit to another by emitting or absorbing energy. • The inset shows an electron jumping from orbit n=3 to orbit n=2, emitting a photon of red light with an energy of 1.89 eV. ...
... number n. Electrons can jump from one orbit to another by emitting or absorbing energy. • The inset shows an electron jumping from orbit n=3 to orbit n=2, emitting a photon of red light with an energy of 1.89 eV. ...























