Atomic Theory
... element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of all other element. • 3 Chemical change is the union or separation of atoms • 4 Atoms combine in small whole number ratios to form compounds. ...
... element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of all other element. • 3 Chemical change is the union or separation of atoms • 4 Atoms combine in small whole number ratios to form compounds. ...
Atomic Theory - St John Brebeuf
... Having a molecule (atoms combine in simple whole # ratios) explains the law of constant composition. ...
... Having a molecule (atoms combine in simple whole # ratios) explains the law of constant composition. ...
File
... Therefore, atoms will gain or lose the fewest number electrons possible to achieve a full valence o Metals tend to lose electrons to become positive ions (cations). o Non-metals tend to gain electrons to become negative ions (anions). Example: Magnesium (Mg) is a metal with 2 valence electrons T ...
... Therefore, atoms will gain or lose the fewest number electrons possible to achieve a full valence o Metals tend to lose electrons to become positive ions (cations). o Non-metals tend to gain electrons to become negative ions (anions). Example: Magnesium (Mg) is a metal with 2 valence electrons T ...
chapter 7 quiz
... 10._T__The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus L) cathode of an atom. M) electron cloud 11._Y__Discovered radioactivity. N) Darth Vader 12._C__Discovered three types of radiation. O) chemical symbol 13._J__The charge on an “beta” particle. P) 0 14._A__The charge on an “alpha” particle. Q) ...
... 10._T__The number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus L) cathode of an atom. M) electron cloud 11._Y__Discovered radioactivity. N) Darth Vader 12._C__Discovered three types of radiation. O) chemical symbol 13._J__The charge on an “beta” particle. P) 0 14._A__The charge on an “alpha” particle. Q) ...
Exam #2 Review
... Atomic Model History – MAKE SURE YOU CAN MATCH EACH SCIENTIST TO HIS MODEL!! 1. Draw and name each scientist’s model of the atom: a. Dalton Billiard Ball Model ...
... Atomic Model History – MAKE SURE YOU CAN MATCH EACH SCIENTIST TO HIS MODEL!! 1. Draw and name each scientist’s model of the atom: a. Dalton Billiard Ball Model ...
Chemistry A - Montgomery County Public Schools
... Atomic Structure describe the characteristics of protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of location, charge and mass. illustrate the structure of the atom by using the Bohr model, including the charge, relative mass and location of the sub-atomic particles. use atomic mass, atomic number, an ...
... Atomic Structure describe the characteristics of protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of location, charge and mass. illustrate the structure of the atom by using the Bohr model, including the charge, relative mass and location of the sub-atomic particles. use atomic mass, atomic number, an ...
Rule of Solid Solubility
... must be with in 15 % of each other. • Crystal Structure: the type of crystal structure must be same. • Chemical Valence: The valence of the two elements must differ by no more than one. • Electro negativity: It must be nearly equal if not, a compound may be formed as a result of the difference in af ...
... must be with in 15 % of each other. • Crystal Structure: the type of crystal structure must be same. • Chemical Valence: The valence of the two elements must differ by no more than one. • Electro negativity: It must be nearly equal if not, a compound may be formed as a result of the difference in af ...
Unit 2 Notes
... and the orbitals gain energy the _______________ they get from the nucleus How the Bohr model relates to light • When an atom is at rest, each electron lies in its _____________________________________________ • Energy is __________________to an atom, the electrons ____________ it and jump to _____ ...
... and the orbitals gain energy the _______________ they get from the nucleus How the Bohr model relates to light • When an atom is at rest, each electron lies in its _____________________________________________ • Energy is __________________to an atom, the electrons ____________ it and jump to _____ ...
P-Atomic_Structure_Ppt - McKinney ISD Staff Sites
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
SCIENCE: EIGHTH GRADE CRT FIRST QUARTER
... An atom’s identity is determined by which subatomic particle? In what period is calcium (Ca) located? Find the number of protons given the group number and period. Which of the following elements are halogens: What is the name of group 16 on the periodic table? Locate elements by period number. How ...
... An atom’s identity is determined by which subatomic particle? In what period is calcium (Ca) located? Find the number of protons given the group number and period. Which of the following elements are halogens: What is the name of group 16 on the periodic table? Locate elements by period number. How ...
Notes matter energy
... number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen atoms (and 7 total atoms). Subscripts indicate the number of atoms in the formula ( ...
... number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen atoms (and 7 total atoms). Subscripts indicate the number of atoms in the formula ( ...
Ch. 4-7 Review Answers pg. 3-7
... 5) What does it mean if energy is quantized? energy can only be gained/lost in specific/whole-number amounts 6) The particle that holds a quantum of energy is a photon 7) What are the three possible energy states of the atom and how does the atom go between these states? Ground (lowest energy state) ...
... 5) What does it mean if energy is quantized? energy can only be gained/lost in specific/whole-number amounts 6) The particle that holds a quantum of energy is a photon 7) What are the three possible energy states of the atom and how does the atom go between these states? Ground (lowest energy state) ...
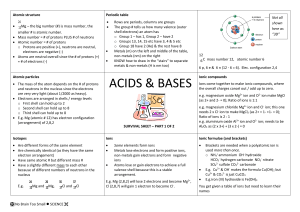
acids and bases - No Brain Too Small
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
SCI 10 REVIEW
... they behave, particularly how and why they react in the way they do. • It also explains the groupings of elements in the periodic table and periodicity. ...
... they behave, particularly how and why they react in the way they do. • It also explains the groupings of elements in the periodic table and periodicity. ...
1 Atomic Theory
... • According to the modern atomic model, at atom still has small positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large electron cloud region in which there are enough electrons to make an atom neutral. • This cloud is really Most of the volume of an atom • Cloud is a ‘Probability region’ where electron ma ...
... • According to the modern atomic model, at atom still has small positively charged nucleus surrounded by a large electron cloud region in which there are enough electrons to make an atom neutral. • This cloud is really Most of the volume of an atom • Cloud is a ‘Probability region’ where electron ma ...
electrons = # protons
... to a lower available level emitting the same amount of energy it absorbed to go to the higher energy level. This energy is seen as light. While the light appears as one color, it is actually composed of many different wavelengths, each of which is seen as a different line when viewed through an inst ...
... to a lower available level emitting the same amount of energy it absorbed to go to the higher energy level. This energy is seen as light. While the light appears as one color, it is actually composed of many different wavelengths, each of which is seen as a different line when viewed through an inst ...
Atoms are not the smallest thing
... Cathode rays are negatively charged particles 1897.J. Thomson demonstrates that cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles. The first sighting of the electron: a particle much smaller than an atom. ...
... Cathode rays are negatively charged particles 1897.J. Thomson demonstrates that cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles. The first sighting of the electron: a particle much smaller than an atom. ...
30-2 Ch 3 Test Review Atomic Theory DEBRIEF KEY
... A FOOTBALL FIELD). ELECTRONS OCCUPY MOST OF THE SPACE OF AN ATOM. ...
... A FOOTBALL FIELD). ELECTRONS OCCUPY MOST OF THE SPACE OF AN ATOM. ...
Atomic Theory - Wallingford-Swarthmore School District
... in half you would eventually end up with an “uncutable” particle. Which he called an atom • Greek: Atomos - indivisible ...
... in half you would eventually end up with an “uncutable” particle. Which he called an atom • Greek: Atomos - indivisible ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 83. What is molarity? 84. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .30 L of solution, what is the molarity? 85. If I have 700.0 mL of a 5.0 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 86. What is meant by chemical equilibrium? 87. What factors affect the rate of a reacti ...
... 83. What is molarity? 84. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .30 L of solution, what is the molarity? 85. If I have 700.0 mL of a 5.0 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 86. What is meant by chemical equilibrium? 87. What factors affect the rate of a reacti ...
4.1 Studying Atoms
... • Democritus (460-370 B.C.): was the first to use the word “atomos”( which meant atoms); stated that matter is composed of atoms; atoms are indestructible and indivisible ...
... • Democritus (460-370 B.C.): was the first to use the word “atomos”( which meant atoms); stated that matter is composed of atoms; atoms are indestructible and indivisible ...
Notes ATOM - Eldred Central School
... the Greek word meaning “invisible” or “that which cannot be further cut”. This comes for the Greek thinker Democritus more than 2000 year ago. ...
... the Greek word meaning “invisible” or “that which cannot be further cut”. This comes for the Greek thinker Democritus more than 2000 year ago. ...
Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. You will also learn about ions, which are atoms that have the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons. What are isotopes? In addition to its a ...
... In this skill sheet, you will learn about isotopes, which are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. You will also learn about ions, which are atoms that have the same number of protons and different numbers of electrons. What are isotopes? In addition to its a ...
Document
... the Greek word meaning “invisible” or “that which cannot be further cut”. This comes for the Greek thinker Democritus more than 2000 year ago. ...
... the Greek word meaning “invisible” or “that which cannot be further cut”. This comes for the Greek thinker Democritus more than 2000 year ago. ...