ap chemistry – 2013-2014
... AP CHEMISTRY – 2013-2014 Course Description: This AP Chemistry course is designed to be the equivalent of the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of college. This course is structured around six big ideas that include: Structure of matter, properties of matter-characteristic ...
... AP CHEMISTRY – 2013-2014 Course Description: This AP Chemistry course is designed to be the equivalent of the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of college. This course is structured around six big ideas that include: Structure of matter, properties of matter-characteristic ...
ISOSTOPE NOTES - Mr. Collier`s 9th Grade Physical Science
... Notes on Isotopes • Remember Protons are (+) and Electrons are (-). • Neutrons were the last subatomic particles to be discovered because they have no electrical charge. ...
... Notes on Isotopes • Remember Protons are (+) and Electrons are (-). • Neutrons were the last subatomic particles to be discovered because they have no electrical charge. ...
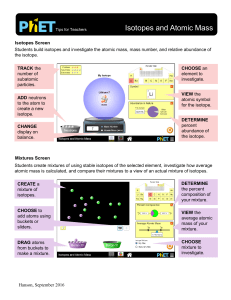
Isotopes and Atomic Mass
... • In college interviews, students wanted to select other common elements such as gold; investigation into other elements could be incorporated as part of an activity. • On the Mixtures screen, students attempted to match Nature’s Mix using My Mix view. This is not possible for all elements shown in ...
... • In college interviews, students wanted to select other common elements such as gold; investigation into other elements could be incorporated as part of an activity. • On the Mixtures screen, students attempted to match Nature’s Mix using My Mix view. This is not possible for all elements shown in ...
Physical Science
... D. It is the measure of the amount of nitrogen in the atmosphere. Nitrogen is only a part of what makes up all of the air molecules pushing down on a surface. S.C.8.4.3b DOK1 ...
... D. It is the measure of the amount of nitrogen in the atmosphere. Nitrogen is only a part of what makes up all of the air molecules pushing down on a surface. S.C.8.4.3b DOK1 ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on the food label are if they are not elements? ...
... • Can you predict what that means about the food item? • Why do you think the baby formula has such a variety of elements? • Can you predict what the other items on the food label are if they are not elements? ...
Introduction to Atoms
... 6. The _______ _________ tells us how many protons are in the nucleus. -Atomic number ...
... 6. The _______ _________ tells us how many protons are in the nucleus. -Atomic number ...
Lecture 3: Matter: What it is Slide 2: What does it Matter? What is a
... What do we mean by saying that atoms are the fundamental unit of matter? What is the structure of atoms? What are nucleons? What are the electric charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons? If ...
... What do we mean by saying that atoms are the fundamental unit of matter? What is the structure of atoms? What are nucleons? What are the electric charges of protons, neutrons, and electrons? If ...
Atomic structure
... • Ions are atoms that have become charged. Atoms become ions in two ways: – They loose electrons and become + – They gain electrons and become - ...
... • Ions are atoms that have become charged. Atoms become ions in two ways: – They loose electrons and become + – They gain electrons and become - ...
Document
... 1) Find your element on the periodic table. 2) Determine the number of electrons – remember, it is the same as the atomic number. 3) This is how many electrons you will draw. ...
... 1) Find your element on the periodic table. 2) Determine the number of electrons – remember, it is the same as the atomic number. 3) This is how many electrons you will draw. ...
Atoms, Ions, and the Periodic Table
... orbits a fixed distance from the nucleus. This is similar to the way the planets orbit the sun. However, electrons do not have neat orbits like the planets. Diagram of Bohr model: ...
... orbits a fixed distance from the nucleus. This is similar to the way the planets orbit the sun. However, electrons do not have neat orbits like the planets. Diagram of Bohr model: ...
Chemistry NYOS Dr. McPhee December 2015 Learning Objectives
... Make an accurate electron count from a molecular formula for a covalent molecule Make an accurate electron count from a molecular name for a covalent molecule Know that dots indicate single electrons in a Lewis dot structure Know that lines indicate two electron bonds in a Lewis dot structure Draw a ...
... Make an accurate electron count from a molecular formula for a covalent molecule Make an accurate electron count from a molecular name for a covalent molecule Know that dots indicate single electrons in a Lewis dot structure Know that lines indicate two electron bonds in a Lewis dot structure Draw a ...
Unit 2 Notes unit_2_atomic-nuclear-electronic
... lowest energy levels are close to the nucleus. The farther from the nucleus corresponds to higher energy levels. Electrons tend to occupy the lowest energy levels available. 3)Light is emitted when an electron jumps from a higher orbit to a lower orbit. Light is absorbed when it jumps from a lower t ...
... lowest energy levels are close to the nucleus. The farther from the nucleus corresponds to higher energy levels. Electrons tend to occupy the lowest energy levels available. 3)Light is emitted when an electron jumps from a higher orbit to a lower orbit. Light is absorbed when it jumps from a lower t ...
Chapter 3 - Industrial ISD
... 4. Which scientist discovered the electrons? 5. Which scientist discovered the nucleus? 6. Which scientist discovered that electrons where in energy levels? 7. Which scientist said atoms where neutral because they had equal number of protons and electrons? ...
... 4. Which scientist discovered the electrons? 5. Which scientist discovered the nucleus? 6. Which scientist discovered that electrons where in energy levels? 7. Which scientist said atoms where neutral because they had equal number of protons and electrons? ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions The Evolution of the Atomic Model (from
... became known as Dalton’s Atomic Theory and he proposed this the year 1803. The primary difference between Dalton’s theory and previous ones was that Dalton’s was based on reproducible laboratory evidence. ...
... became known as Dalton’s Atomic Theory and he proposed this the year 1803. The primary difference between Dalton’s theory and previous ones was that Dalton’s was based on reproducible laboratory evidence. ...
History of Atomic Theories
... “atomic model” proposed by Democritus, Aristotle was so influential that the “four element” model was accepted for almost 2000 years. ...
... “atomic model” proposed by Democritus, Aristotle was so influential that the “four element” model was accepted for almost 2000 years. ...
Document
... 6. A substance made up of two or more elements that have chemically combined is 1. a mixture 2. an atom 3. a compound 4. an element ...
... 6. A substance made up of two or more elements that have chemically combined is 1. a mixture 2. an atom 3. a compound 4. an element ...
ATOM ATOMIC SYMBOL ATOMIC NUMBER
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
... Number of Protons = Atomic Number (Use the large colored marshmallows for protons) Number of Neutrons = Atomic Mass – Atomic Number (Use the large white marshmallows for neutrons) Number of Electrons = Number of Protons (Use the small colored marshmallows for electrons) ...
Honors Chemistry Exam Review Questions
... A A scientific law fully explains a natural phenomenon. B The scientific method is a logical, systematic approach to the solution of a problem. C For the results of an experiment to be accepted, the experiment must produce the same results no matter how many times it is repeated. D The scientific pr ...
... A A scientific law fully explains a natural phenomenon. B The scientific method is a logical, systematic approach to the solution of a problem. C For the results of an experiment to be accepted, the experiment must produce the same results no matter how many times it is repeated. D The scientific pr ...
Atomic structure
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
... which was only a few atoms thick. they found that although most of them passed through. About 1 in 10,000 hit ...
History of the Atom
... energy with negative particles imbedded throughout. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics in 1906 for discovering the electron. ...
... energy with negative particles imbedded throughout. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics in 1906 for discovering the electron. ...
First Semester complete review with answers
... o Noble gases are nonreactive (inert) because their valence energy level is full o Elements are generally reactive when the valence energy level is not full o Highly reactive = valence energy level is almost full, or the valence energy level is almost empty Understand how to read chemical formulas ...
... o Noble gases are nonreactive (inert) because their valence energy level is full o Elements are generally reactive when the valence energy level is not full o Highly reactive = valence energy level is almost full, or the valence energy level is almost empty Understand how to read chemical formulas ...
Contributor to the Atomic Theory
... The concept that small indivisible particles compose all matter was reawakened. Dalton built support for the particle theory through experimentation. In the first decade of the 1800's John Dalton created the modern atomic theory which had five major parts: 1. All matter is composed of small particle ...
... The concept that small indivisible particles compose all matter was reawakened. Dalton built support for the particle theory through experimentation. In the first decade of the 1800's John Dalton created the modern atomic theory which had five major parts: 1. All matter is composed of small particle ...